2.2 First observations from Tenerife – the All-Sky camera
For your first observations from Tenerife you will be using the Open University’s All-Sky camera located close to the dome that houses the COAST telescope itself. This camera is mounted on a pole, together with a number of other weather instruments that are used to assess the quality of the sky and weather in order to determine when it is safe to open the telescope dome. There are also webcams showing views of the site and of the telescopes inside the COAST and PIRATE domes.
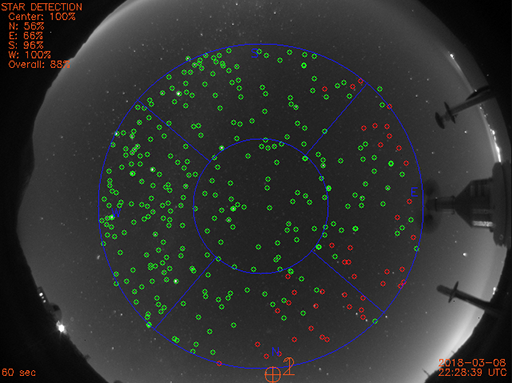
As you can see from the image above, the All-Sky camera gives a rather odd view of the night sky. Because it uses a fisheye lens giving a very wide angle of view, the image from the camera captures the horizon all the way around the edge of the circular image and the sky directly overhead in the middle.
Marked in blue you can see the cardinal points – north, south, east and west - and you can check that the image is live by looking at the time and date noted in the bottom-right corner. The image updates every few minutes. Using these images, the observatory counts the number of stars it can see – marked by green circles – and gives a star detection percentage in the top-left of the screen for each region of the sky as defined by the blue lines.
In later weeks you can return to these webcams to check the weather and observing conditions for when you plan to take images. For now, you can use the All-Sky camera view to observe the apparent motion of the sky. As the Earth rotates, objects in the sky will move from right to left (or east to west) across the image during the course of a night.
Activity 3 Observing the apparent motion of the sky using the All-Sky camera
You can view a live image from Tenerife by visiting the telescope.org website. This is the website that you will also use later to request and collect images from the COAST telescope. For now you are going to look at the webcam feeds, which can be done without logging in or creating an account.
- Use the telescope.org [Tip: hold Ctrl and click a link to open it in a new tab. (Hide tip)] link to visit the webcams page.
- On this page there are four webcam feeds, which can be selected using the Cameras panel below the main image. Click on each of the four cameras in turn to see live images from the site. Note that the view from the PIRATE and COAST internal cameras may appear dark as the telescopes inside the domes are not illuminated for much of the time.
- If you are viewing during the daytime in Tenerife the All-Sky camera view will not show any stars. You should aim to return after dark, preferably when you have time to check back several times during an evening.
- If the sky is clear, you should see green circles indicating stars that the camera has identified. Make a note of any clearly identifiable stars or patterns of stars so that you can check back later to see how they have moved. One way to do this would be to take a copy of the webcam image, which you can do by right-clicking on the image and selecting Save image as . . . Give the image a meaningful name and make a note of where you have saved it, so that you can find it later.
Come back to the webcam page at hourly intervals and repeat Step 4, noting how the pattern of stars has changed. If the sky has remained clear you should see a general movement from East to West, with some stars setting in the West and new stars rising in the East.
