 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
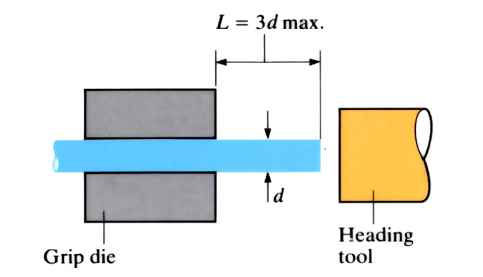
Upset forging
A heading tool or ram is positioned perpendicular to the cross sectioned end face of a rod or bar gripped in a die. On application of pressure, the length of the rod is reduced and the diameter is increased (upset). This manufacturing process is used extensively in the production of fasteners, to form bolt heads, screw heads etc.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
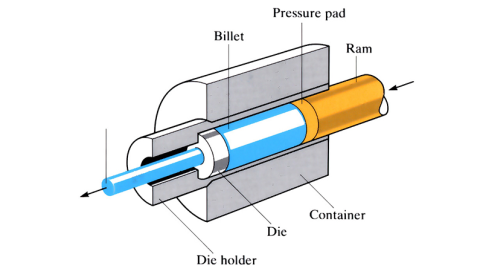
Hot extrusion
A ram forces a heated billet to flow through a shaped hole in a die. Can be forward, backward or hydrostatically extruded.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
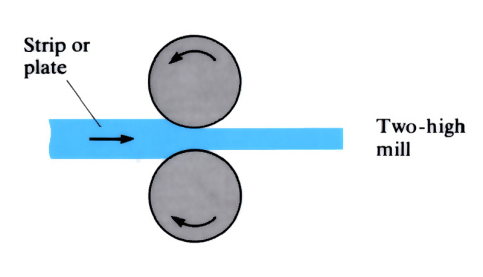
Hot rolling
Plates, flat sheets or billets of metal, heated to above their material recrystallisation temperature, are passed between two rollers. The result is a thinner cross section of material with a finer grain structure.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
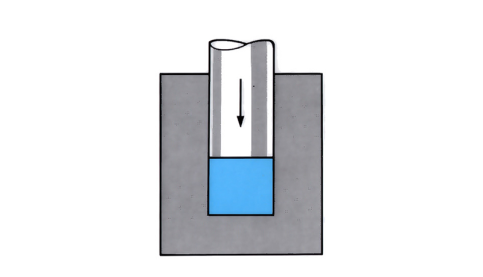
Hot forging (closed die)
Two halves of a heated die move towards each other, incorporating the metal material to be forged and filling the die cavities. The two die halves are clamped together, and the metal is left to solidify. After extraction from the dies, flash is removed from the forging. To eliminate flash formation, a single part heated die can be used instead, ...
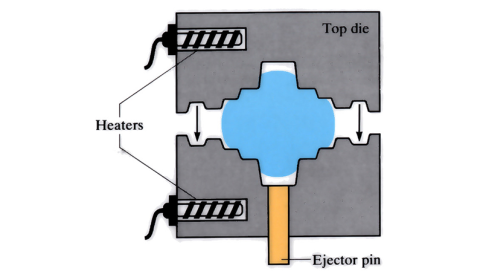 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
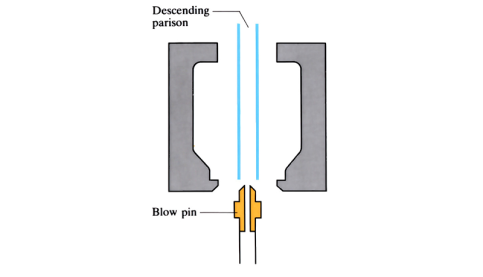
Hot forging (open die)
Open die forging is a hot forming process in which the metal is shaped by hammering or pressing between two flat or simple contoured dies.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
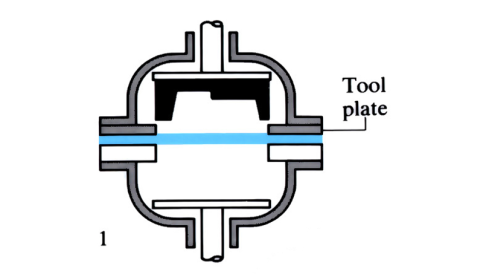
Blow moulding
A process for forming plastic, thin walled, hollow containers such as bottles. Raw thermoplastic in the form of pellets, or granules, is melted and extruded to make parison tubes. The parisons are clamped centrally between two halves of a closed mould. Pressurised air is used to inflate the parisons, until they conform to the shape of the mould ...
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
Superplastic forming
A sheet of metal is clamped into position above or below a die or die cavity. Under the correct combination of temperature, strain rate and microstructure many metals become superplastic, enabling them to be deformed into complex die shapes in a single operation using low pressure air and low cost tooling.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
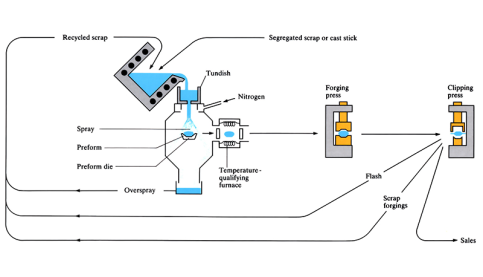
Osprey process
Molten metal poured into a tundish is atomised by a mixture of argon and nitrogen gas. The particulate droplets are sprayed onto a preform die. The established preform then undergoes hot working processes to result in its final shape.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
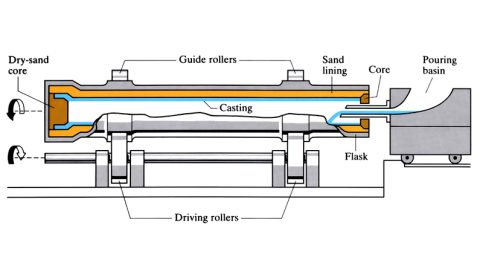
Centrifugal casting
Typically used to cast hollow cylinders or pipes. The casting process is not by gravity or applied pressure, but by centrifugal forces. Molten metal is poured directly into a mould, which is rotated at high speed. Centrifugal force projects the metal outwards from the rotational axis and onto the walls of the mould.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
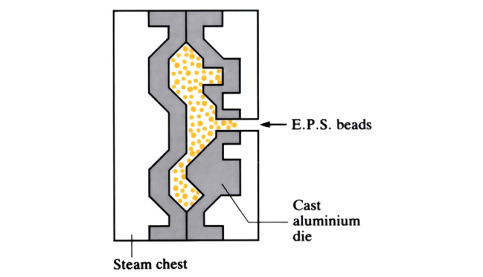
Full mould casting (evaporative pattern)
A pattern is made from fused polystyrene beads heated in an aluminium die. Once cooled, the pattern is coated with a refractory compound, before being placed in a flask and surrounded by sand. A vacuum is applied to the flask and molten metal is poured into the pattern. Molten metal vaporises the polystyrene material as it flows into ...
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
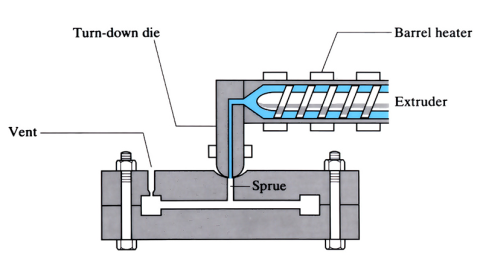
Melt casting
Molten polymer is extruded, via a sprue, into the closed mould cavity formed from two parts bolted together. The mould is vented, and once polymer leaks from the vent, extrusion stops and the material is left in the mould to solidify. Bolts are removed and the component is extracted.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
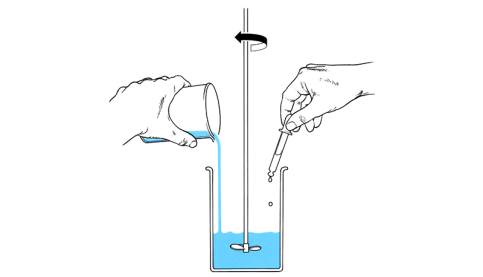
Monomer casting
A non-pressurised casting process using a controlled chemical reaction of polymer materials. The monomer is mixed with an initiator (catalyst), before pouring into the mould. Whilst the mixture is curing inside the mould, polymerisation takes place. Once cooled, the component is removed from the mould.

