3. Energy Use and Smart Devices
3. Energy Creation and Consumption
We use energy in different ways. We use energy to heat or cool buildings and to run lights, devices, and appliances. We use energy to power vehicles such as cars, buses, boats or planes. Machines and factories also use energy. However, have you ever thought about where your energy comes from and what types of energy were used to produce the energy or objects that you use? Let’s look at the journey from energy creation to consumption in more depth.
Fossil fuels such as coal, oil and natural gas can be burned to generate electricity and heat. Renewable sources such as sunlight and wind can also be used to produce electricity. These energy sources are called primary energy, as they don’t need to be modified or processed before they are used in energy production.
Electricity is called secondary energy as it has been produced from primary energy sources. Primary energy sources, such as fossil fuels, are often transformed into more useful or practical forms before being used. For example, crude oil is refined into many different types of fuels and products.
Final energy is how energy is made available to us, as consumers, so that we can make use of it. For example, electricity is provided directly to our home from a power plant via a grid system.
Useful energy is the term used to describe the intended outcome of our energy use. For example, using energy sources such as electricity to power appliances or produce heat for cooking or warmth.
To help illustrate the journey from primary energy to useful energy, let’s take a closer look at some examples of how we produce and consume energy in the following diagram.
Diagram One: The four ways of measuring energy.
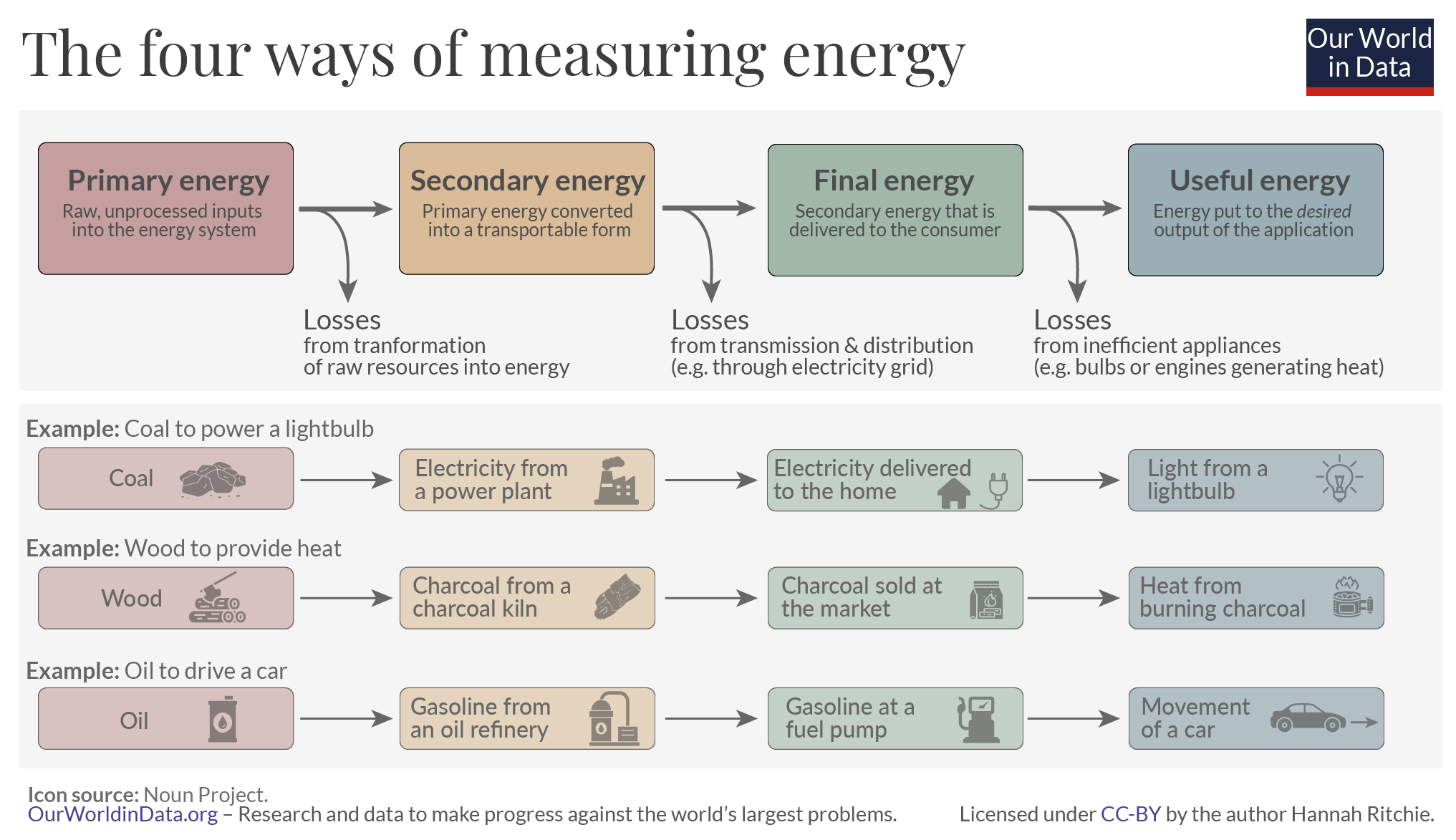
As the above diagram shows, at each stage energy is lost as it is transformed, transported or used. We can not only make decisions about where our final energy comes from (e.g. choose clean energy sources, where possible) but also prevent energy being wasted through how we consume it.
For example, we might be able to use energy efficient lightbulbs, or energy saving devices to reduce our energy consumption at home or work. If we use a car, we can reduce our fuel consumption through changing the way we drive or decluttering our car boot, so we are not carrying so much weight.