4.2 Home water filters
Many people use home water filters. These effectively remove both hardness and impurities that may alter the taste of tap water, such as residual chlorine. Have you ever wondered what is inside a refill cartridge (Figure 23)?
- The filter contains an adsorbent material that adsorbs a wide range of compounds, including organic molecules such as pesticides.
- Activated carbon is commonly used as it has a high surface area.
- The structure of activated carbon is similar to graphite. It differs in having a smaller particle size and lower crystallinity.
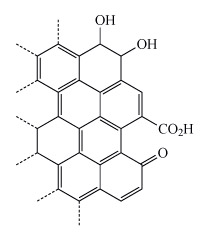
- Also the edge of the graphite-like sheets (Figure 24) have been oxidised which helps improve its absorbent properties.
Why might the additional functional groups from oxidation make activated carbon a better adsorbent than graphite with a similar surface area?
The additional functional groups enable additional intermolecular interactions between the adsorbent and the pollutant. For example, the hydroxyl groups can hydrogen bond with anions such as chloride or nitrate. Similarly the carboxylic acid and carbonyl groups can coordinate cations such as calcium or magnesium.
Activated carbon is also widely used as an adsorbent to treat industrial wastewater.