1.16 Barriers to eco-innovation
In the same way that organisations may experience a range of drivers for eco-innovation, they will also experience obstacles and barriers.
Activity 15 Barriers and obstacles to eco-innovation
For the same organisations you chose earlier, identify some of the possible obstacles and barriers to eco-innovation.
Provide your answer...
Discussion
Some possible barriers to introducing eco-innovations in the restaurant are likely to include:
- costs and availability of funds to pay for the eco-innovation up front
- uncertainty of effectiveness
- uncertainty over payback time
- staff resistance (will it make their lives easier?)
- customer experience.
The latter is an important consideration. For example, paying for new energy-efficient hand-dryers and light bulbs in the restaurant toilets will ‘backfire’ if the hand-dryers don’t actually dry within a given time and the lights make the toilet areas look ‘dingy’. The restaurant would surely want to avoid customer complaints.
The Technopolis report referred to earlier also explored innovation performance and potential in the EU in several sectors: food/drink, machinery/equipment, textiles, chemicals, energy, ICT, space and aeronautics, and automotives. The findings suggest that amongst barriers on eco-innovation, costs are the most important factor for both innovative and non-innovative business organisations. Lack of finance for the investment required for innovation and concerns about the economic risk are also major concerns. The following table shows the main barriers.
| Innovation barrier | Eco-innovation (% of companies) | |
| Innovative companies | Non-innovative companies | |
| Innovation costs too high | 29.6 | 25.6 |
| Lack of appropriate sources of finance | 22.7 | 19.3 |
| Excessive perceived economic risks | 20.4 | 16.8 |
| Lack of qualified personnel | 14.1 | 12.7 |
| Insufficient flexibility of regulations or standards | 12.0 | 8.1 |
| Lack of customer responsiveness to new goods or services | 8.8 | 6.9 |
| Lack of information on markets | 7.4 | 5.4 |
| Organisational rigidities within the enterprise | 6.8 | 5.9 |
| Lack of information on technology | 6.1 | 4.2 |
More recent research on behalf of the European Commission’s (EC) Directorate-General of the Environment (EC, 2012) suggests little has changed since 2007, particularly amongst business organisations. In response, initiatives to promote eco-innovation more widely in the EU have been promoted as part of the EU Eco-Innovation Action Plan (EcoAP) from 2011 onwards. The EcoAP initiative aims to expand from a focus on green technologies to include products and services. Analysis undertaken by the EU survey used by the EcoAP on the main barriers for eco-innovation in small and medium enterprises (SMEs) is shown in Figure 8.
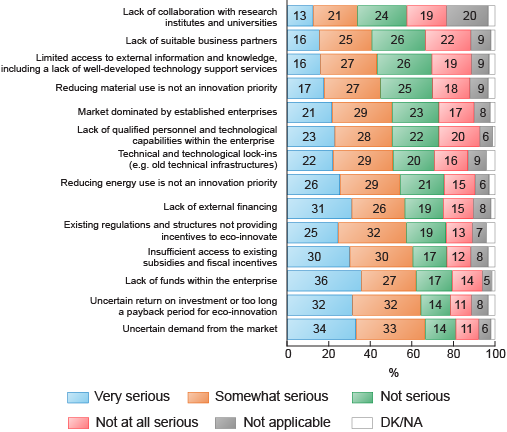
Activity 16 Barriers to eco-innovation uptake
Review Figure 8. Identify the main barriers to uptake of eco-innovation.
Provide your answer...
Discussion
Figure 8 shows that lack of funds within the organisation, uncertainty regarding the market and payback times and lack of external funding, subsidies and incentives are all key barriers.
