4.1.4 Financial viability area
The financial viability area is located in the lower part of the business model canvas (see Figure 5). It focuses on the money a value proposition costs versus what it generates as a revenue. Therefore, the financial viability is composed of two elements: revenue streams and cost structure.
Revenue streams
The revenue streams are revenues that the business model generates. The key question at issue here is: ‘What value are customers willing to pay for?’ (Osterwalder et al., 2010, p. 31). In the business models of fast couriers such as DHL, a German multinational delivery service provider, and FedEx, an American multinational delivery services company, the revenue streams rely on the customers’ willingness to pay more for speedy deliveries.

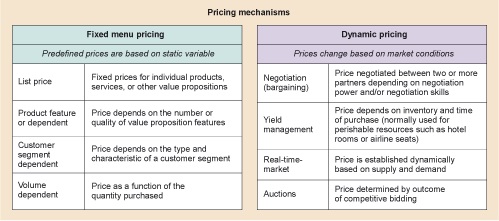
It is also important to clarify how revenues are collected or, in other words, how customers pay. The two possibilities are shown in Figure 6.
Cost structure
Cost structure identifies the costs underlying the business model. A business model involves using resources. Each resource has its own cost. Therefore, the key question to be considered here is: ‘What costs are generated by the resources employed?’
Also, a business model involves a series of activities an organisation needs to perform to generate value. Therefore, an additional important question here is ‘What are the costs associated with the activities of the business model?’ For instance, some customers see value in greener solutions with carbon neutral deliveries; yet, it is costly to develop such offers. Usually more innovative, they require additional investments of time, attention and money to develop. Also, they do not always reflect the conventional meaning of efficiency measured in financial terms. This may be the case of green solutions. Yet, despite their higher costs, green value propositions are at the core of business models in many companies. For example, DPD, the largest parcel delivery company in Europe, offers carbon-free bicycle deliveries to customers interested in, and ready to wait and pay more for, green solutions.

Now you have considered all the different areas of the business model canvas, you will consider your own business model canvas.