1.2 Use of calculator memory
A portable calculator is an extremely useful tool for a bookkeeper or an accountant. Although PCs normally have electronic calculators, there is no substitute for the convenience of a small, portable calculator or its equivalent in a mobile phone or personal organiser.
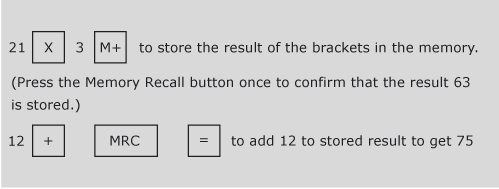
When using the calculator, it is safer to use the calculator memory (M+ on most calculators) whenever possible, especially if you need to do more than one calculation in brackets. The memory calculation will save the results of any bracket calculation and then allow that value to be recalled at the appropriate time. It is always good practice to clear the memory before starting any new calculations involving its use. You do so by pressing the MRC key, representing Memory Recall or its equivalent, twice. (Note: this key is often labelled R.MC or R.CM. The first time the key is pressed memory is recalled and the second time it is cleared. If in doubt about your calculator, consult its manual.)

Taking the previous example we can recalculate it using the memory function.
12 + (21 x 3) = 75
Activity 3
Use the memory on your calculator to calculate each of the following:
Part (a)
(a) 6 + (7 – 3)
Answer
(a) 10
Part (b)
(b) 14.7 / (0.3 + 4.6)
Answer
(b) 3
Part (c)
(c) 7 + (2 x 6)
Answer
(c) 19
Part (d)
(d) 0.12 + (0.001 x 14.6)
Answer
(d) 0.1346
