3.4 Cylinders and shapes with a uniform cross-section
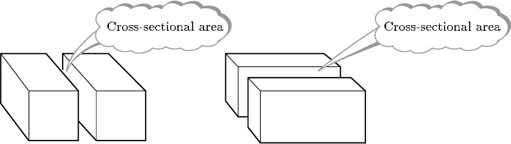
An important idea when calculating volumes of simple shapes is that of a cross-section. In the case of the rectangular box considered above, it is possible to slice through the box horizontally so that the sliced area is exactly the same as the area of the base or top; in other words, the areas of the horizontal cross-sections are equal.
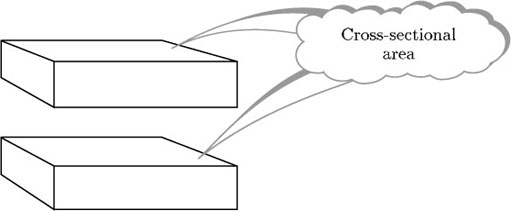
Likewise, you could slice through the box vertically in either of two different directions, producing cross-sections that are the same as either the end faces or the front and back faces.
For objects that have a constant cross-sectional area, there is a very useful formula for the volume.
Volume = cross-sectional area × length
(length is measured at right angles to the cross section)
Notice that this fits with the formula for the volume of a rectangular box.
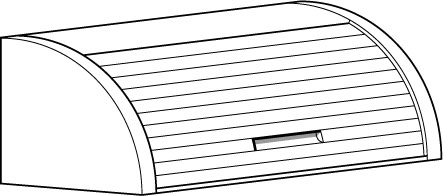
Bear in mind that many objects can only be sliced in one direction to produce a constant cross-sectional area. This bread bin is one example.
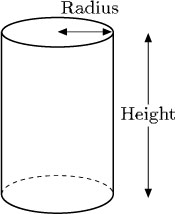
Another example is a cylinder. The formula at the top of the page can be used to find the volume of a cylinder because a cylinder has a constant cross-sectional area if it is sliced parallel to the circular face – the cross-sectional area is the area of the circle that forms the base of the cylinder, that is ![]() × (radius)2. The following formula can then be deduced.
× (radius)2. The following formula can then be deduced.
Volume of cylinder = ![]() × (radius)2 × height
× (radius)2 × height
Example 15
Find the volumes of these objects.
Answer
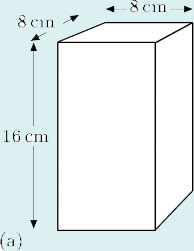
(a) For this object,
cross-sectional area = 8 cm × 8 cm = 64 cm2,
therefore
volume = 16 cm × 64 cm2 = 1024 cm3.
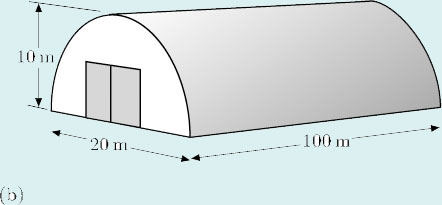
(b) For this object,
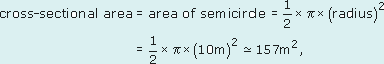
therefore
volume ≅ 157 m2 × 100 m = 15 700 m3.