 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
Reaction injection moulding (RIM) and Reinforced reaction injection moulding (RRIM)
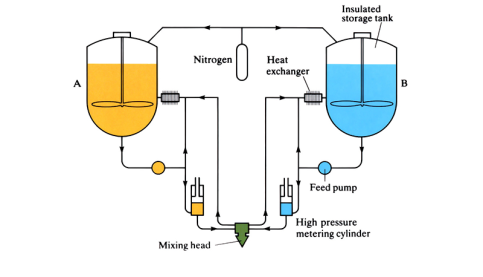
In reaction injection moulding, two types of monomers are mixed together before being injected into a mould, where they polymerise to form the plastic component. In reinforced reaction injection molding, reinforcing agents are added to the monomer mixture.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
Transfer moulding
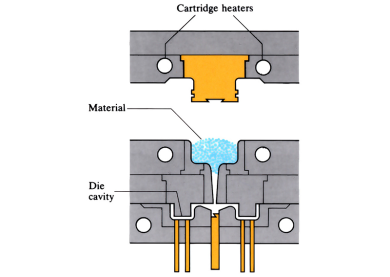
Similar to compression moulding, however, the polymer material is not placed directly into the die, but is often pre-heated before being loaded into a separate heated pot chamber situated above the die. A hydraulic plunger (ram) forces the polymer into the die cavity via a sprue. When cured, the moulded component is released using ejector pins.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
Rotational moulding (Rotational or rotary casting)
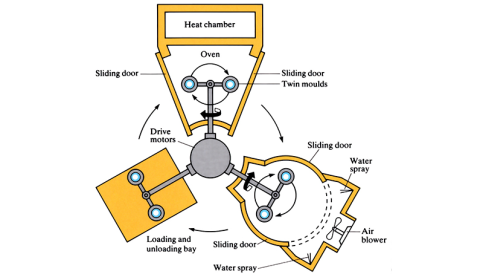
A low pressure and high-temperature process for moulding hollow plastic components. Three separately rotating ‘arms’, with moulds connected to each, revolve bi-directionally around their axes. One arm is for loading and unloading of moulds, another arm is rotating within an oven, and the third arm holds a cooling chamber. The mould is opened to ...
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
Compression moulding
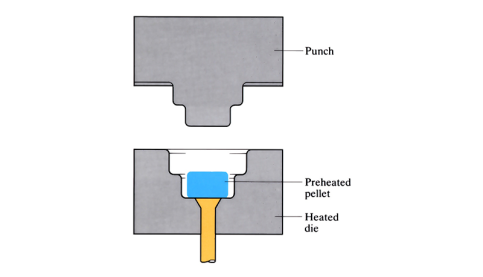
A preheated pellet of thermoset plastic is placed into the bottom half of a heated die. The top half of the die (punch) compresses the molten plastic into the shape of the die. After curing under heat and pressure, the moulded component is ejected.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
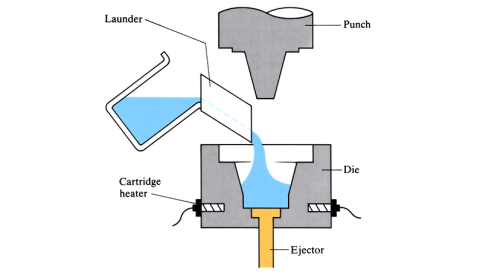
Squeeze casting and squeeze forming
Molten metal is poured into the bottom half of a pre-heated die cavity. As the metal starts to solidify, the top half of the die (punch) is pressed into the bottom half and held in position until the casting has solidified. The cast component is then ejected.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
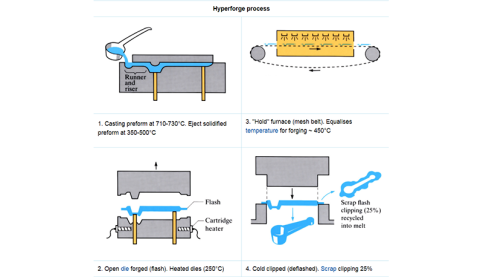
Hyperforge process
A process which combines casting and forging to give components with mechanical properties comparable with forged materials. Uses retained heat from casting process.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
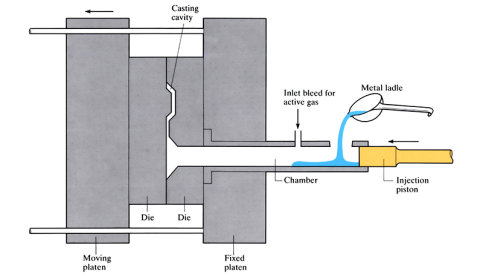
Pore-free die casting (active atmosphere casting)
Porosity is almost eliminated by the injection of an ‘active gas’ into the die cavity, prior to molten metal being piston forced into the cavity at high pressure. The gas combines chemically with the metal to form a finely dispersed solid casting.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
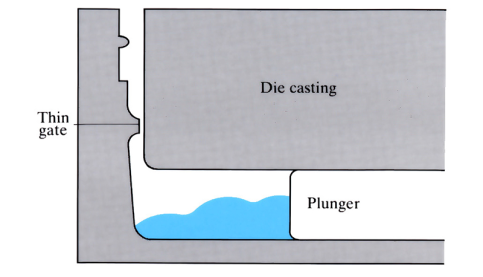
Acurad process
Similar to high pressure die casting, but has wider gate to reduce turbulence, and a secondary plunger fitted inside the primary plunger. Pressure is applied to the molten metal forcing it through the gate and into the die cavity. The inner plunger operates, seconds after the primary plunger, ensuring any pores are filled, hence reducing ...
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
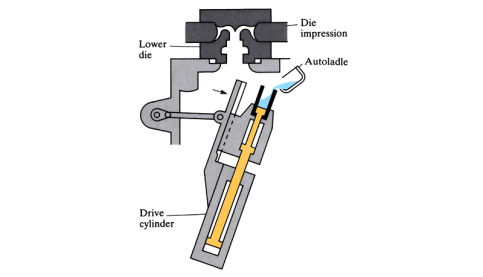
Vertical high pressure die casting
Molten metal is poured slowly into a shot chamber situated at the top of a drive cylinder that’s slightly tilted off vertical. The drive cylinder is moved back to vertical, and raised to a position at the base of the die. Pressure is applied to the shot piston so that the molten metal is forced vertically into the die cavity, and left to ...
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
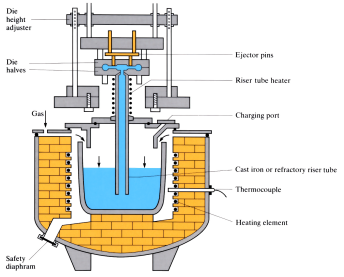
Low pressure die casting (counter-pressure casting)
Low pressure air is introduced into a sealed furnace holding a tank of molten metal. The metal feeds up slowly through a riser tube and into the die cavity. Once the casting has solidified in the die, air pressure is released, allowing any residue molten metal still in the riser to fall back into the tank for recycling. When cooled, the casting ...
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
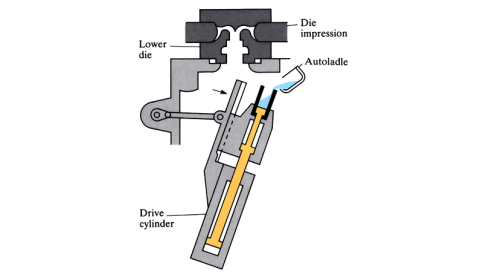
High pressure die casting
Molten metal is forced into a metal die at a high pressure. There are two main types: “cold-chamber” and “hot-chamber” processes.
 article icon
article icon
Science, Maths & Technology
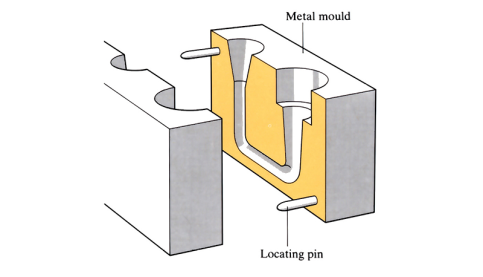
Gravity die casting
Molten material is gently poured into a mould, using only the forces of gravity, then left to solidify.

