3.1 Introduction to computers
| Site: | OpenLearn Create |
| Course: | 3 Digital Skills |
| Book: | 3.1 Introduction to computers |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Monday, 2 March 2026, 7:39 AM |
1. What is a computer?
A computer is an electronic device that stores and processes data.
The infographic below shows the different stages of the information processing cycle.
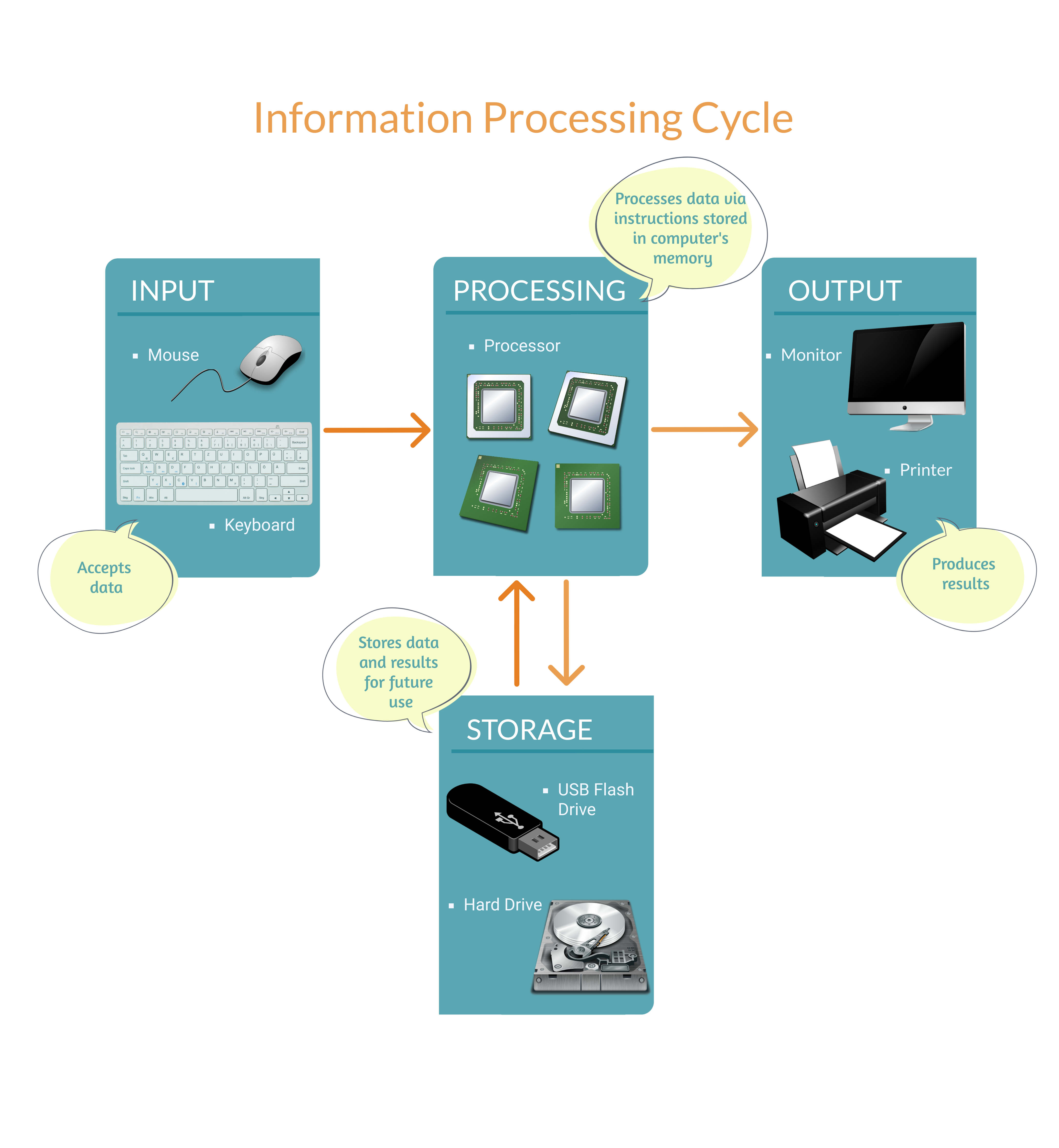
Types of computers
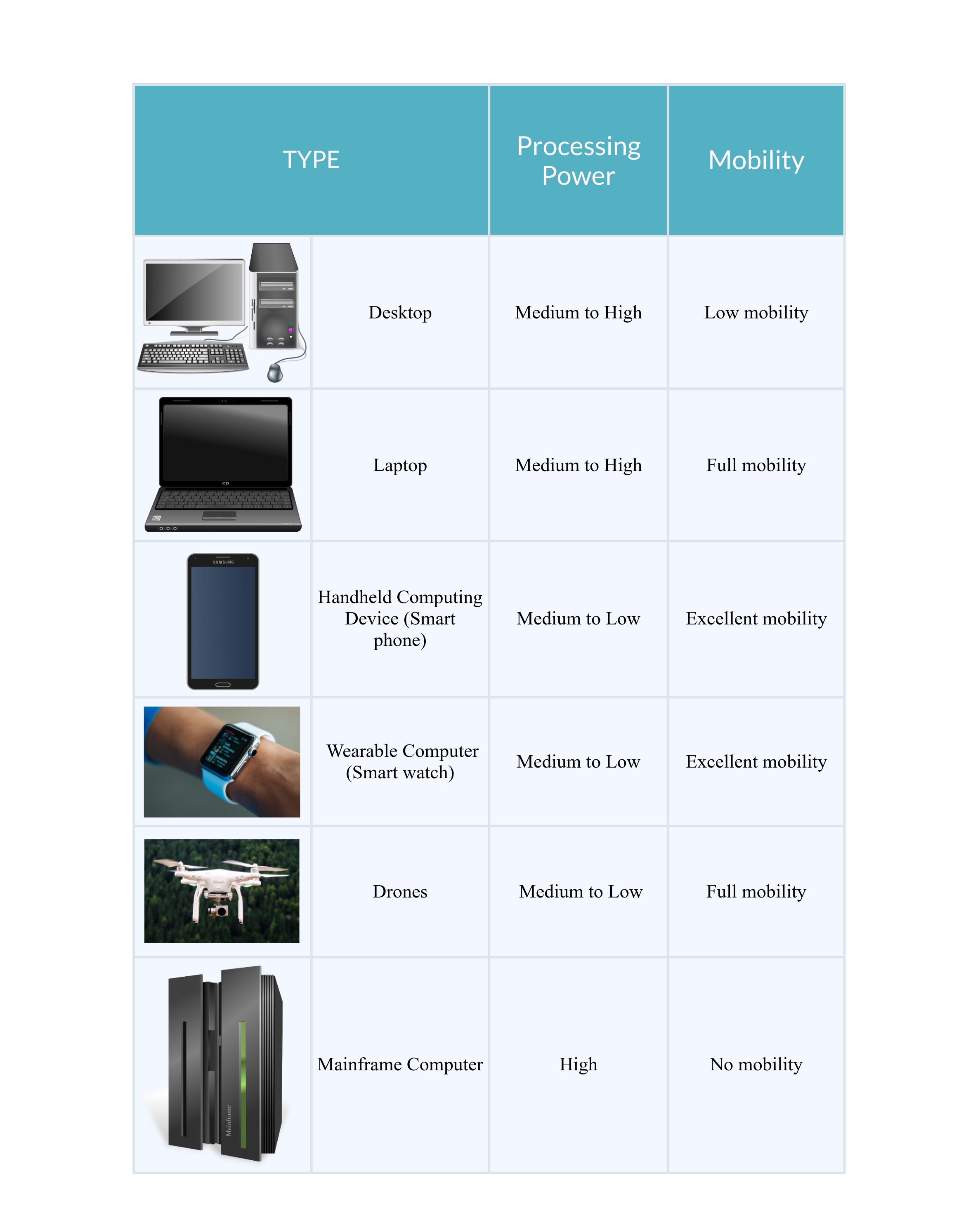
There are many different types of computers. The first computers were very large physical devices and usually took up several rooms. They were first developed around the 1940s. Over the years, the size of computers has decreased, whereas their power and efficiency have increased due to the discovery of technologies such as transistors and integrated circuits.
The Desktop or Personal Computer (PC) also known as the desktop computer or workstation was designed with individual users in mind. Personal computers first appeared in the late 1970s, with the Apple II and IBM PC being the more popular ones. Nowadays, personal computers range from a few hundred to thousands of US dollars in price. They are also typically used in offices and community hubs and probably what you have in mind when you hear the term ‘computer’.
Laptops are small portable computers, also known as notebooks. They are nearly equivalent to personal computers in terms of their processing power and storage capacity. However, they are a bit more expensive than personal computers.
Handheld computing devices are small enough to fit in your hand. Common examples of handheld computing devices include tablets, smartphones and personal digital assistants. Handheld computing devices often have touch screens or soft keypads, memory card storage and the ability to send files or connect with other devices via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. You can use these to connect to accessoires like headsets and keyboards. Many handheld computing devices also have inbuilt GPS technology that allows them to use the Global Positioning System to determine your location.
Wearable Computers are, as the name says, computers that can be worn on your body such as smartwatches. They are usually used for health monitoring systems, communication or recreation. One main advantage of the wearable computer is its ability to allow users to multi-task.
Drones, also known as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV), can be flown via remote control by a person on the ground or via an onboard computing system, which makes use of flight plans, sensors, and GPS technology. Drones can be equipped with different equipment, such as cameras or sensors. . Drones are used for a wide range of applications, like surveillance, search and rescue, weather and traffic monitoring, photography, videography or environmental monitoring.
Mainframe computers are one of the fastest and largest computers today. They are normally used at banks and other enterprises that require high speed and efficiency to handle many transactions. They are very expensive and rely on several high-speed central processing units (CPUs) and lots of memory.
The infographic below shows the main different types of modern computers.
2. Computer Hardware
Output Devices are responsible for outputting information from the computer. Some examples of output devices are monitors, printers, projectors, sound cards, video cards and speakers.What is hardware?
Computer hardware are all the components that you can see and touch, so all physical parts and devices of the computer.
Types of hardware:
- Processing Devices: The central processing unit (CPU) is also known as the brain of the computer and performs all types of data processing operations.
- Input devices are responsible for sending signals or data to the CPU. They are generally used for interacting or communicating with the computer. Some examples of input devices are keyboards, mice, joysticks, microphones, webcams, and scanners.



Microphone - Webcam - Joystick
- Output Devices are responsible for outputting information from the computer. Some examples of output devices are monitors, printers, projectors, sound cards, video cards and speakers.

Projector - Speaker
- Input/Output Devices have elements of both, input and output devices. They accept inputted data and are capable of outputting information in return. Examples include modems and digital cameras.

Modem - Digital Camera
- Storage Devices are designed to store information for longer periods of time. Information can be shared by connecting them to the computer either internally or externally and then saving information on them.
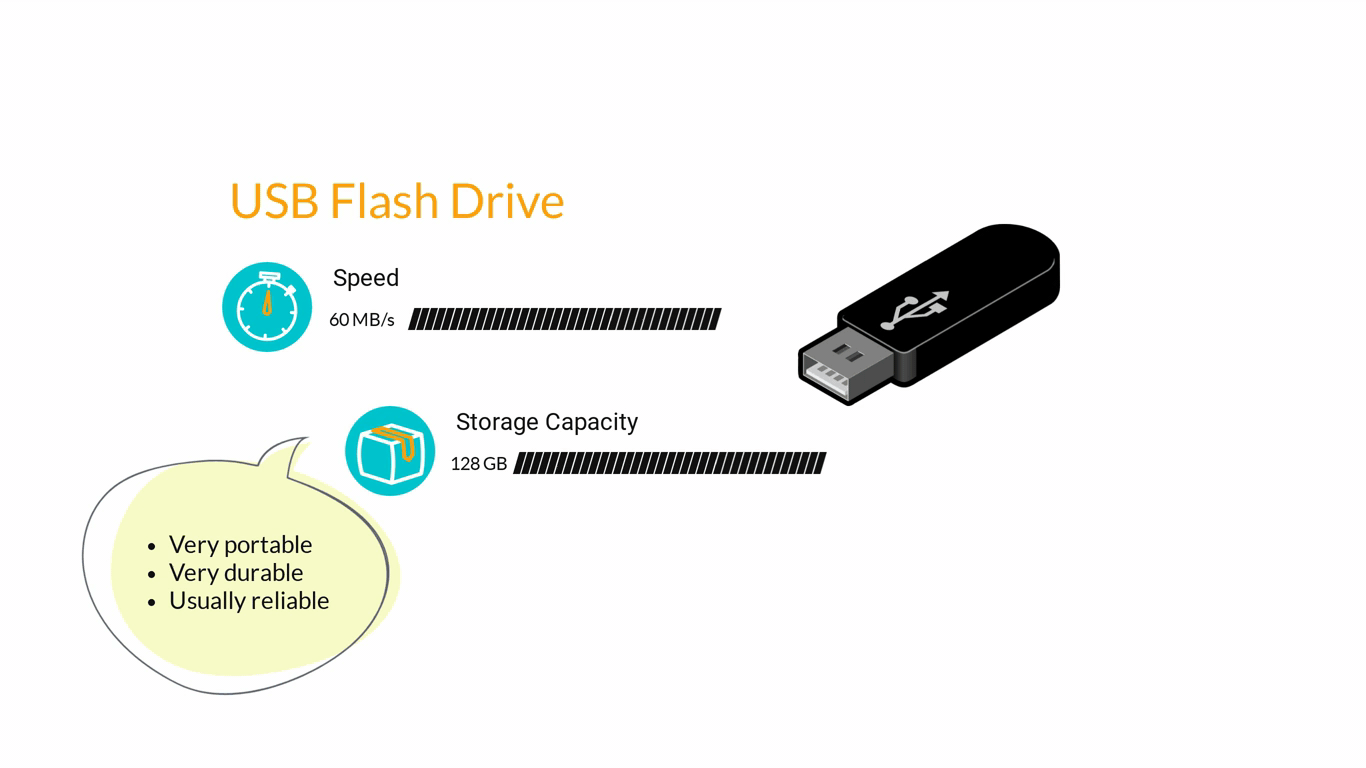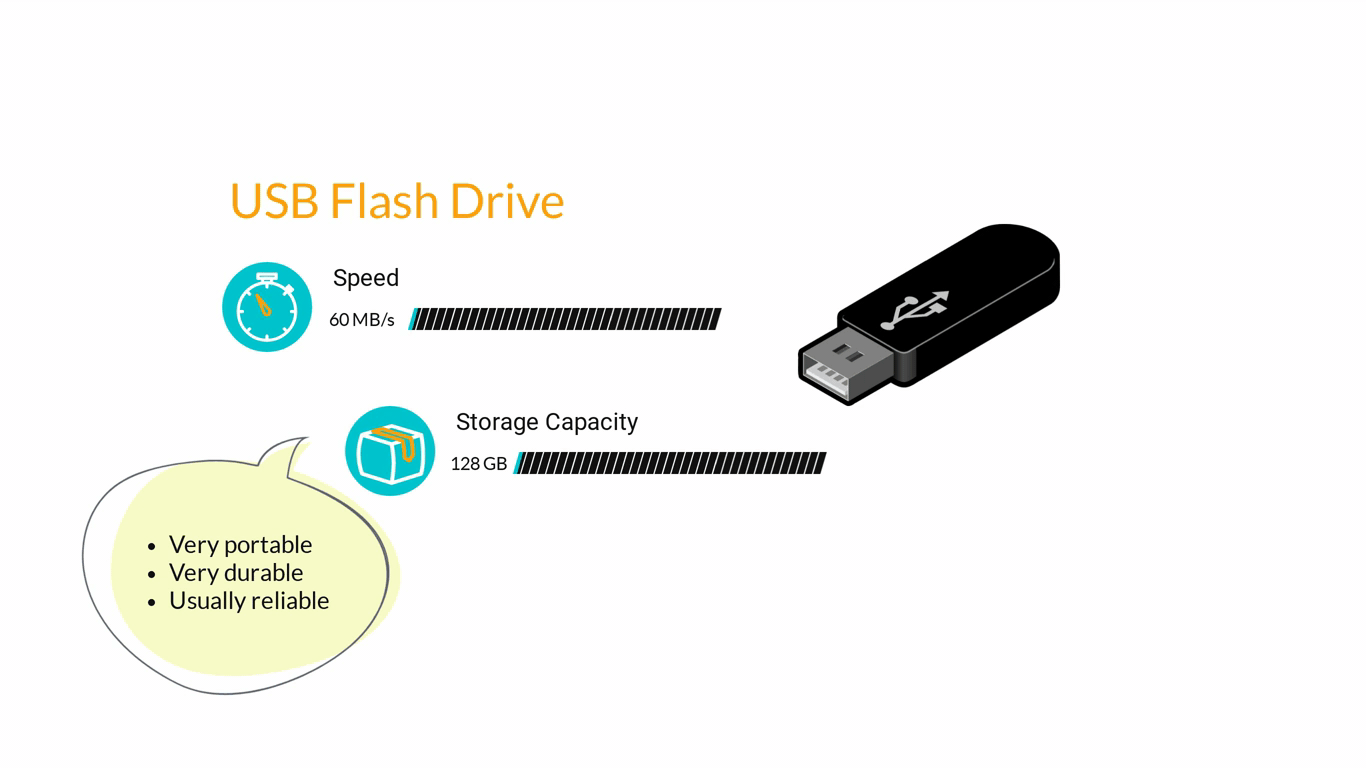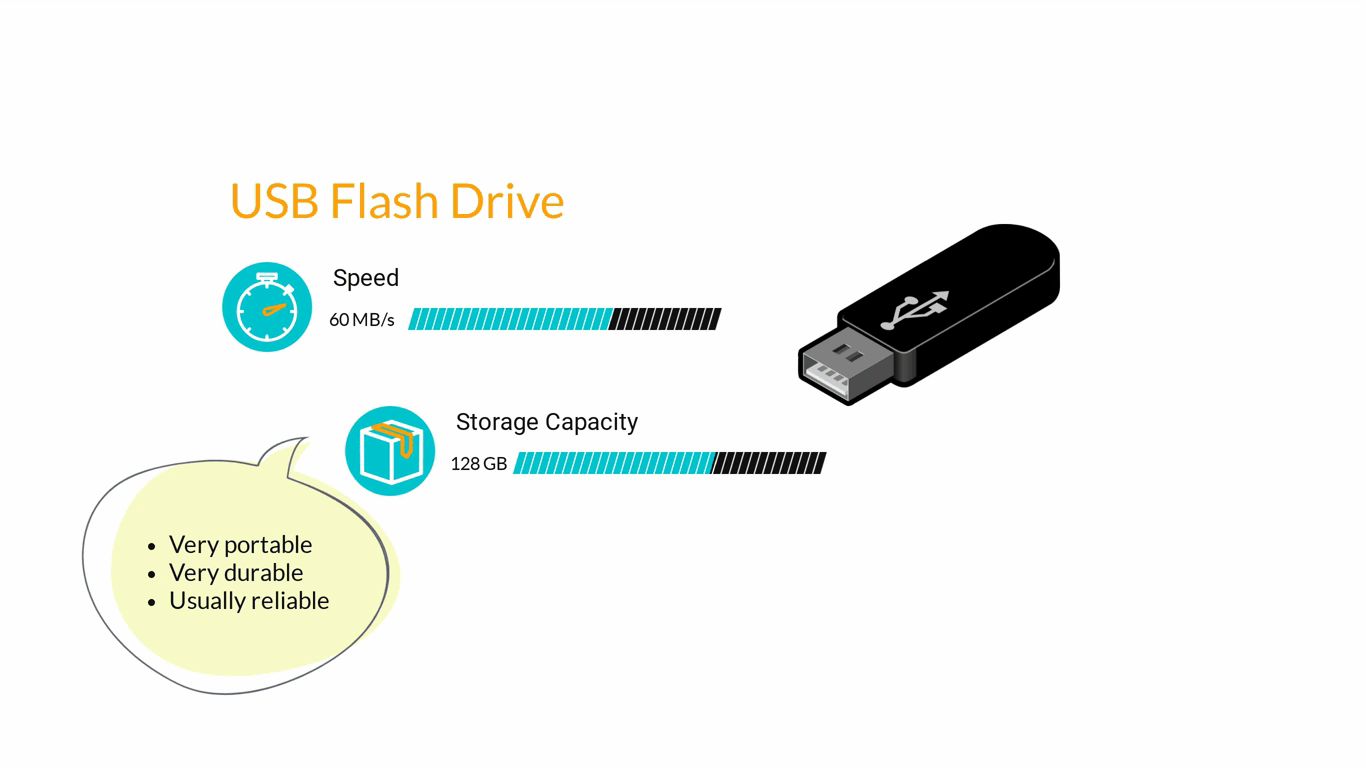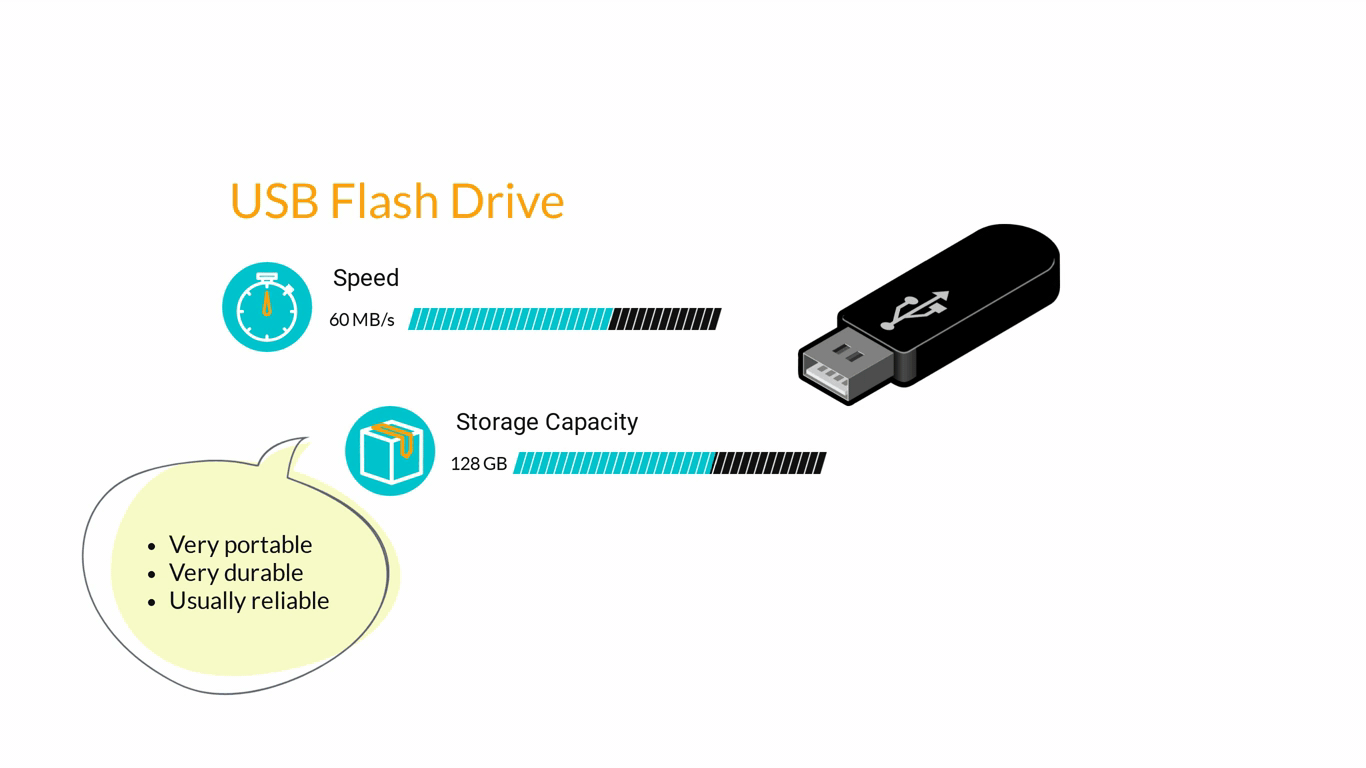
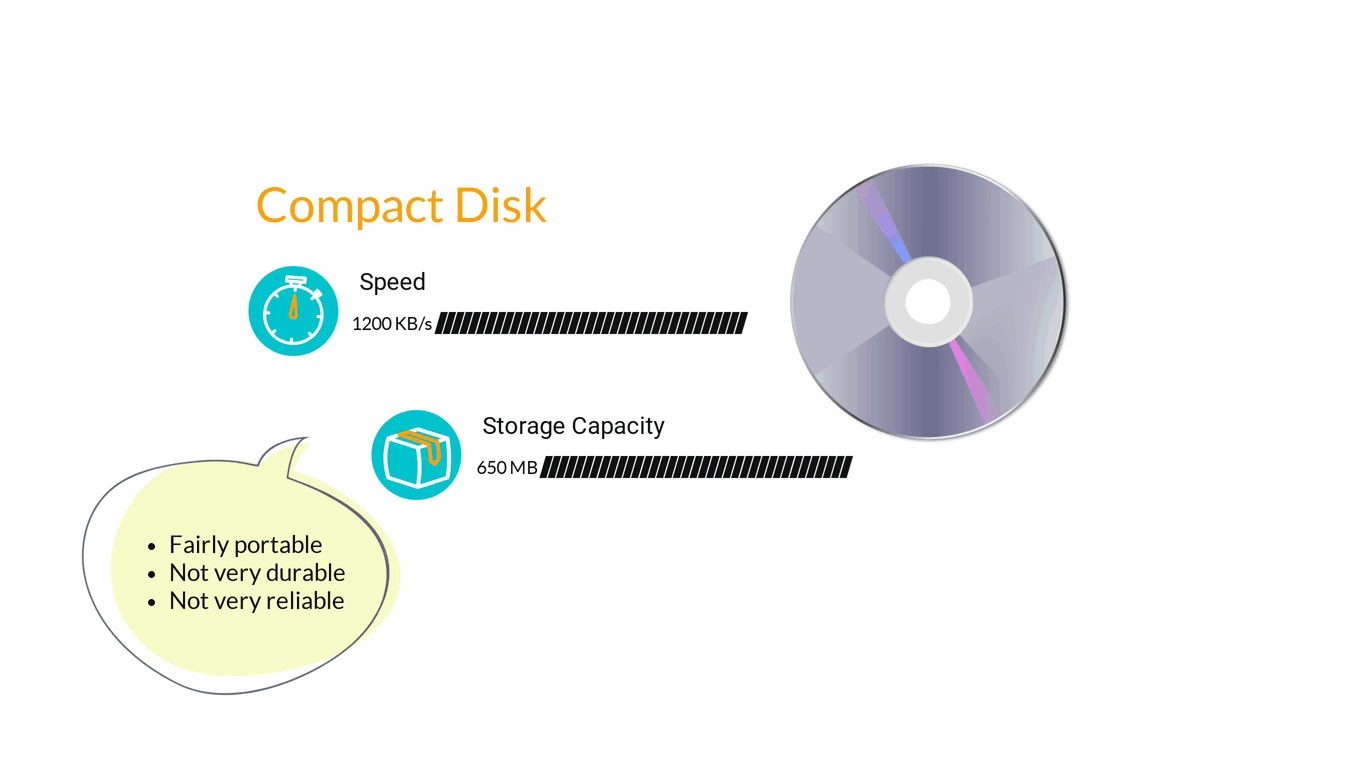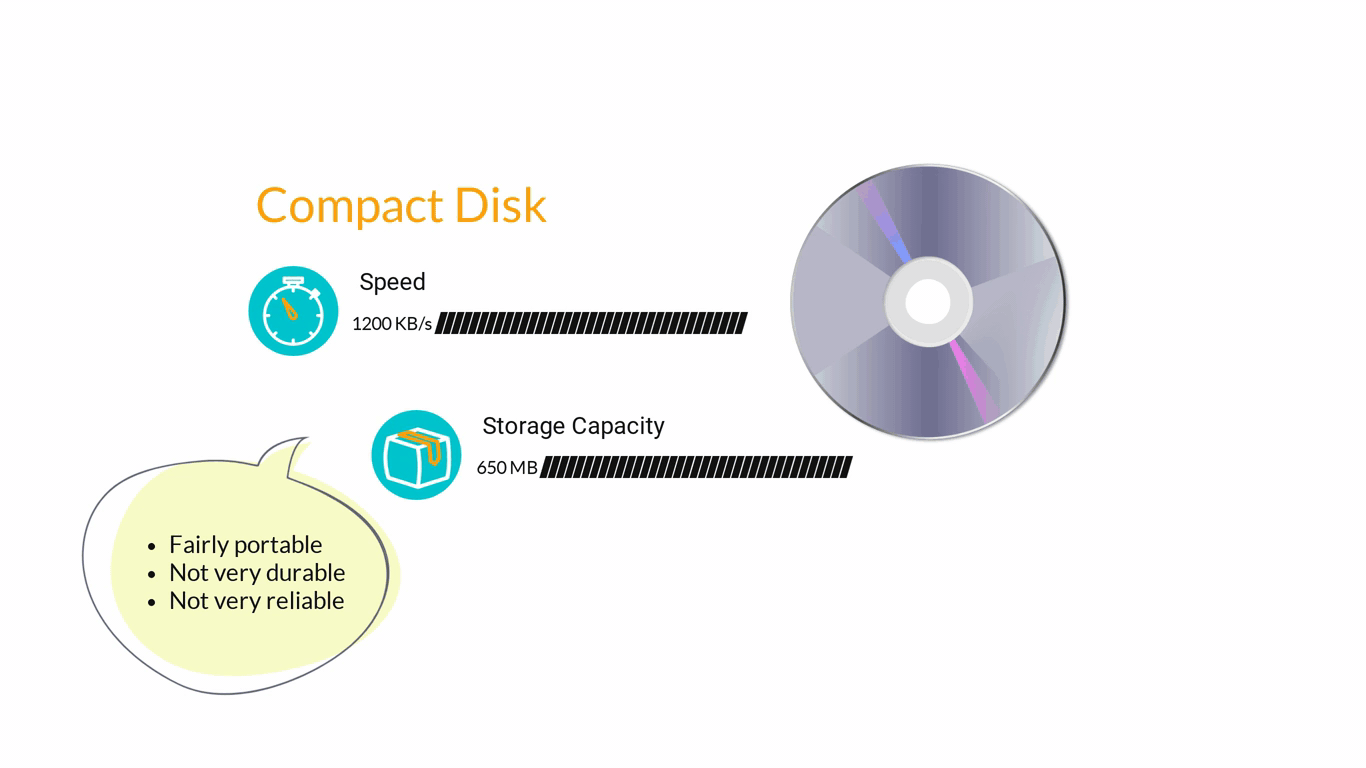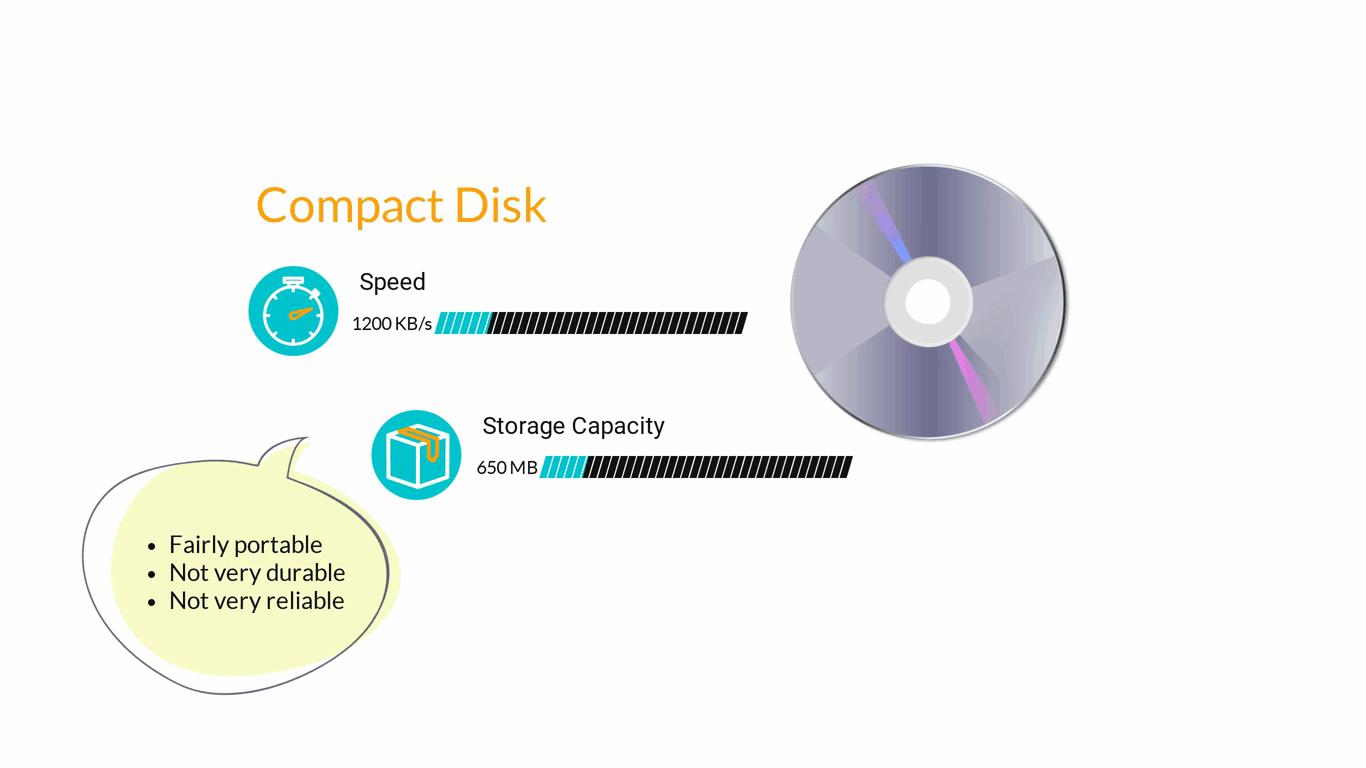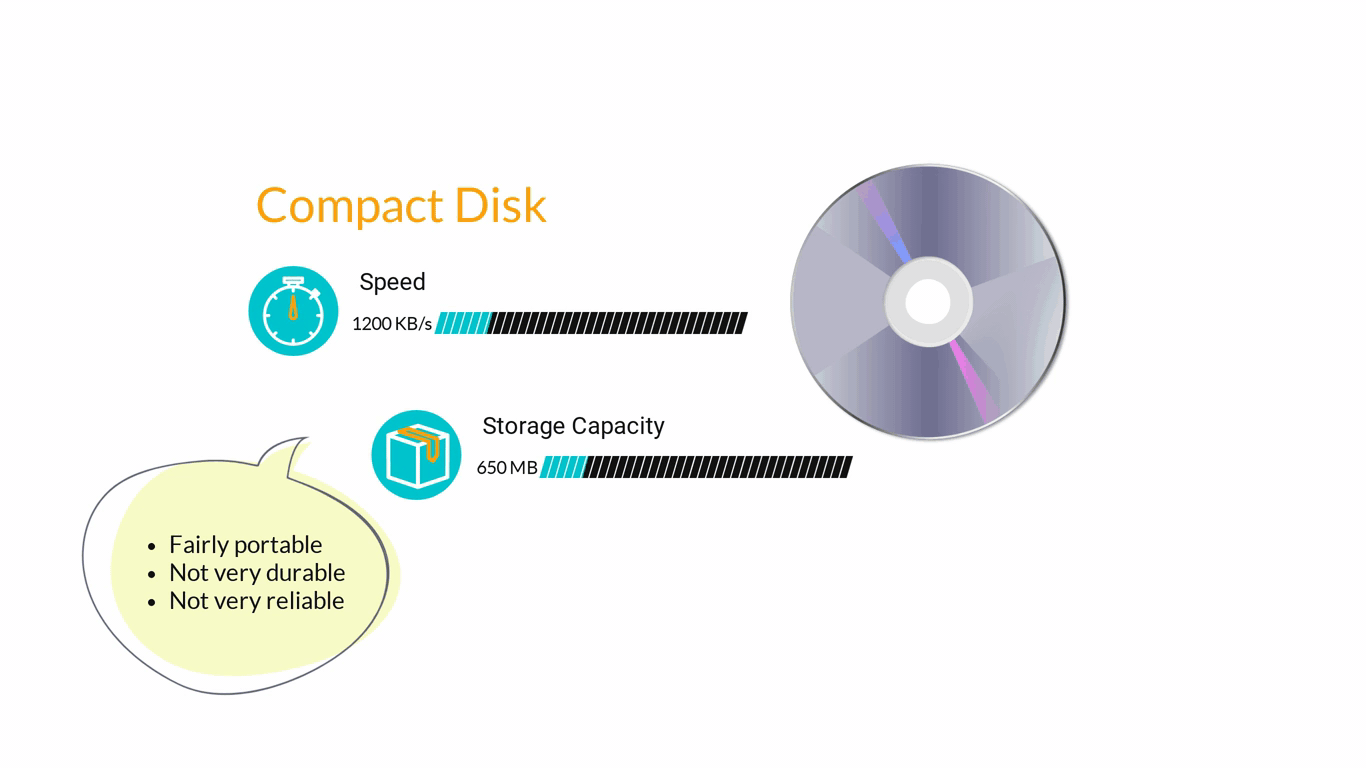
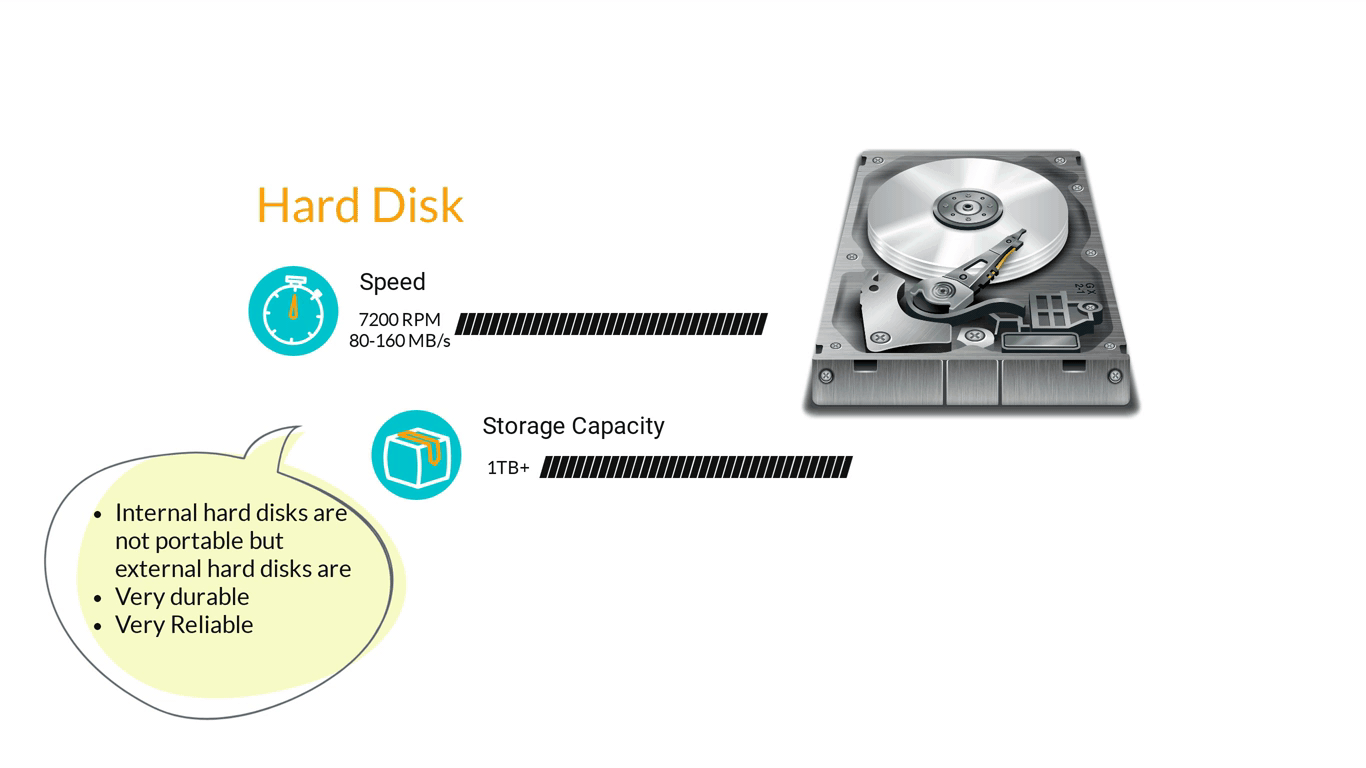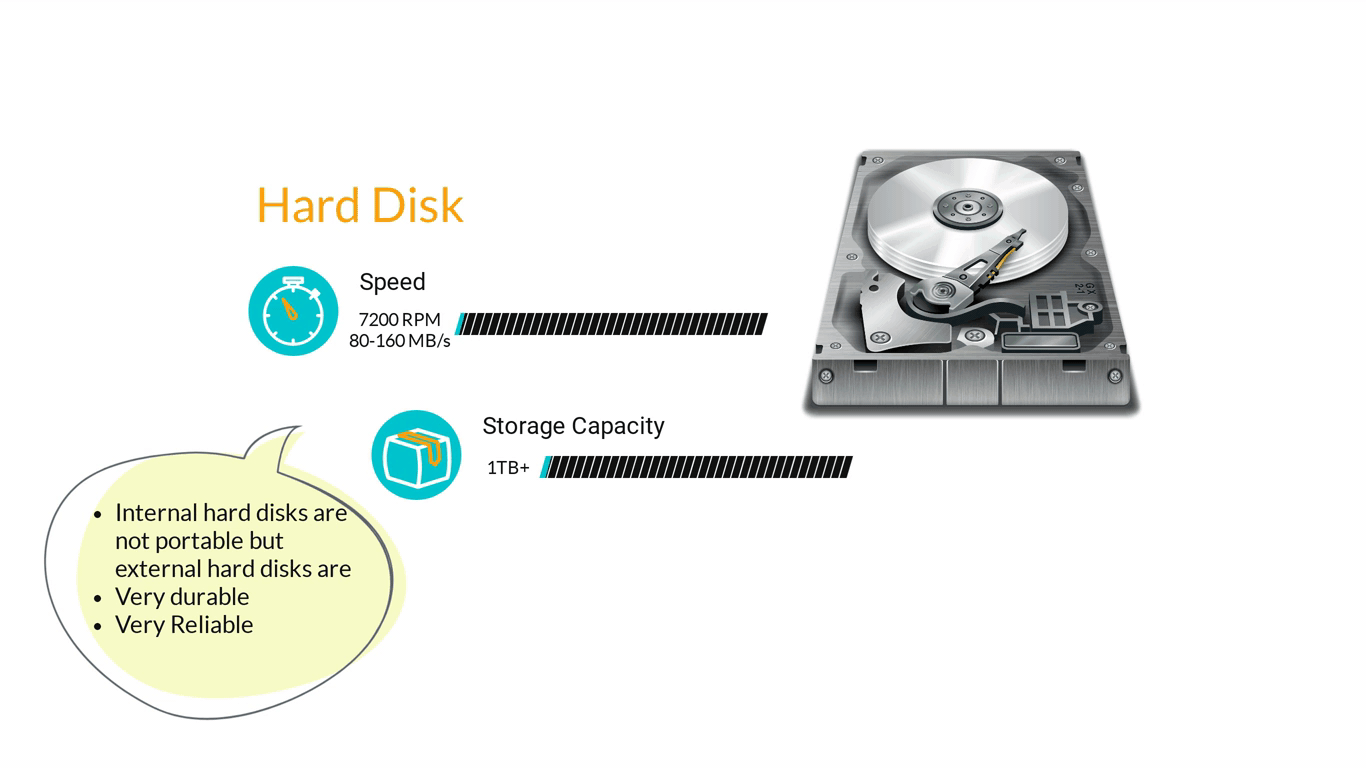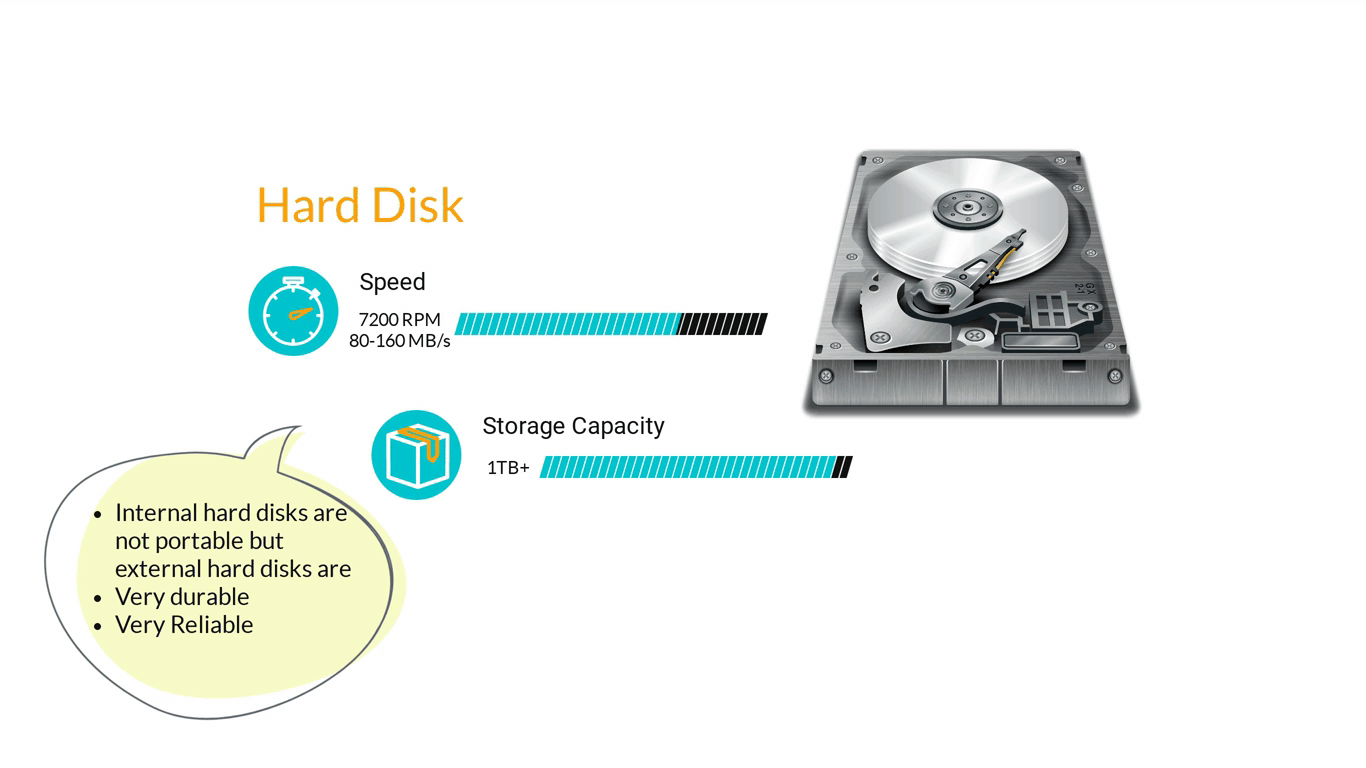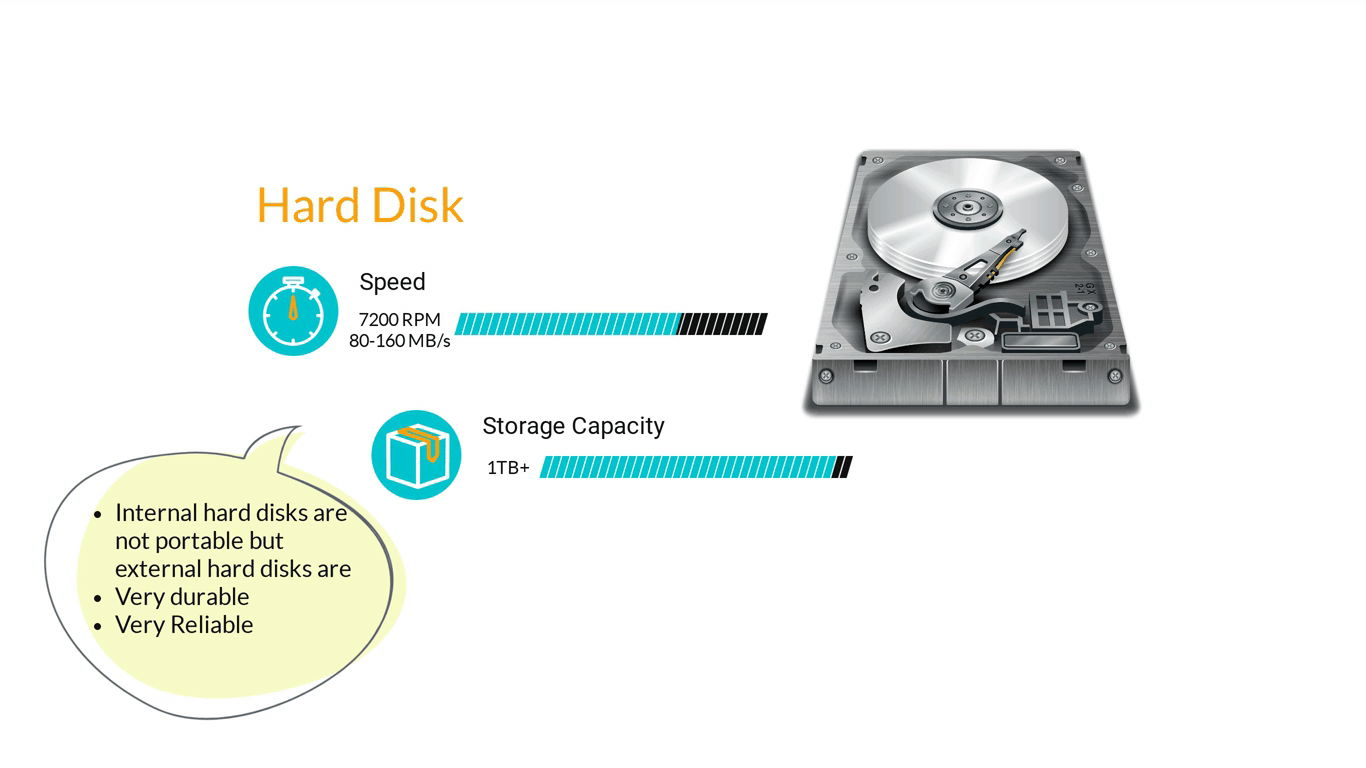
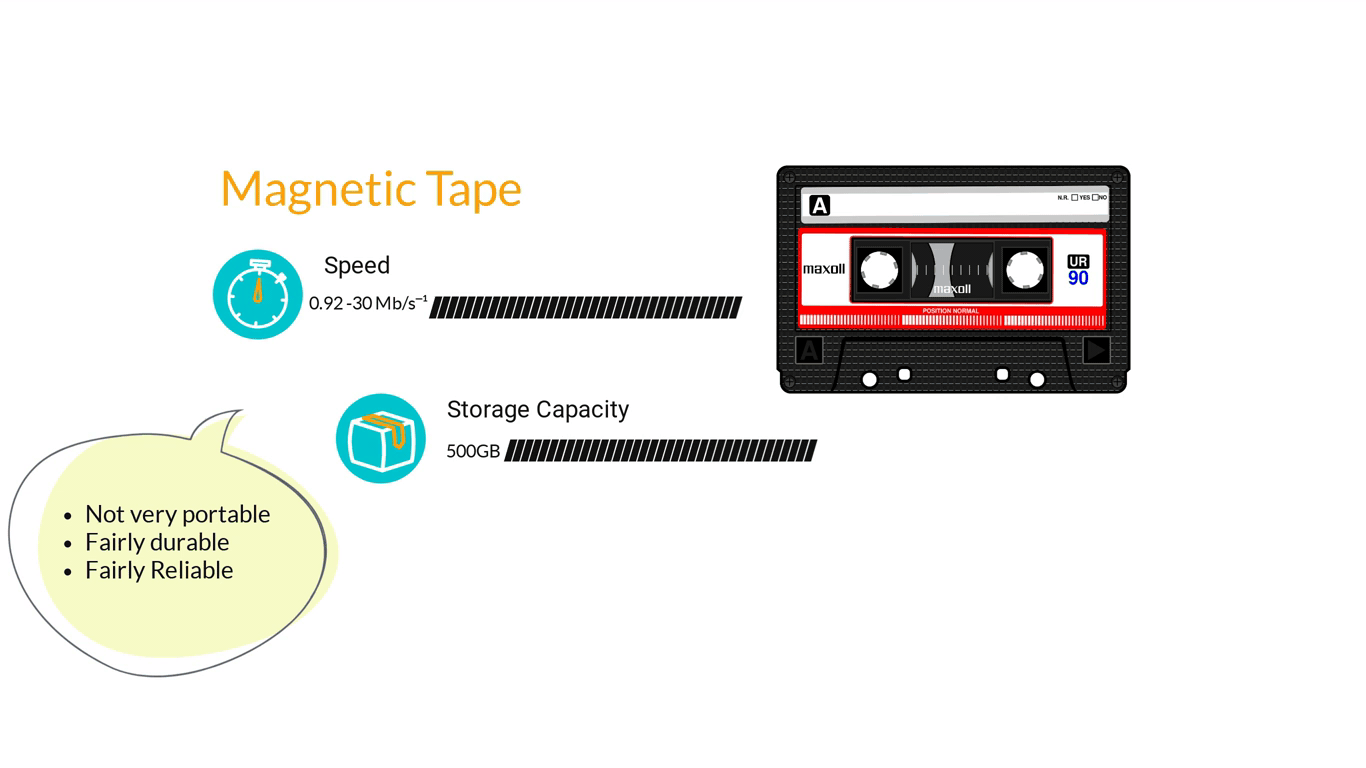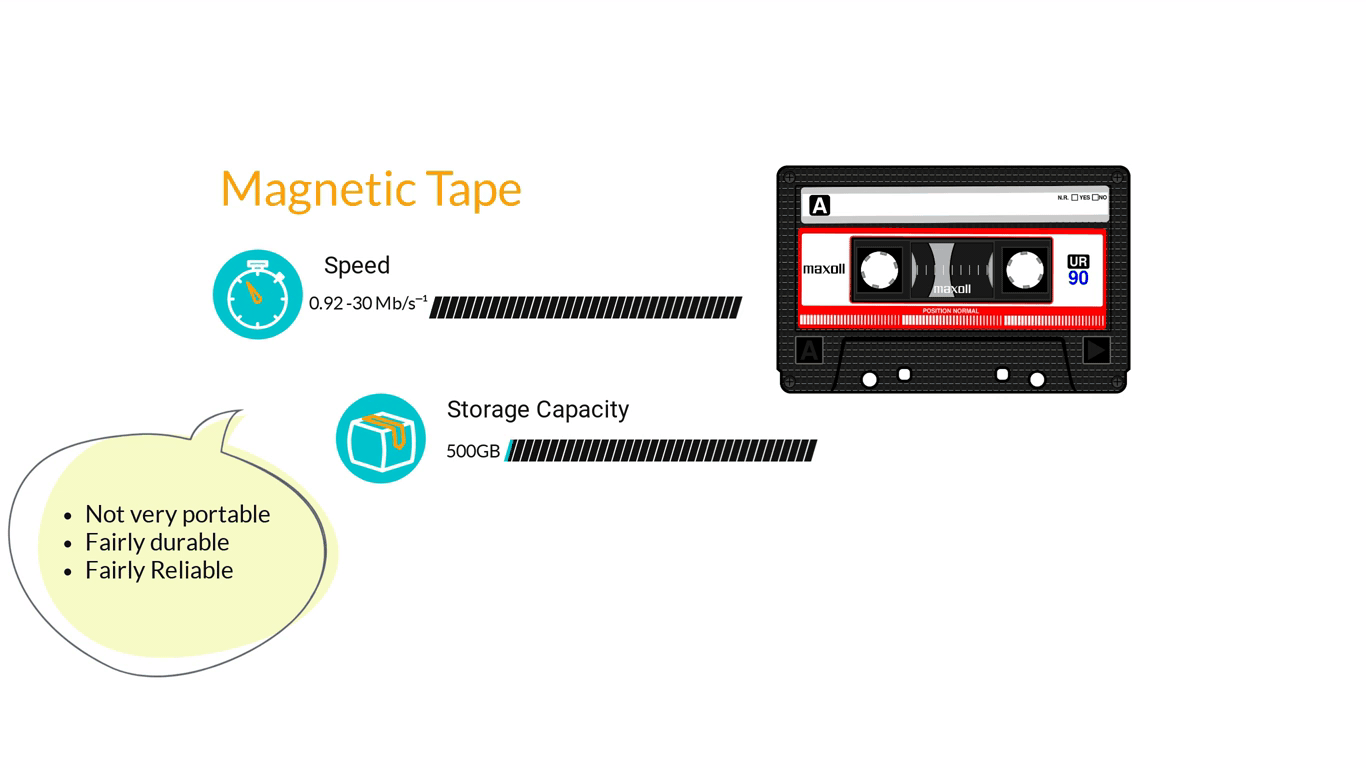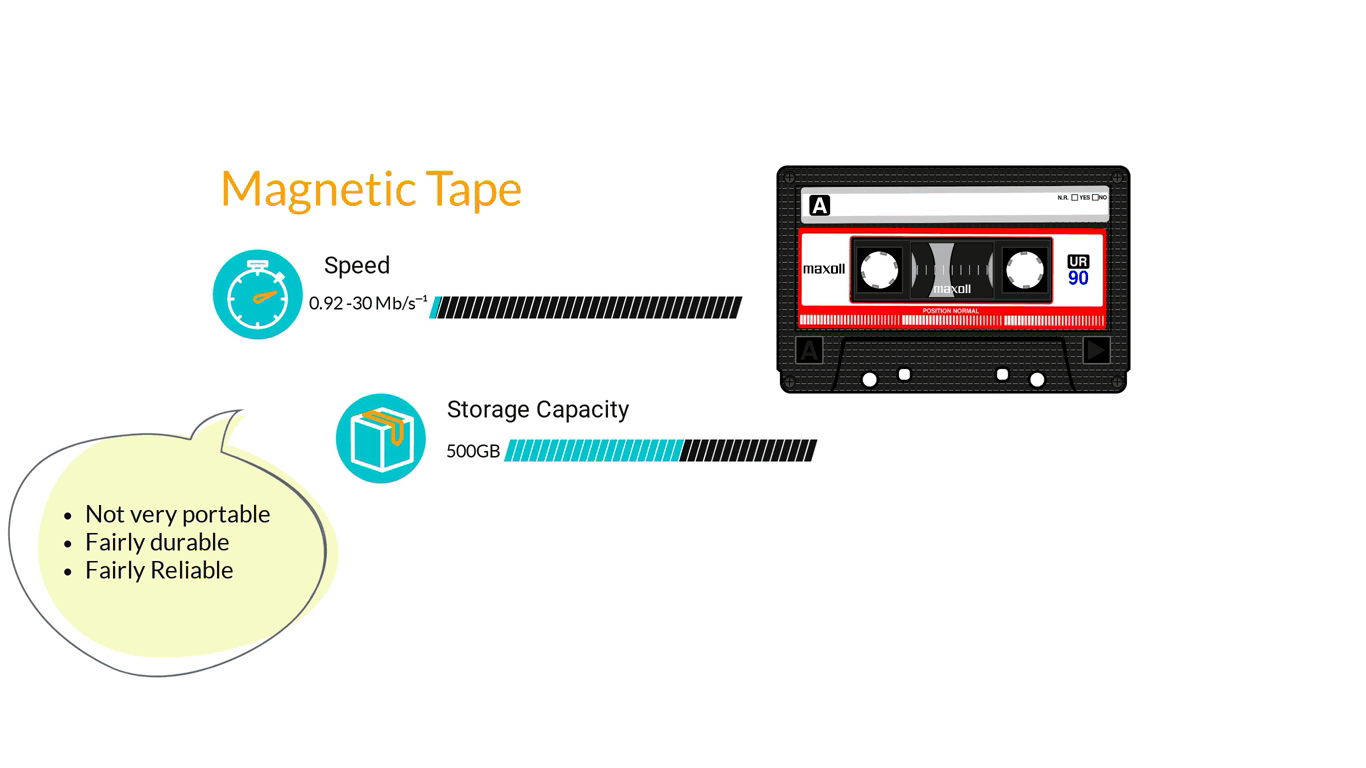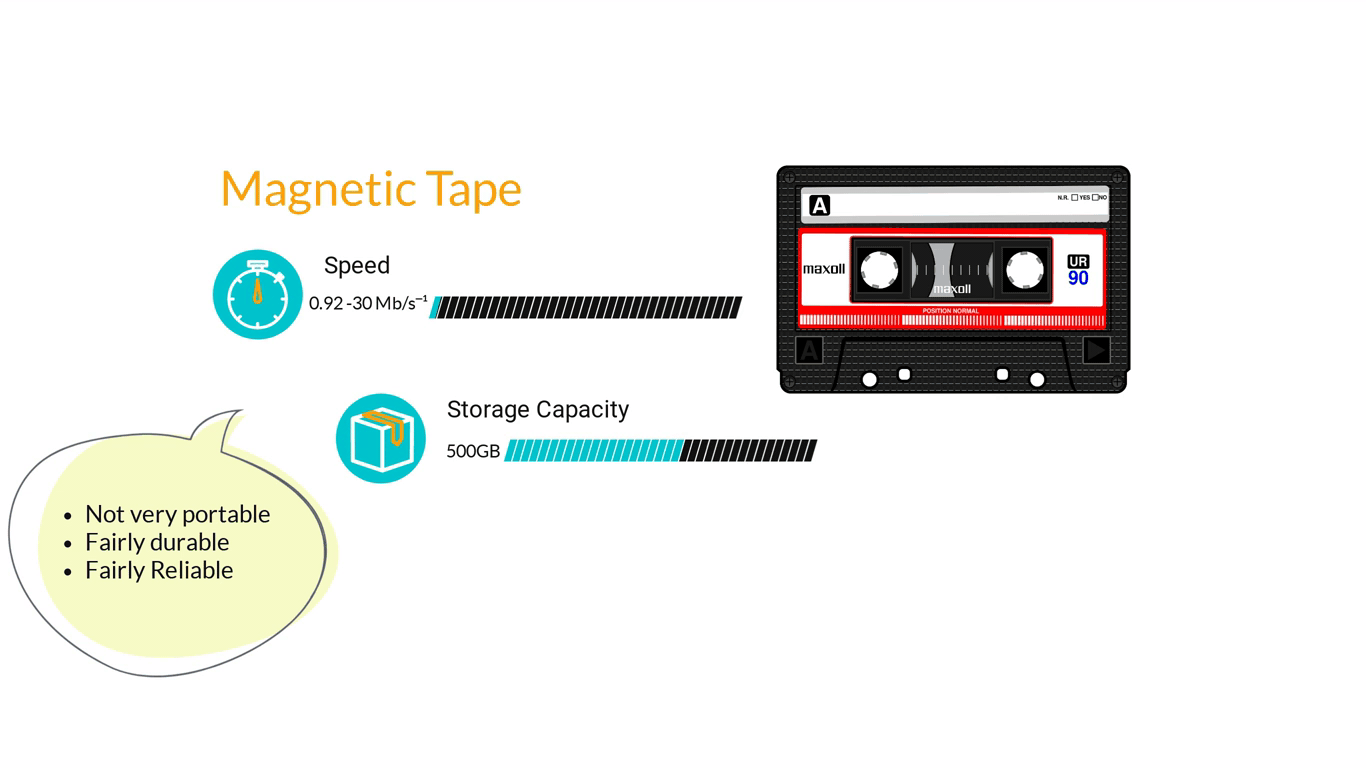
3. Computer Software
What is software?
Computer software are all applications that can be run on a computer. They are basically the instructions that tell the hardware of a computer what to do. The infographic below shows in a very simple way how the different layers and the different elements of a computer system interact.
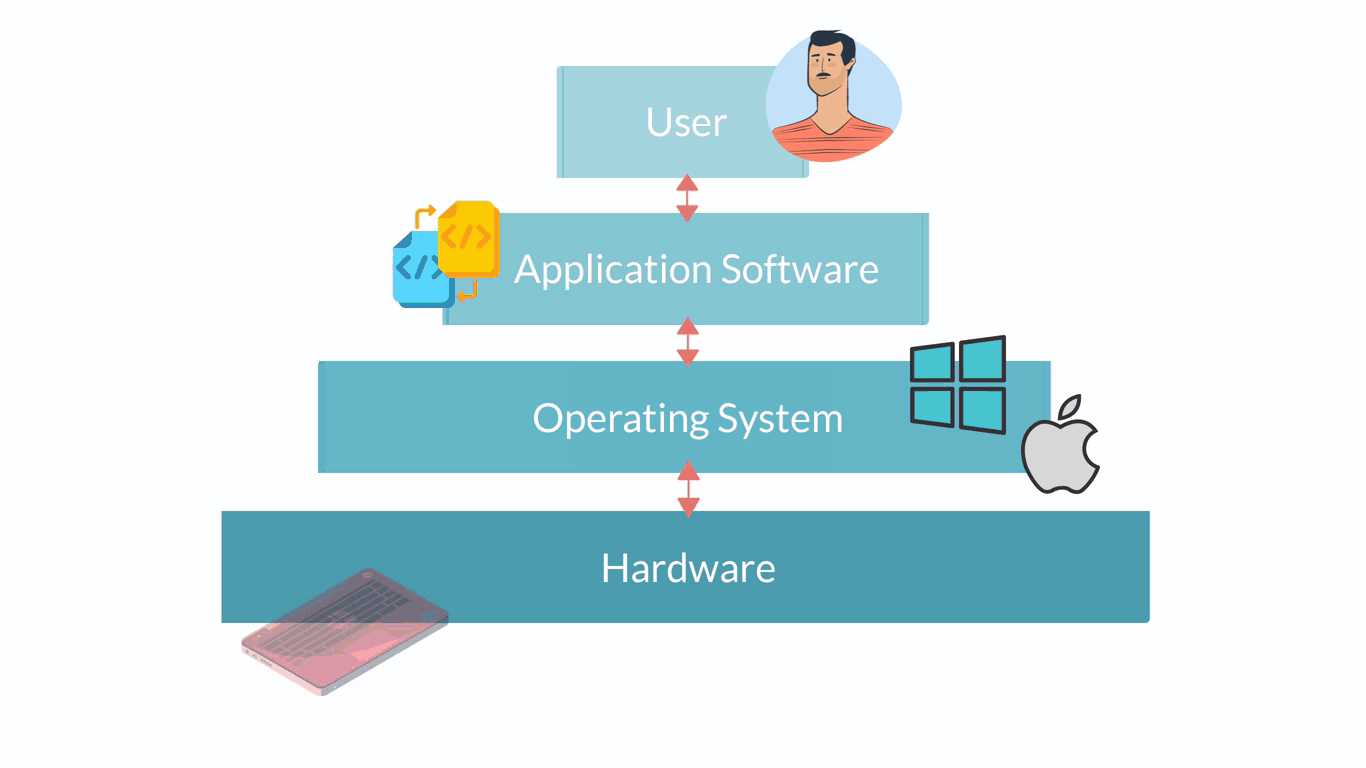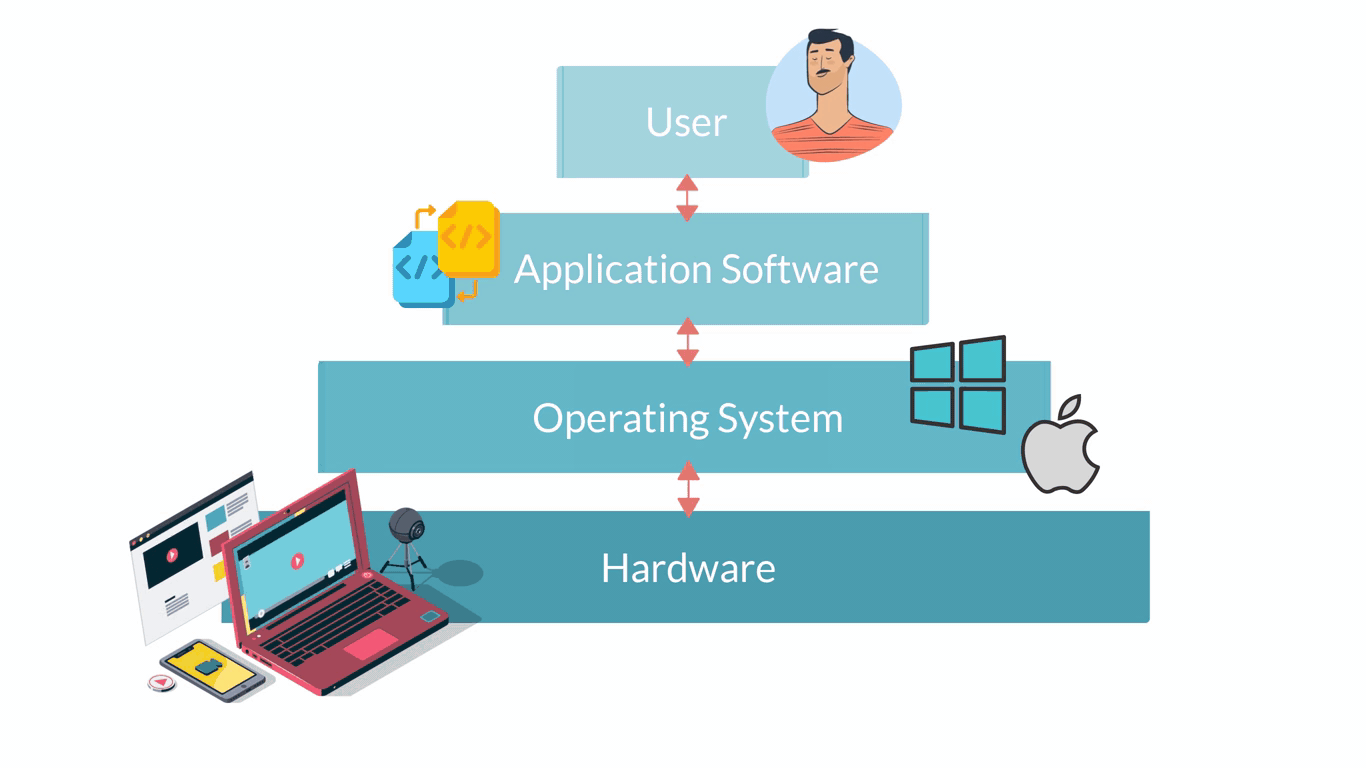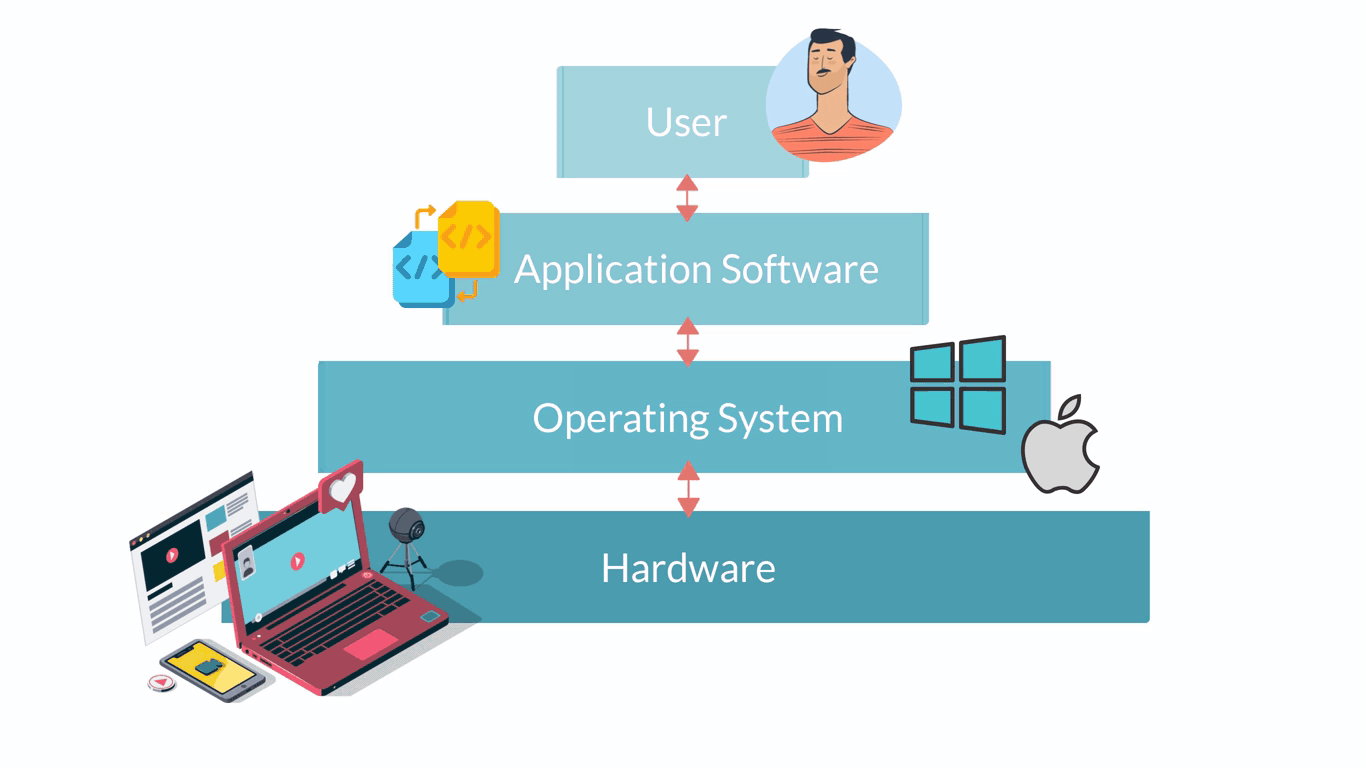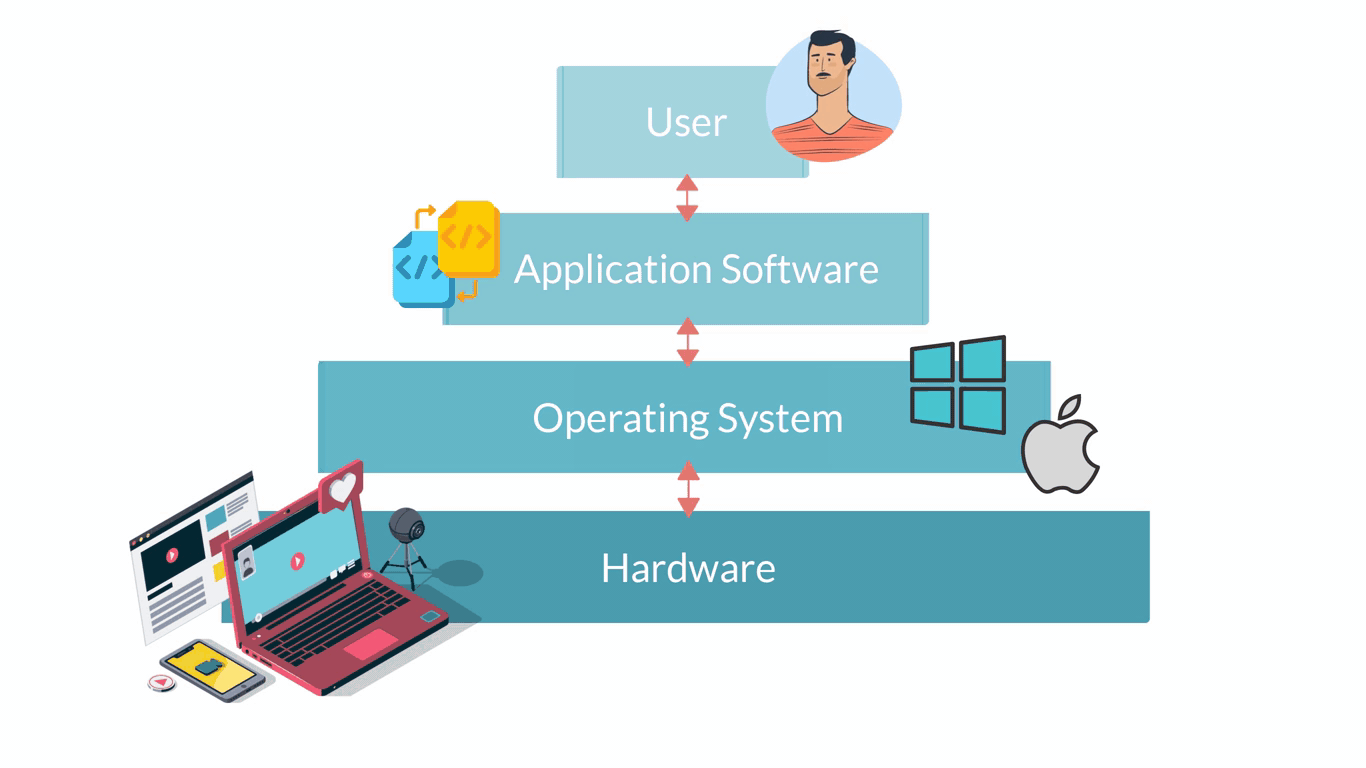
Software describes all computer programs, so non-physical elements important for the functioning of a computer that cannot be touched. Software can be considered as a set of instructions that tell the computer’s hardware how to behave.
Types of Software
There are a few different types of software that can be grouped into two categories: Application Software and System Software
Systems software are those programmes that control a computer's internal functioning through an operating system.
- Operating System Software (OS) manages all other Software on the computer and allows Application Software to communicate with the hardware. Some of its main functions are:
- Allowing multiple programs to run
- Coordinating tasks when the user switches from program to program
- Sharing memory among multiple programs
- Sending the user or programs status messages or warning and error messages from the computer
- Examples of Operating System Software:
- Windows 10, Windows 8, Apple MacOS
- Mobile OS: Windows 10, Apple iOS, Android e.g. 11
- Utility Software provides supporting features such as analysing, optimising, configuring and maintaining a computer.
Application software are computer programmes designed to carry out specific tasks and commands given by the user such as image editing or word processing. Application Software require an Operating System Software to be able to run. So, if you look back at the infographic showing the different elements of a computer system, Application Software is on top of Operating System Software. Some examples of Application Software are:
- Word Processors – are used for composing, editing, formatting, and printing documents.
- Graphics tools – are used for creating and editing drawings and images. Many support the creation of both 2D and 3D images.
- Web browsers – are used for retrieving, presenting and browsing information on the Internet.
- Database programs – are used for managing information in a database structure.
- Audio and Video Editing programs – are used for creating and editing audio and video files.
Turning your computer on
The first steps for using your computer means becoming familiar with turning the computer on and off, getting comfortable with using the input devices (e.g. keyboard, mouse/touchpad, touchscreen) and opening/closing programs.
- Locate your computer’s power button with the symbol on the right in the picture below.
- If you are using a desktop computer, it is normally on the front of the system unit as shown in the picture on the left.
- Press the power button. A yellow status light should appear.
- Next, locate and turn on your monitor’s power button, which is normally located on the lower front. A yellow status light should appear near the power button.


- If you are using a laptop computer, you will need to flip open your computer and find the power button, often located in the top right corner of your keyboard as shown in the image below.
- Press the power button. A yellow status light should typically appear.

When the Startup process is complete, your Desktop is displayed on your monitor’s screen.
If your computer was configured with a user account, you may be asked to type/ enter a username and password via a Login screen. After typing the username and password, press the Enter button on your keyboard. If the information entered was correct, your Desktop should be displayed on your monitor’s screen.
4. Mouse and keyboard fundamentals
The Mouse
A mouse is a peripheral device that you can use to provide input in your desktop computer or laptop. Even though laptops come with a built in touchpad, having a mouse can be helpful and easier to use if you’re going to spend long periods of time on the computer or for activities that require a bit more precision, such as graphic design.


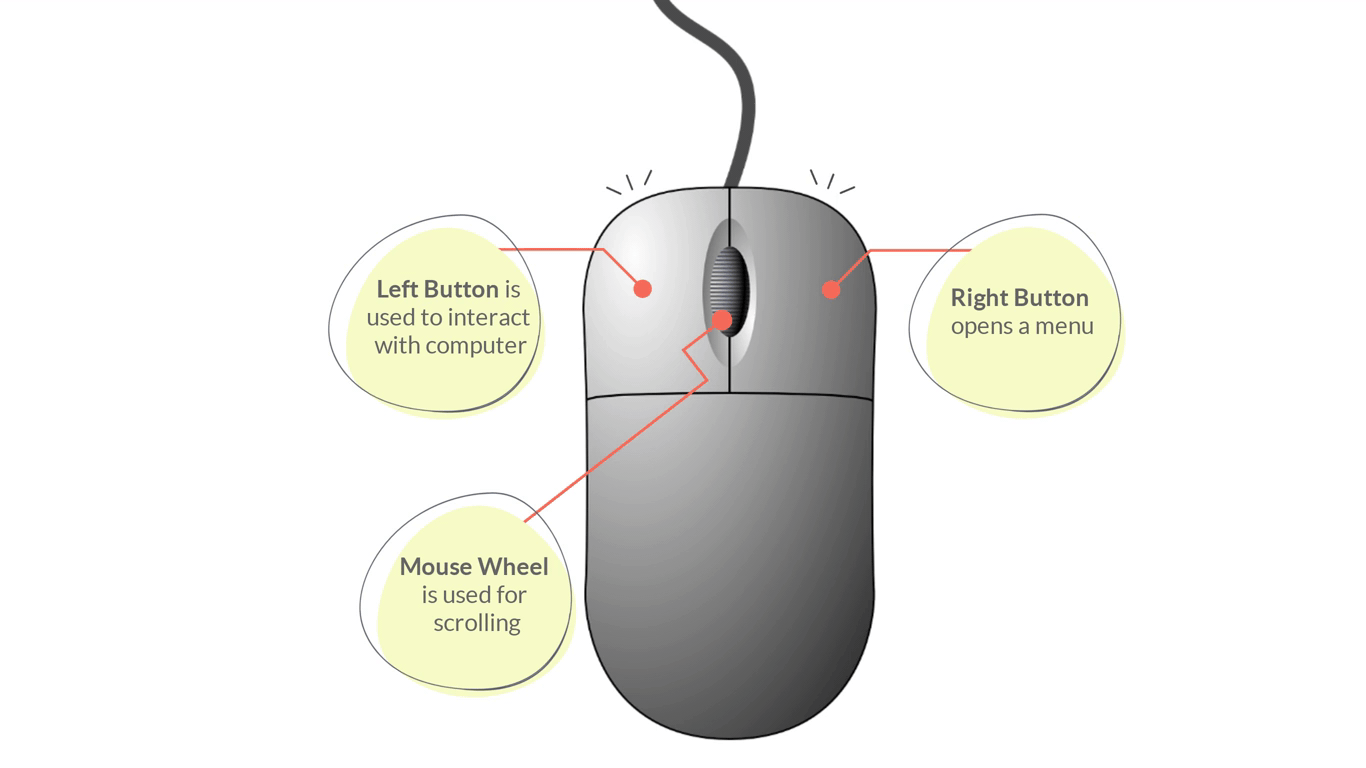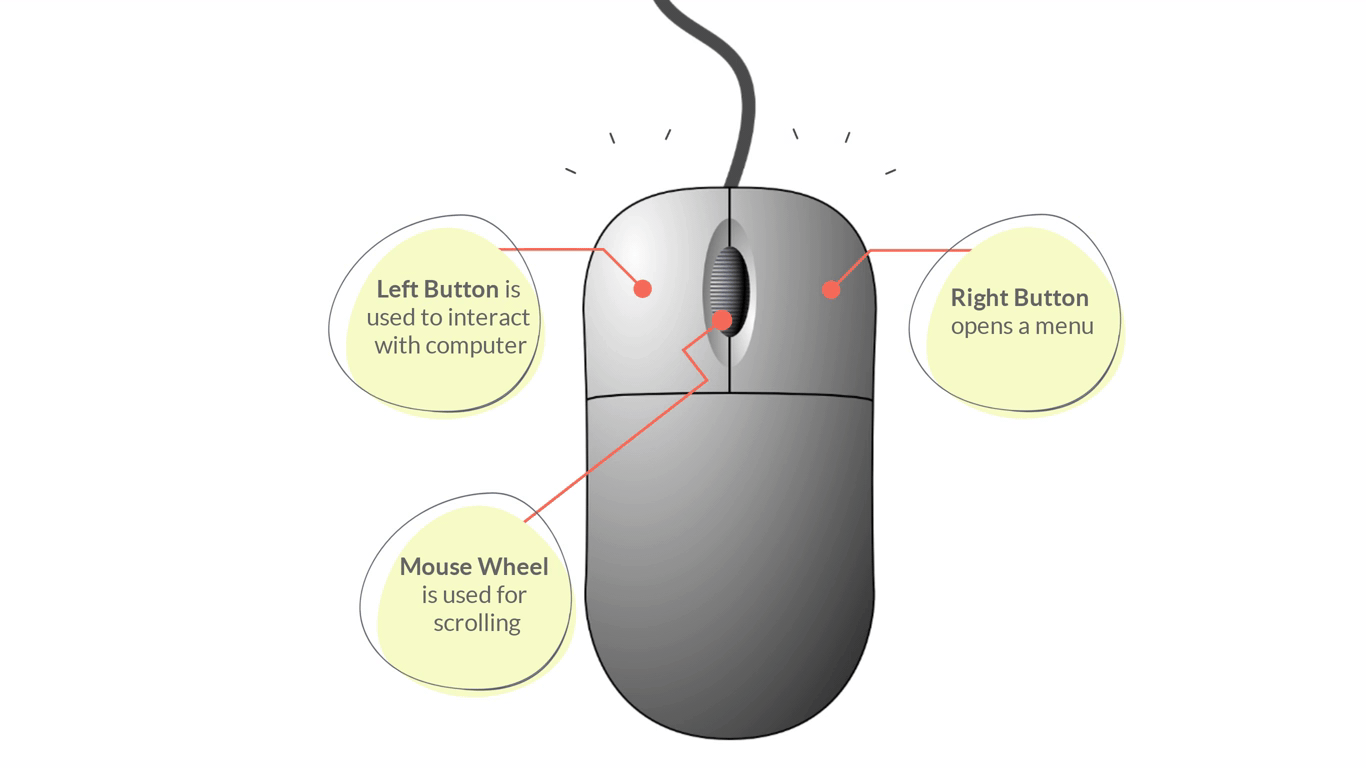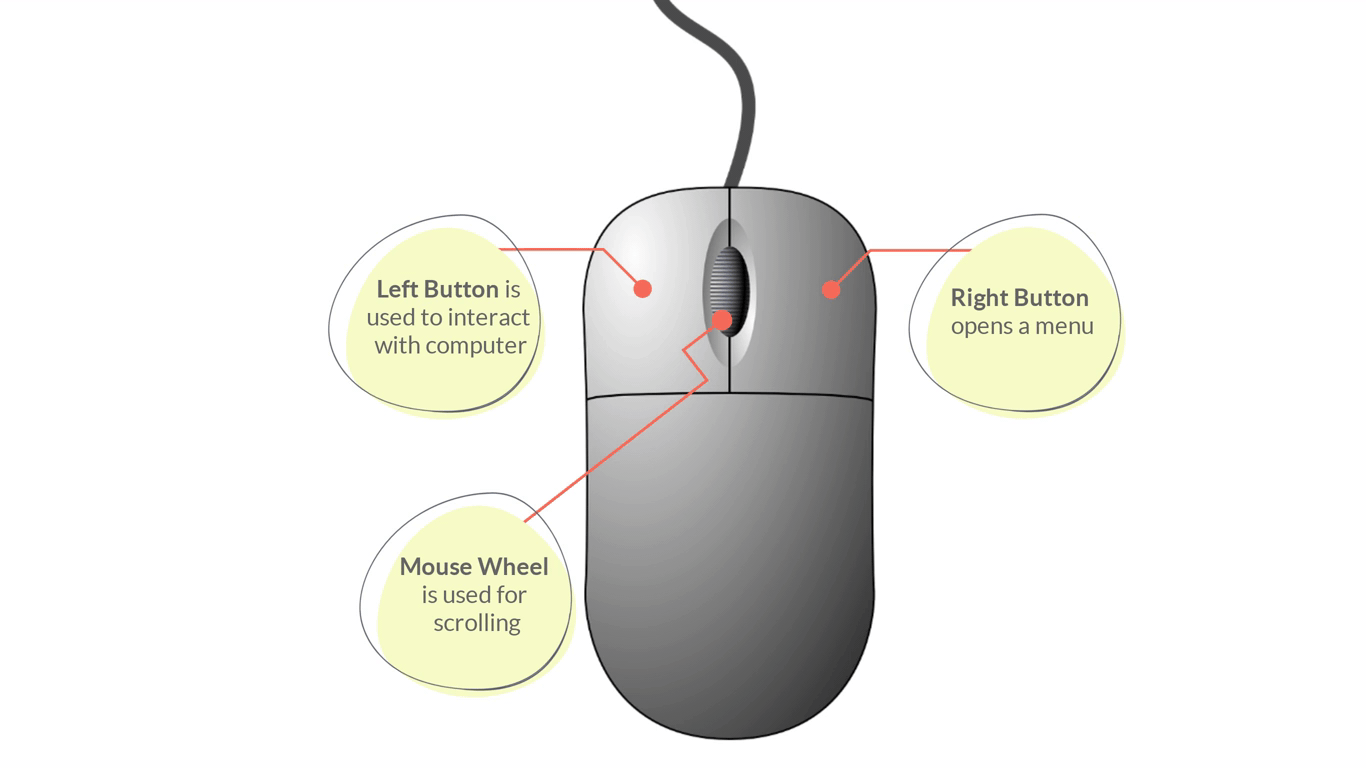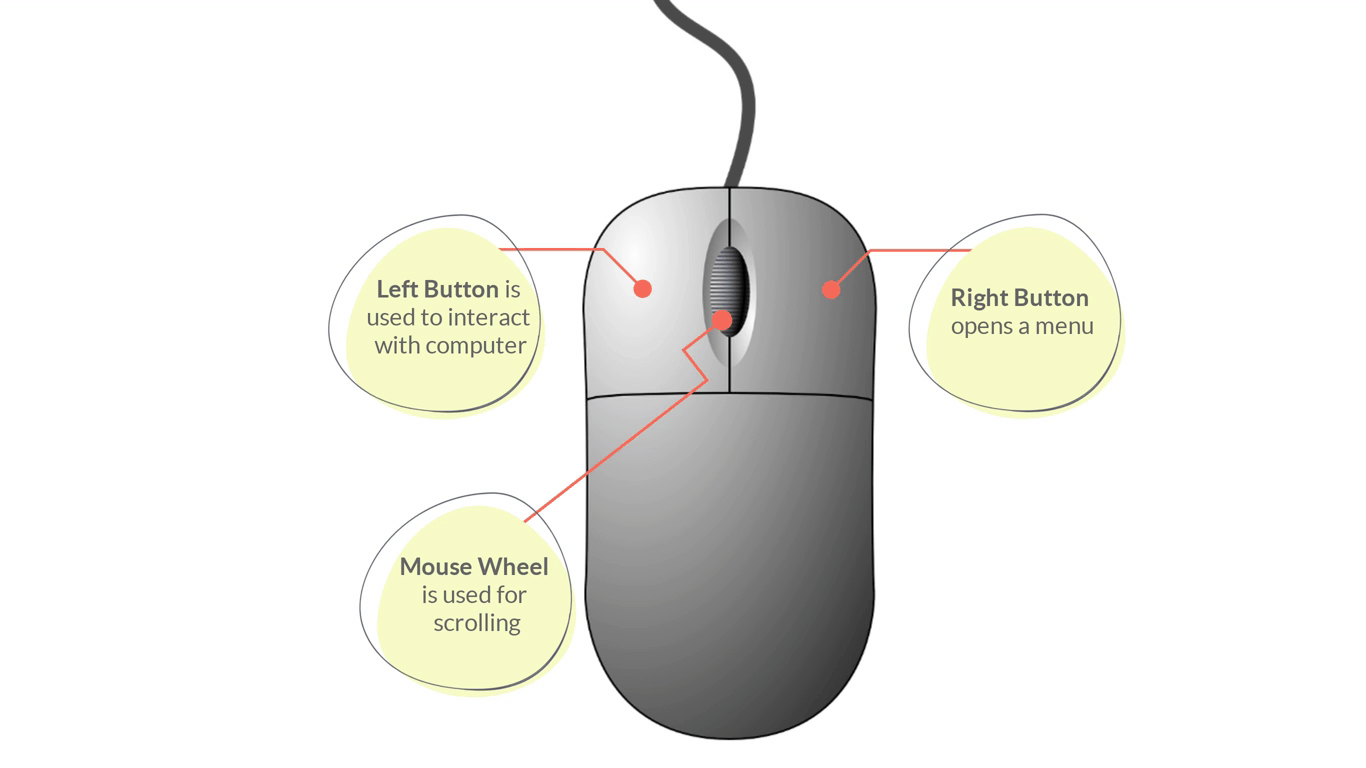
Parts of a Mouse:
- Left/Primary Button – is used most of the time, when interacting with the computer to make a selection.
- Right/Secondary Button – is used less often. When you click the Right button, you can usually access a menu that pops up with several options.
- Mouse Wheel - can be used for scrolling through documents or web pages. However, not all mice have this component.
Mouse operations: Point, Click, Double click, Drag
Placing your mouse on a mouse pad can make it easier to move. As you move your mouse around, you will notice an arrow on the screen moving in the same direction. This arrow is called the mouse pointer and it may appear differently from time to time.
- Pointer pic - Used as a guide for pointing at objects on the computer’s screen.
- Cursor pic - Appearance when editing text documents
- Clickable or Link pic (hand) - Indicates that an item is clickable e.g. button or hyperlink
Mouse pointers can also be customised to take on different appearances.
The Keyboard
The infographic below shows a typical keyboard with its labelled parts e.g. Esc, Function keys, arrow keys, space bar, numeric keys
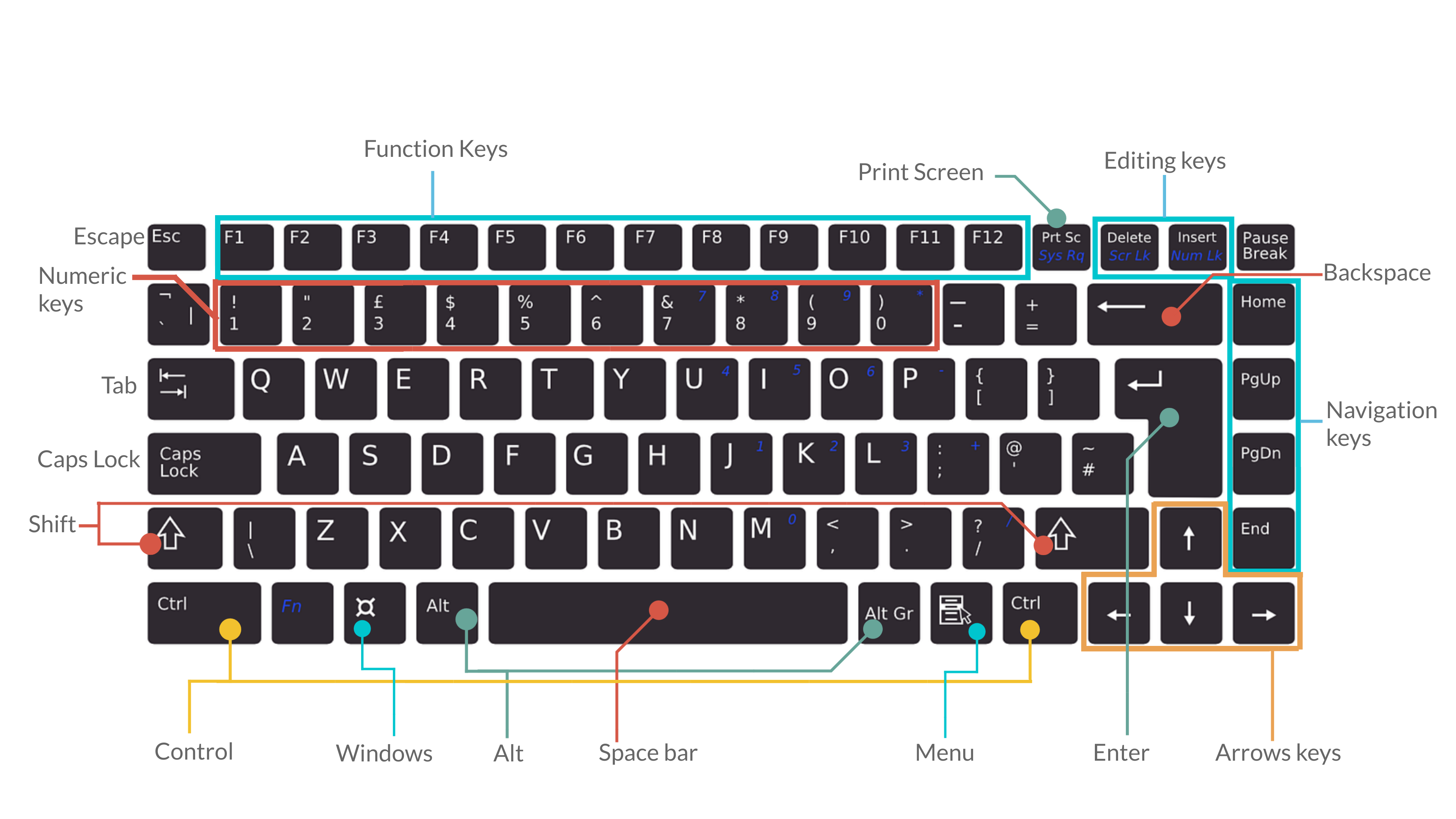
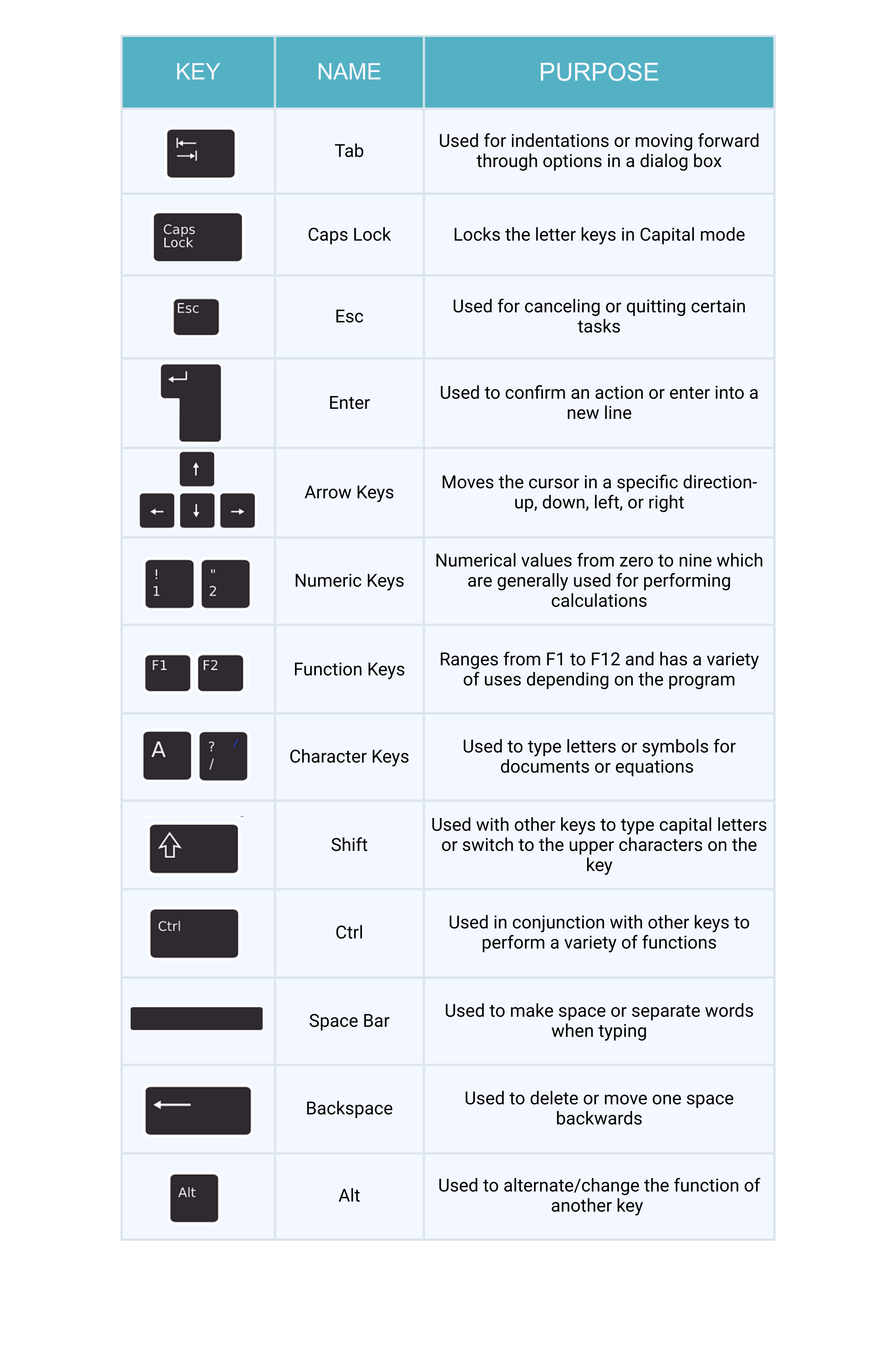
- Tab - For indenting words in a document or for moving forward through options in a dialog box.
- CapsLock - Locks the keyboard in capitals mode, allowing you to type in capital letters.
- Esc - For cancelling or quitting certain tasks in some programs.
- Enter - Also known as the “Hard Return”, the Enter key is used for creating a new line in a document or for selecting/pressing a dialog box button.
- Function keys - These have a variety of uses depending upon the program e.g. F1 offers help in many application programs.
- Arrow keys - To move your cursor and move in specific directions: up, down, left or right.
- Numeric keys - Most of these keys can be used for performing calculations. Some repeat themselves on the keyboard e.g. the number keys are found below the Function keys as well.
5. File Management
File management means actions that help you organise your files on your computer including functions like naming or storing them. Checking file attributes or searching for or within files.
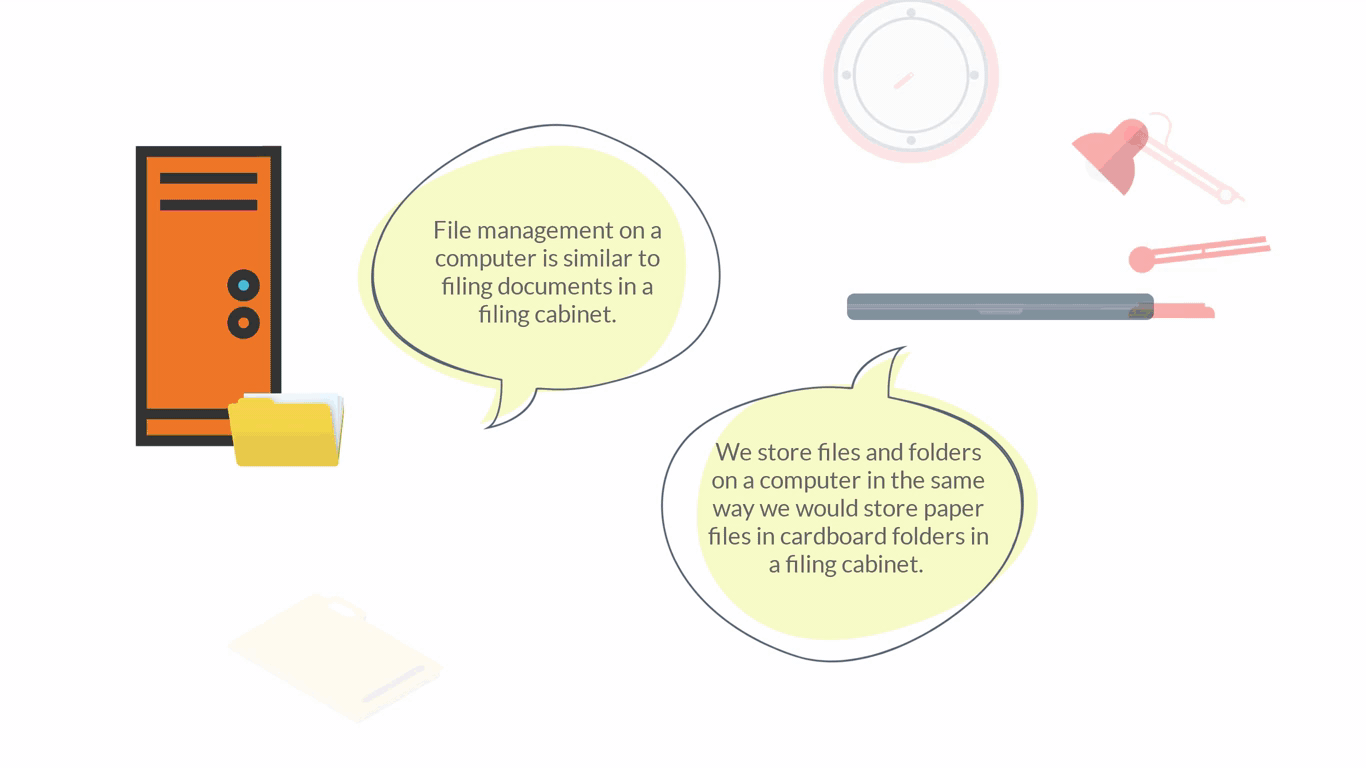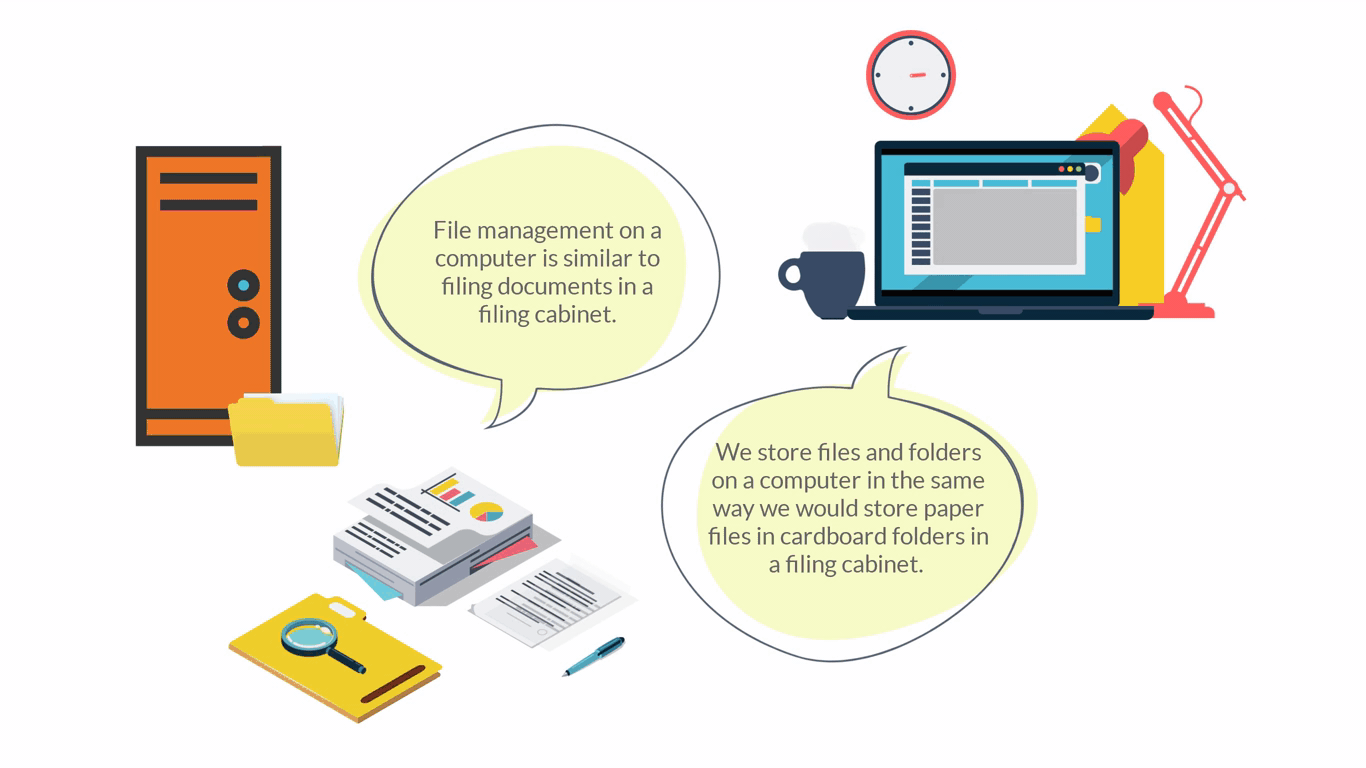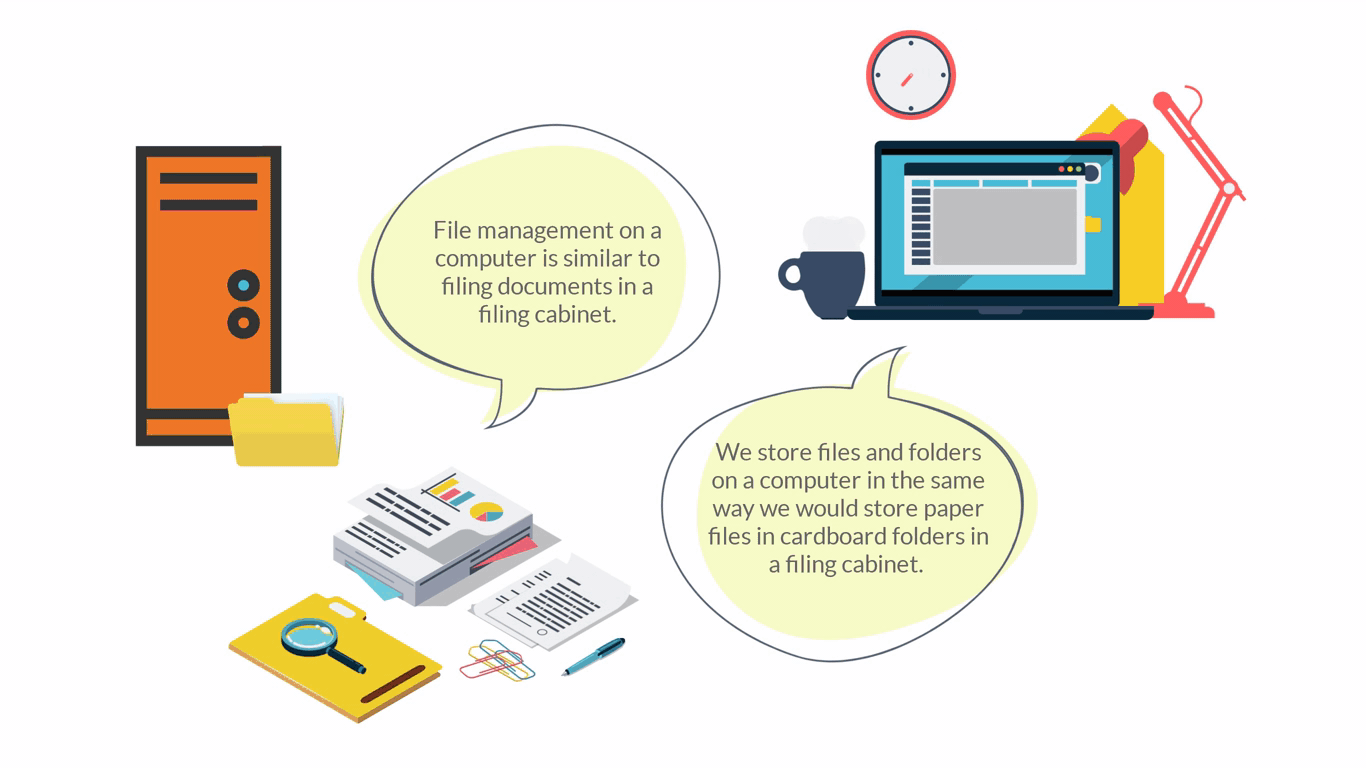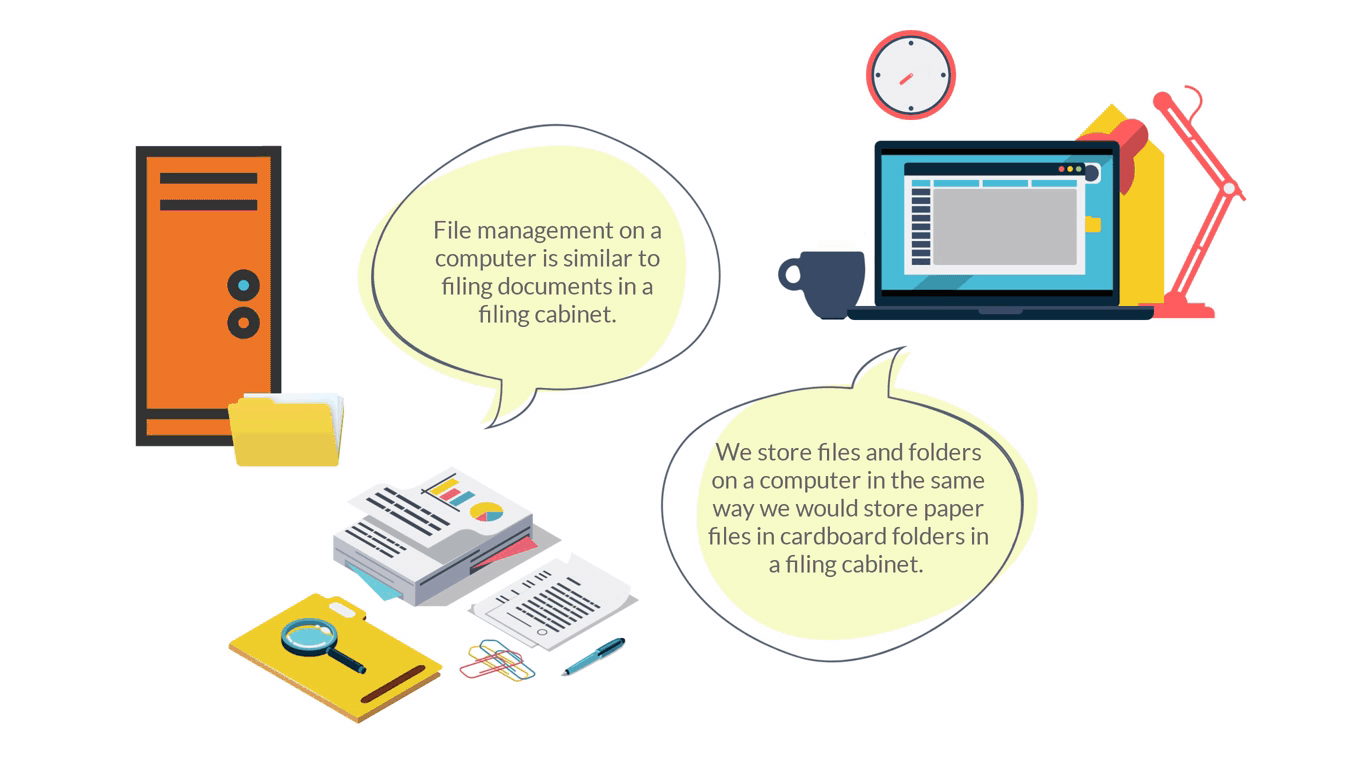
The OS is responsible for creating, deleting, renaming, and making back-up copies of files and folders. These folders are stored on a drive in the computer. The drive will indicate the type of storage medium and this is represented as a capital letter followed by a colon, for example:
C: known as the C-drive, usually refers to the hard disk drive (HDD);
D: known as the D-drive, usually refers to a CD or DVD drive;
Other letters like F: refers to a removable disk (USB).
Note that storage media, such as DVDs, USBs, and hard drives, do not save data to the disks on the computer.
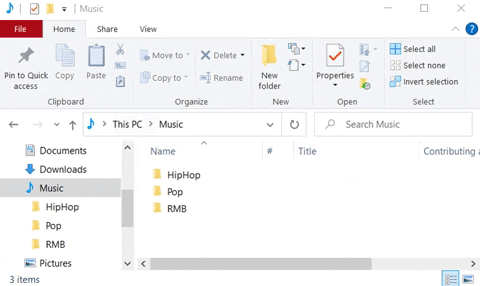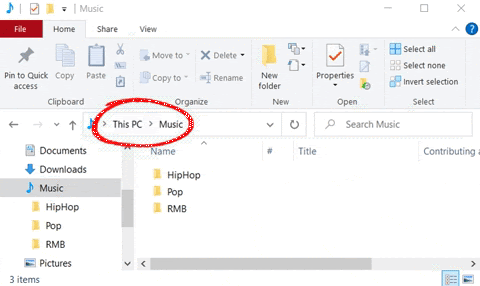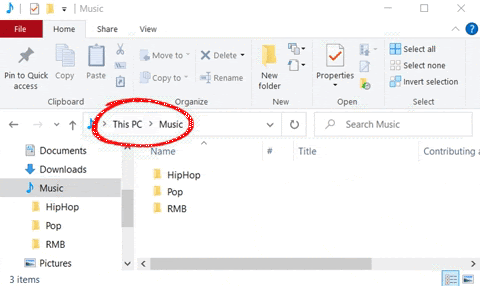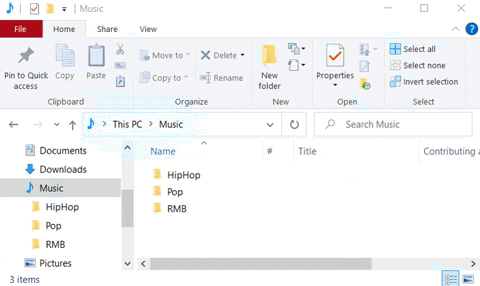
A file can be found via its file path. This shows you which storage device (drive) the file is stored on, the folder and sub-folder it is located in, the name of the file, and finally, the type of file based on the file extension.

The figure above is an example of a file path. To find the file path of a folder, click on the address bar in File Explorer. ![]()
It is important to organise files on your computer well as it will save you lots of time and effort when locating them later on. So, make sure to always place your files in folders and to give them appropriate names that will make them easy to find.
6. Installing Hardware and Software
When you plug a new device into your computer (so a new type of hardware), it should automatically be recognised. If you don’t get any message when plugging in a new device, you can check the “Device Manager”. This is a Control Panel in Microsoft Windows OS that allows users to view and control the hardware attached to the computer.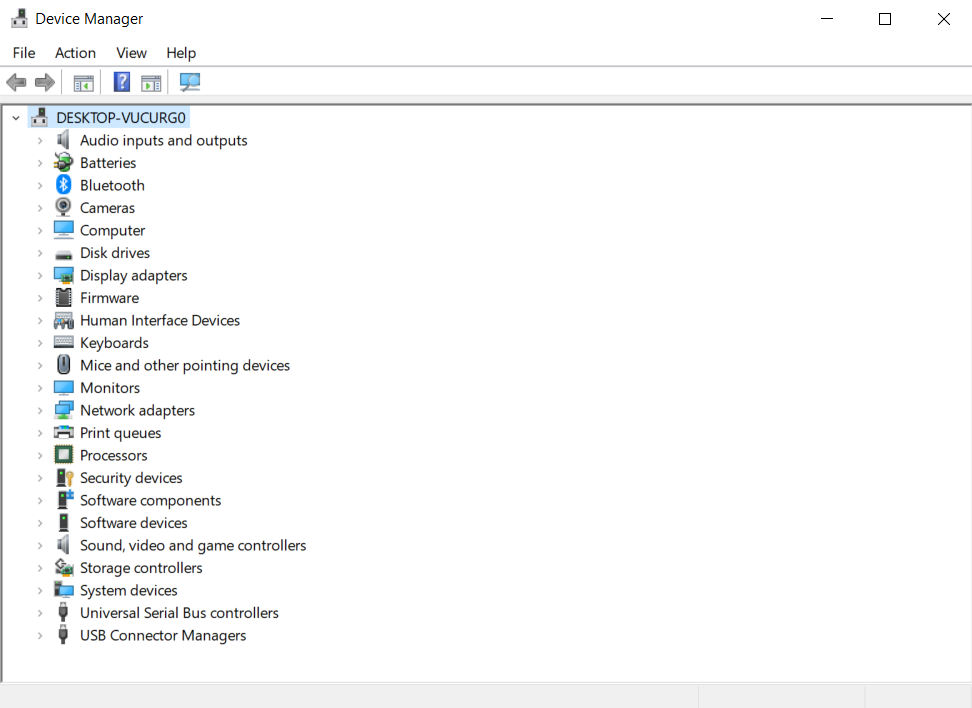
To install new software programs you can either download them from the internet or install them from a folder on your computer or external device, such as a CD/DVD or USB drive. To install a software application from the internet, open your web browser and type the name of the program in the search bar.
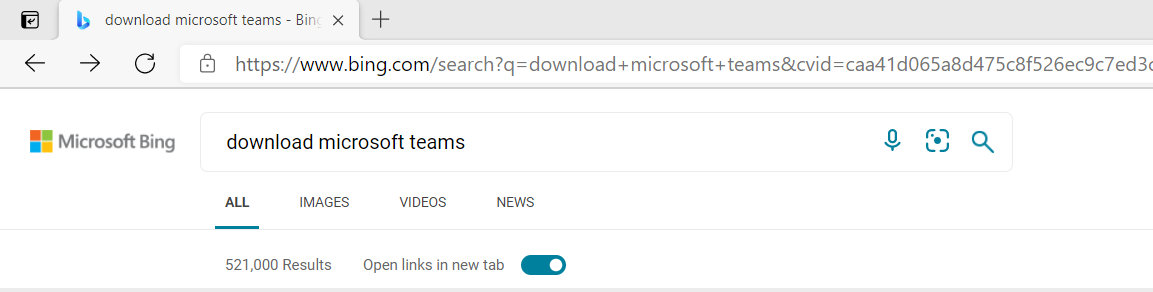

The installation file should be visible via a download button on the webpage as seen in the example below.
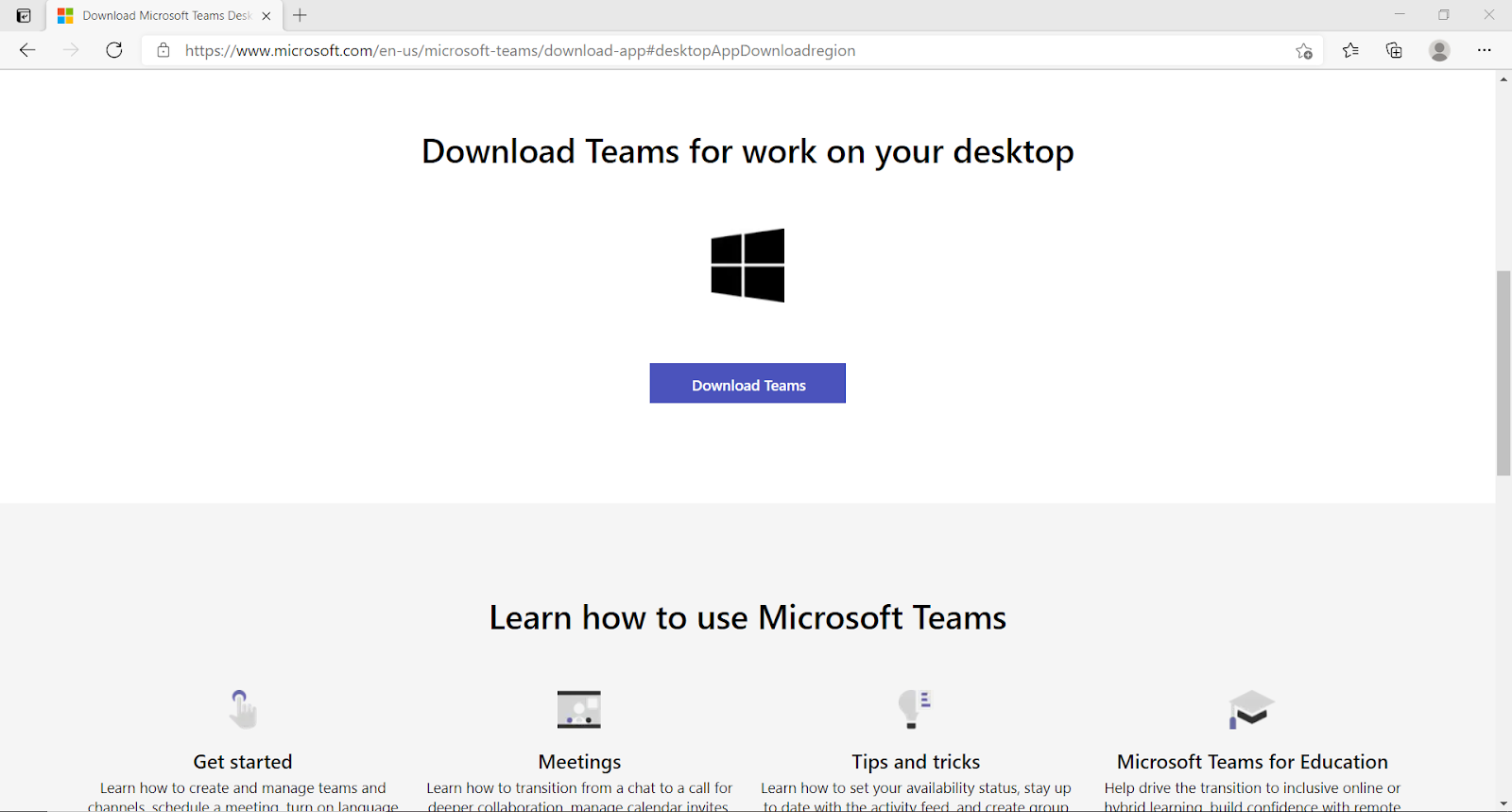
Click ‘Download’ to start the download process. You should be able to view the progress of the download on the bottom left of the webpage. Depending on the speed of your internet connection, this might take some time.
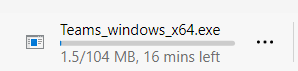
Once the download is complete, simply click on the installation file to start the set up of your new program.
Navigate through the instructions of the installation process. Make sure to read the terms and conditions carefully, if there are any, before agreeing, and fill in any necessary information if required. Finally, select ‘Close’ to complete installation.

7. Computer Care, Safety and Security tips
Paying attention to the maintenance of your device from the start and caring for your computer is the best way to keep it functioning properly for a long time. This way, you might also be able to save money on repairs or replacements in the long run.
Caring for your computer means considering several physical and electronic aspects. Some key considerations are physical cleaning of your computer, having a good anti-virus software to protect you from virus, worms and other threats as well as making sure your data is well-protected. Among those, the main issues that usually cause computers to fail are dust and viruses.
Basic Tips
- Use your computer in a cool environment e.g. install a fan
- Keep your work area clean e.g. remove any dust every couple of days
- Do not eat or drink near your computer to avoid accidental spills
- If you live somewhere where power outages are common, avoid plugging your computer directly into a power outlet. Instead, connect it to a surge protector, which in turn will connect to the power outlet
- Ensure your computer has Antivirus software
- Update this software and run scans regularly
- Turn off and unplug your computer during lightning storms, even if it is surge protected
- Save your work and back-up important information on external drives
- Close all programs before you shut down your computer
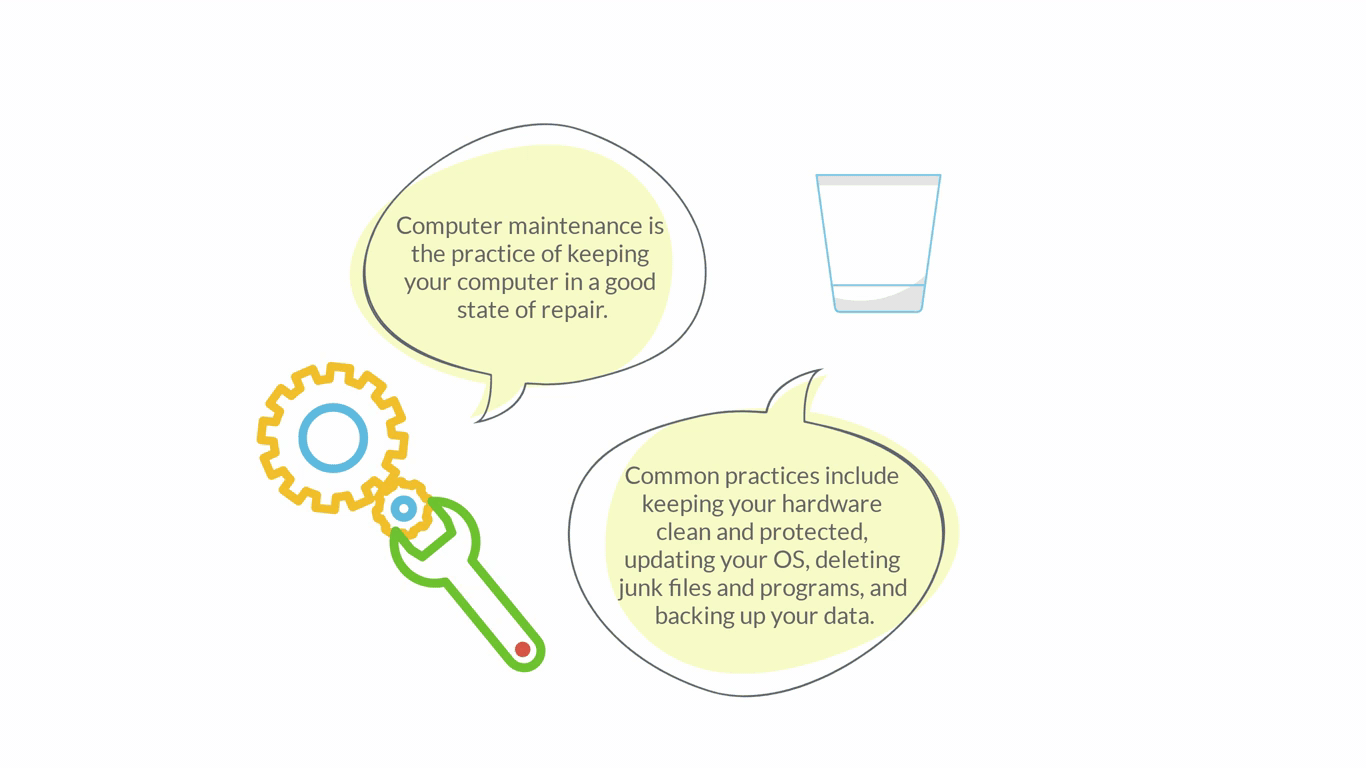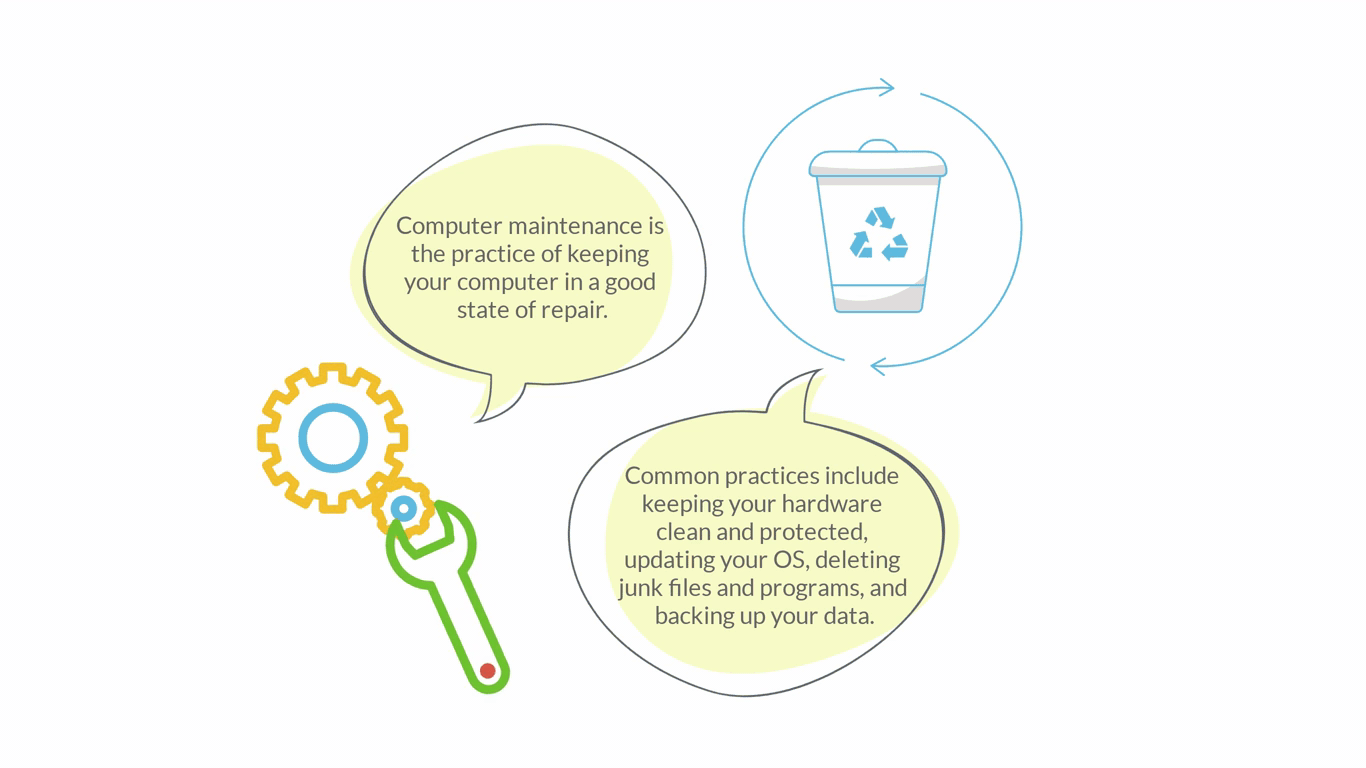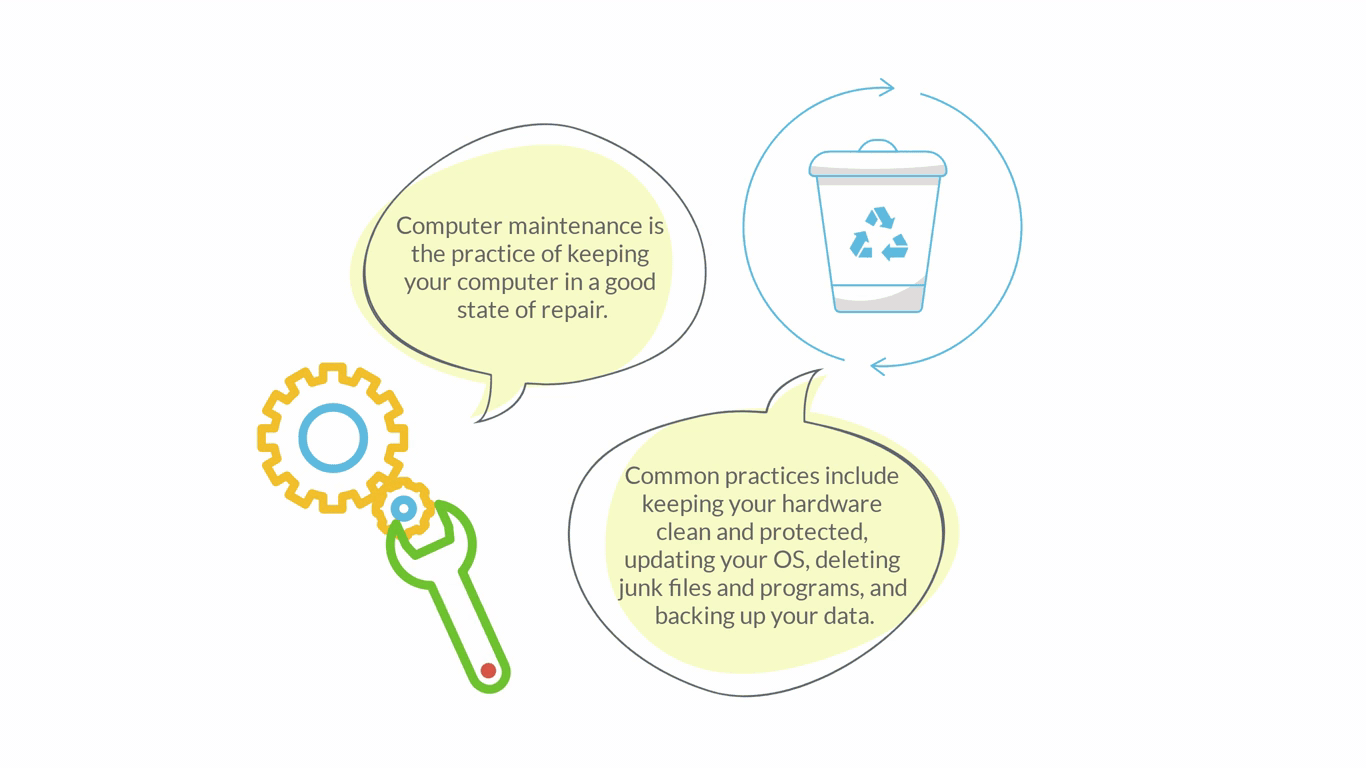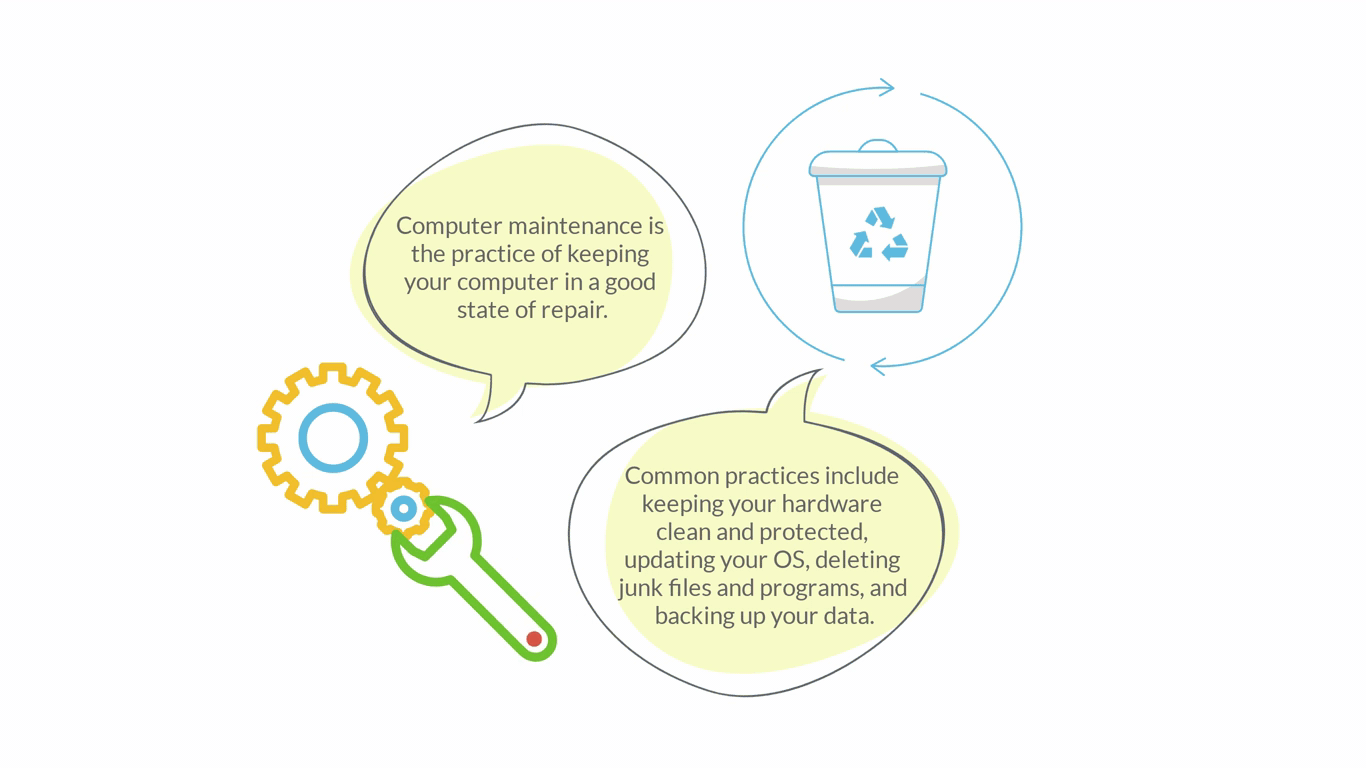
Computer Maintenance
hardware components, data (e.g. disk cleanup, backup, defragmentation), software (e.g. updates)
Now, after having finished this book, make sure to go back to the main page and complete activity 1.