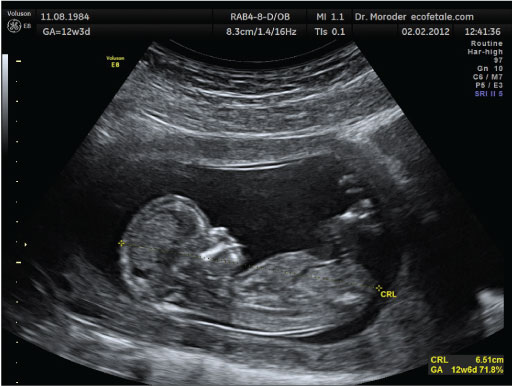
5.2 Ultrasound imaging
A similar use of principles of echolocation has been developed for medical imaging purposes. For example, a pregnant woman can visit a medical practitioner and have an ultrasound scan of their fetus. This scan uses the physics of waves to make a completely safe and non-invasive image of the inside of a human. The practitioner places a piece of equipment called a transducer on the surface of the woman’s skin. The transducer emits very high frequency waves of usually 3–7 MHz (i.e. 3–7 million hertz) into the body. These frequencies are harmless, and the transducer listens for the echoes. Through computer analysis the returning echoes can be turned into an image that depicts what is beneath the skin (Figure 8).