2.2.1 Removal of arsenic oxoanions from drinking water
To remove arsenite and arsenate anions from water one method is to add particles of iron(III) hydroxide and allow time for the anion exchange to take place. However, where the water is pumped directly from a well for use, a better solution is to use a synthetic ion-exchange medium or resin as in Figure 8 and similar to what you previously saw for the removal of nitrate from water.
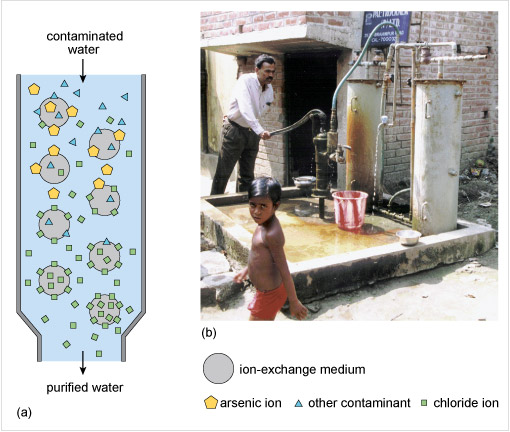
For arsenic contamination, the ion-exchange medium exchanges chloride ions, Cl−, for arsenate ions, AsO43−. Ion-exchange is almost instantaneous, a big advantage over adsorption processes using iron(III) hydroxide. After a few months the medium becomes saturated with arsenate ions and so is regenerated by eluting with a sodium chloride solution. This process presupposes a safe means of disposing of the eluted arsenate containing solution.
In practice, it has been observed that oxidation is beneficial before the removal of arsenic oxoanions. What is the chemistry behind this observation?
Oxidation favours formation of arsenic acid, H3AsO4, which is a stronger acid than arsenous acid, H3AsO3.
At neutral pH, which of the oxoanions, arsenite AsO33− and arsenate AsO43− will bind most strongly to a cation-exchange resin?
Arsenate, AsO43−, binds more strongly to a cation-exchange resin. Arsenate will be more fully deprotonated at neutral pH because arsenic acid is a stronger than arsenous acid. Consequently there will be a higher negative charge and greater electrostatic attraction to the cationic resin.
