3.4 Ice core going back 800 000 years
Throughout this course so far the focus has been on the Arctic, but because some data from the ice cores tell us about conditions over the entire planet (such as Figure 11), you will now look at data from another core, this time from Antarctica. The Antarctica ice cores go back much further in time than any Greenland ones. The particular core you will look at now is called the EPICA (European Project for Ice Coring in Antarctica) – Dome C core.
Dome C is currently the longest ice core and has snow layers going back almost 800 000 years throughout the Quaternary, and includes the period when Homo sapiens evolved. In fact, the EPICA core can be used to reconstruct Antarctic temperatures more than half a million years before Homo sapiens ever walked the Earth (Figure 13).
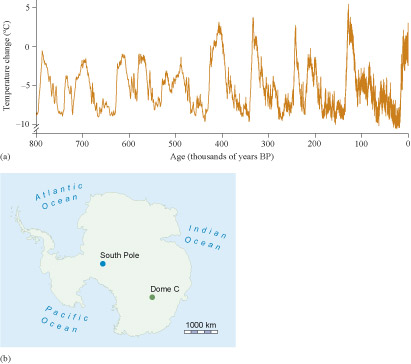
Figure 13(a) shows that Antarctic temperatures have varied considerably, but there also appear to be regular cyclical patterns. At the low points, the temperature shown by the core was as much as 10 °C colder than today: colder periods happen about every 100 000 years, with warmer periods between. Four times in the last 450 000 years, the intervening warm periods have been warmer than today (up to 5 °C warmer around 130 000 years ago). During the nine cold periods shown in Figure 13(a), the snow that fell in winter did not melt in the following summer heat, and the ice sheets grew.
