5.4 Unified models
You are now familiar with the main components for building models of AGNs: a central engine powered by an accreting supermassive black hole (with or without jets), clouds of dust, clouds of gas and accretion processes that can organise the gas and dust into a torus-shaped structure. Many attempts have been made to use these components to explain the different types of AGN. Two basic ideas - or perhaps hopes - underlie these models.
First, all AGNs are essentially the same and differ chiefly in the luminosity of the central engine which in turn depends on the mass of the black hole and the mass accretion rate.
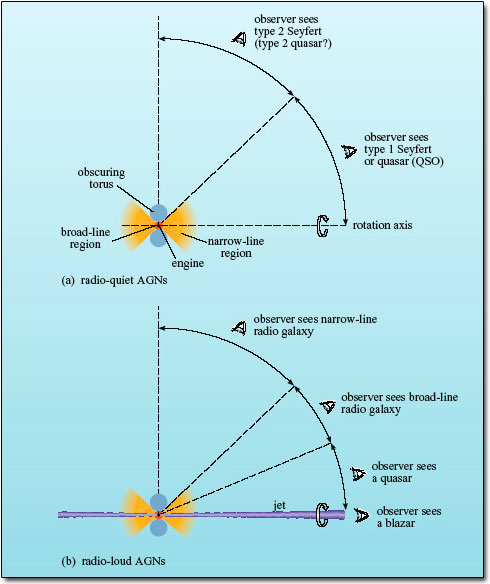
Second, if the AGN contains a dust torus then the radiation observed will depend on the direction from which the AGN is viewed. Two possible schemes for such unified AGN models are shown in Figure 36. One is for radio-quiet AGNs and the other is for radio-loud AGNs.