4.11 Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts, the sites of photosynthesis, are found in plant cells and photosynthetic algae. Like mitochondria, chloroplasts have their own ribosomes and their own DNA, which encodes the proteins of the internal membrane that use light energy to generate ATP in photosynthesis. Most other chloroplast proteins are, however, encoded by the nuclear DNA and must be transported into the chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are typically about 2-4 µm wide, and 5-10 µm in length and have three membrane systems.
In addition to an outer and inner membrane (which encloses a space filled by a fluid substance known as the stroma, described below), chloroplasts have a complex structure of internal membranes (here referred to as lamellae; singular, lamella). The lamellar structure consists of flattened sacs called thylakoids, which consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen (Figure 23a and b). The thylakoids are often stacked into grana (singular granum), which look rather like stacks of pancakes. The grana are linked by stroma lamellae, which join the stacks of grana together to form a single compartment. The thylakoid membranes and stroma lamellae have embedded within them the chlorophylls and other light-absorbing pigments required for photosynthesis.
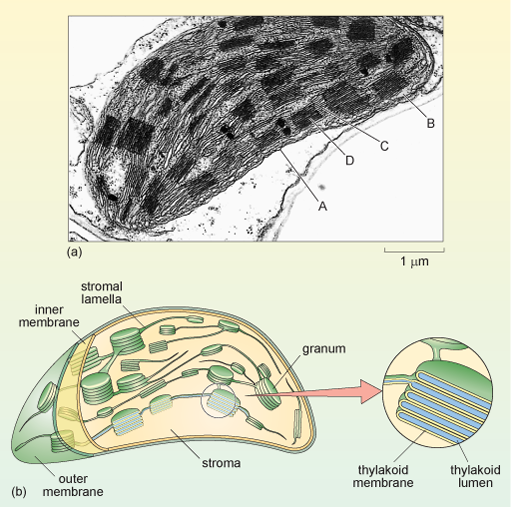
The chloroplast stroma is the site of many important reactions, including the conversion of carbon dioxide into sugars, the production of starch from sugars (starch granules are often seen in chloroplasts) and the synthesis of some chloroplast proteins (there are ribosomes, DNA and RNA within the stroma).