2.4 Immunohistochemistry technique
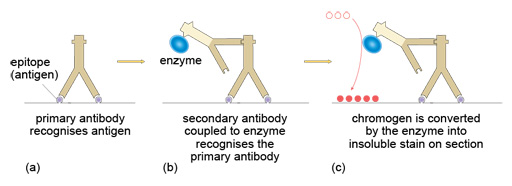
A standard IHC protocol involves treatment of the section with an antibody that recognises the marker. This is referred to as the primary antibody.
The primary antibody is then recognised by a secondary antibody that is linked to an enzyme, or several copies of the enzymes. Such reagents are sometimes called conjugates, although this term can mean different things in other contexts.
Finally, the section is treated with a chromogen, a reagent that is acted upon by the enzyme, to deposit an insoluble coloured compound onto the cell, where the original primary antibody had bound.