3.2 Mobile Devices
| Site: | OpenLearn Create |
| Course: | 3 Digital Skills |
| Book: | 3.2 Mobile Devices |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Sunday, 22 February 2026, 2:31 PM |
1. Types, Features and Uses of Mobile Devices
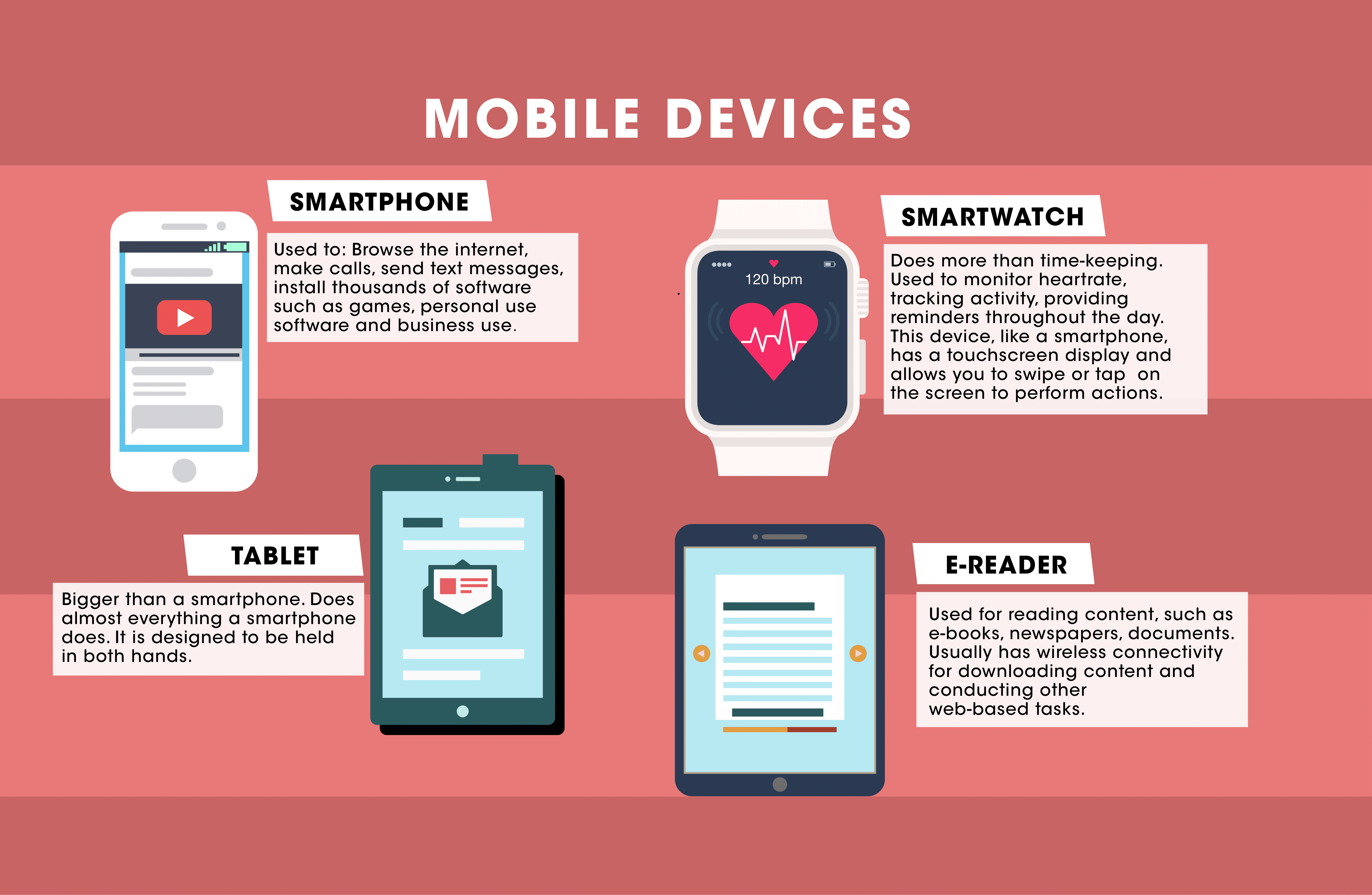
What are Mobile Devices?
Mobile devices are small portable digital mechanisms such as phones or tablets that provide access to the web, apps, and other software.
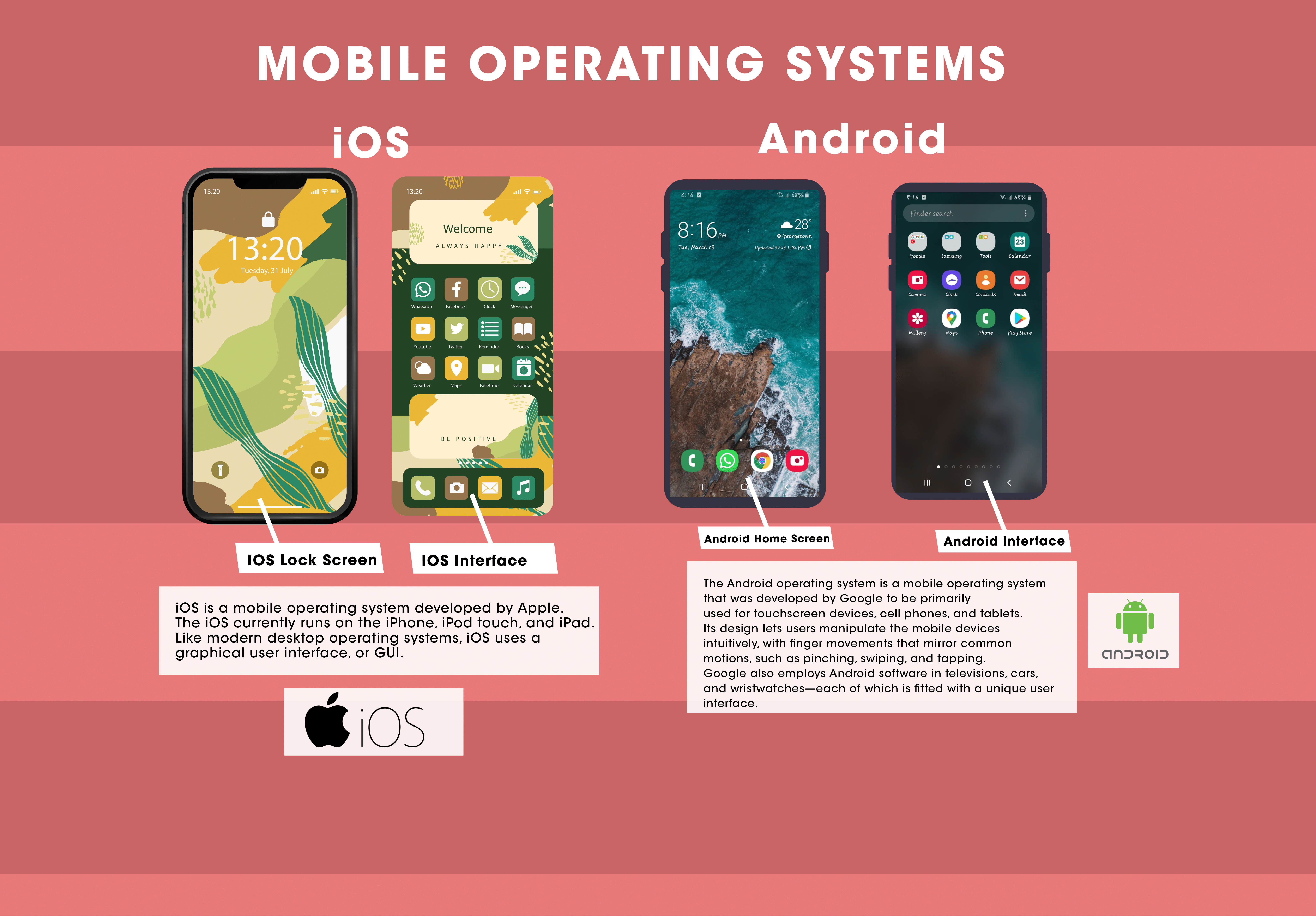
Mobile Operating Systems
Mobile operating systems present a graphical display of buttons, icons, windows, and tiles that you can touch or interact with to perform various tasks. Mobile operating systems also manage the hardware of mobiles and makes it possible for smartphones, tablets, and wearables to run apps.
The two most popular mobile operating systems are Android and iOS.
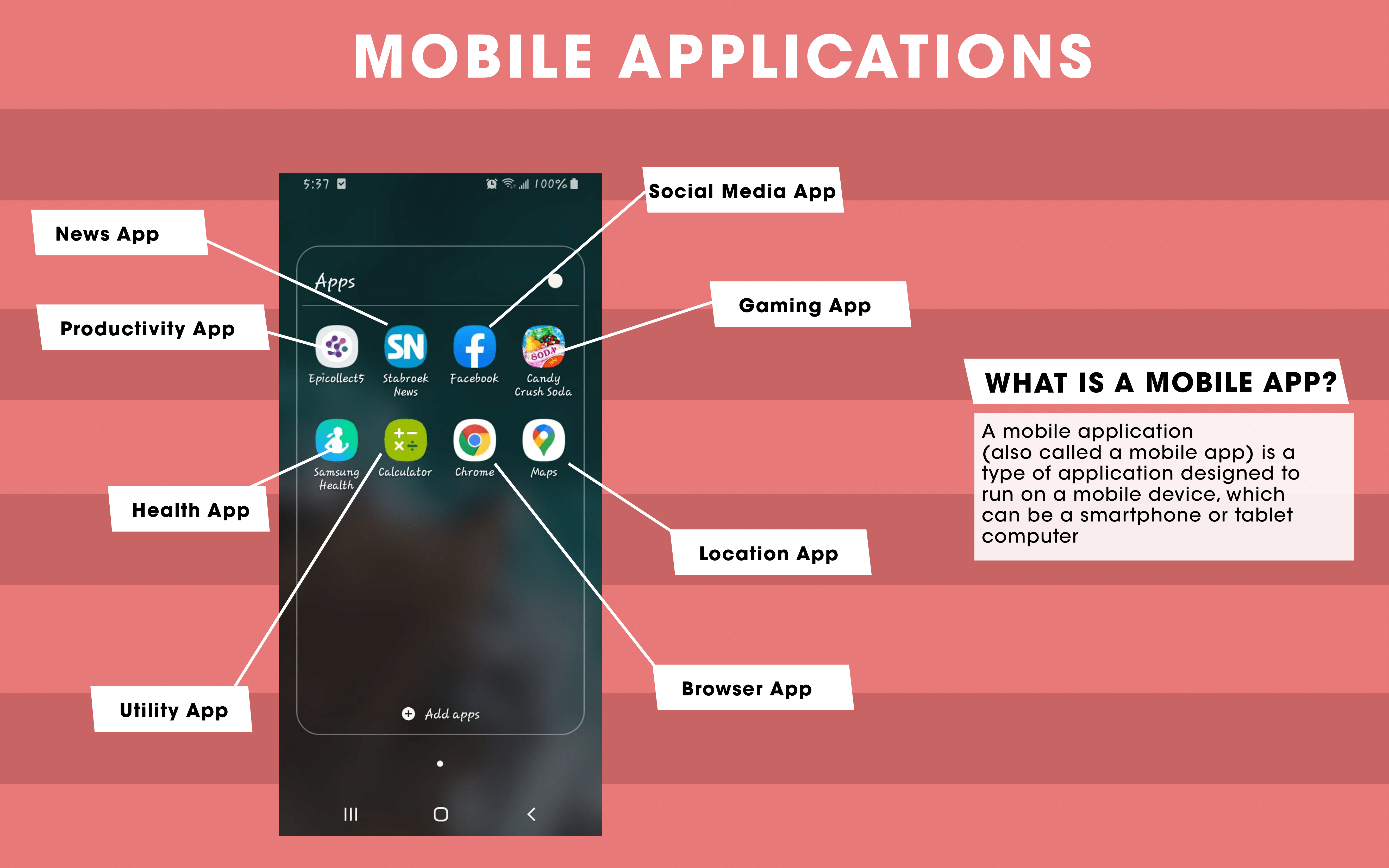
Mobile Applications
A mobile application (also called a mobile app) is a type of application designed to run on a mobile device, which can be a smartphone or tablet computer. There are several categories of mobile applications such as Lifestyle, Social Media, Utility, Games/Entertainment, Productivity and News/Information.
The following infographic presents various types (productivity, social media, gaming) and examples (Epicollect5, Facebook, Candy Crush Saga) of mobile applications.
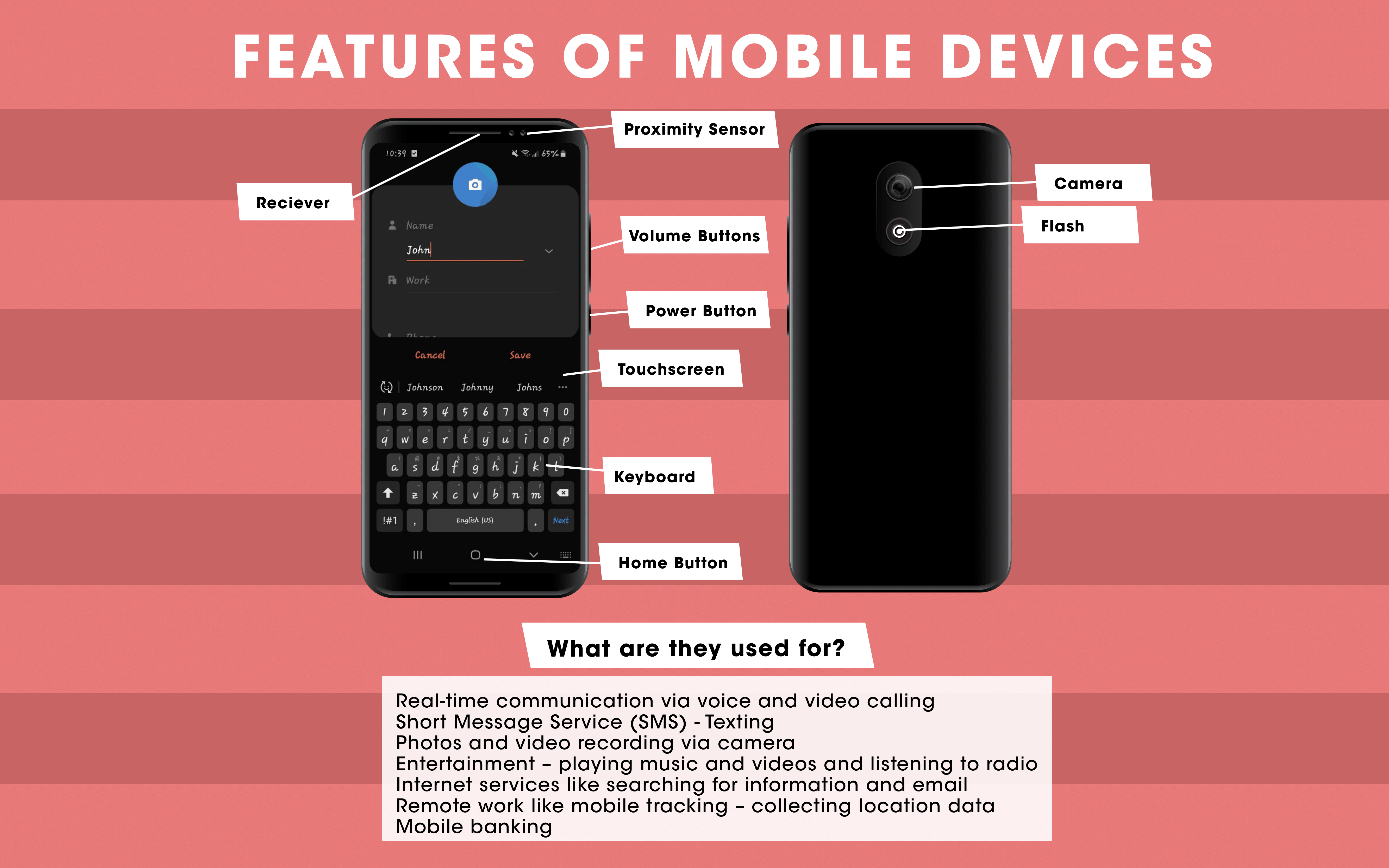
Features and Uses of Mobile Devices (Smartphones)
The following is a list of important features of mobile devices:
- Receiver
- Proximity sensor
- Volume buttons
- Power button
- Home button
- Flash
- Camera
- Touchscreen
- Software-based keyboard
The following is a list of important uses of mobile devices:
- Real-time communication via voice and video calling
- Short Message Service (SMS) - Texting
- Photos and video recording via camera
- Entertainment – playing music and videos and listening to radio
- Internet services like searching for information and email
- Remote work like mobile tracking – collecting location data
- Mobile banking
2. Mobile Devices and the Internet
Android mobile devices can use and connect to the internet using a few different methods described in the infographics below.
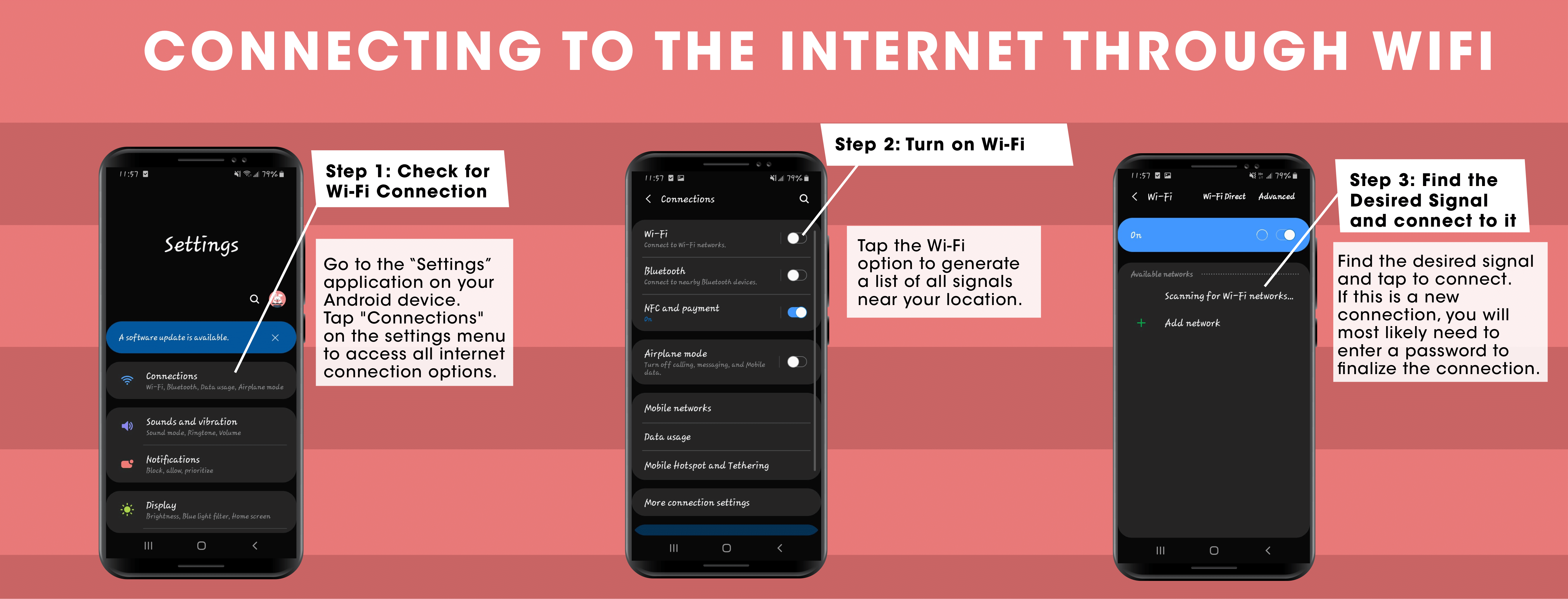
Method 1: Connect via Wi-Fi
A Wi-Fi connection does not use any data from your phone plan; depending on your area and service provider, Wi-Fi connections are usually fast.
See infographic below for a step-by-step description of how to connect to the internet using Wi-Fi:
Method 2: Connect via mobile Data
Android devices can connect to the internet with data, but the speed and quality depends on your provider plan and network connection.
See infographic below describing the process of how to connect to the internet by using your mobile data:

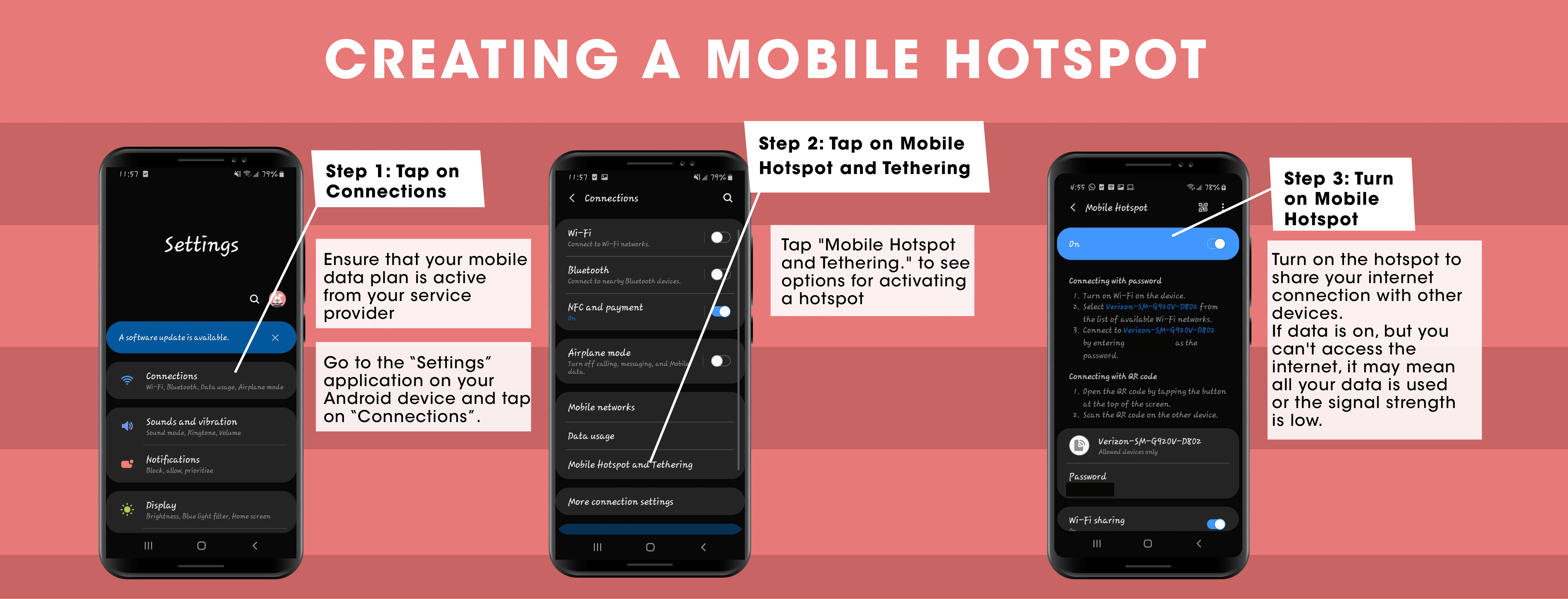
Method 3: Connecting via a Hotspot
If you need to use the internet on your laptop, you can use your phone's data to create a hotspot for it. This will turn your data into an accessible internet connection for the other device.
See infographic below describing the process of how to use your phone to create a hotspot to access the internet:
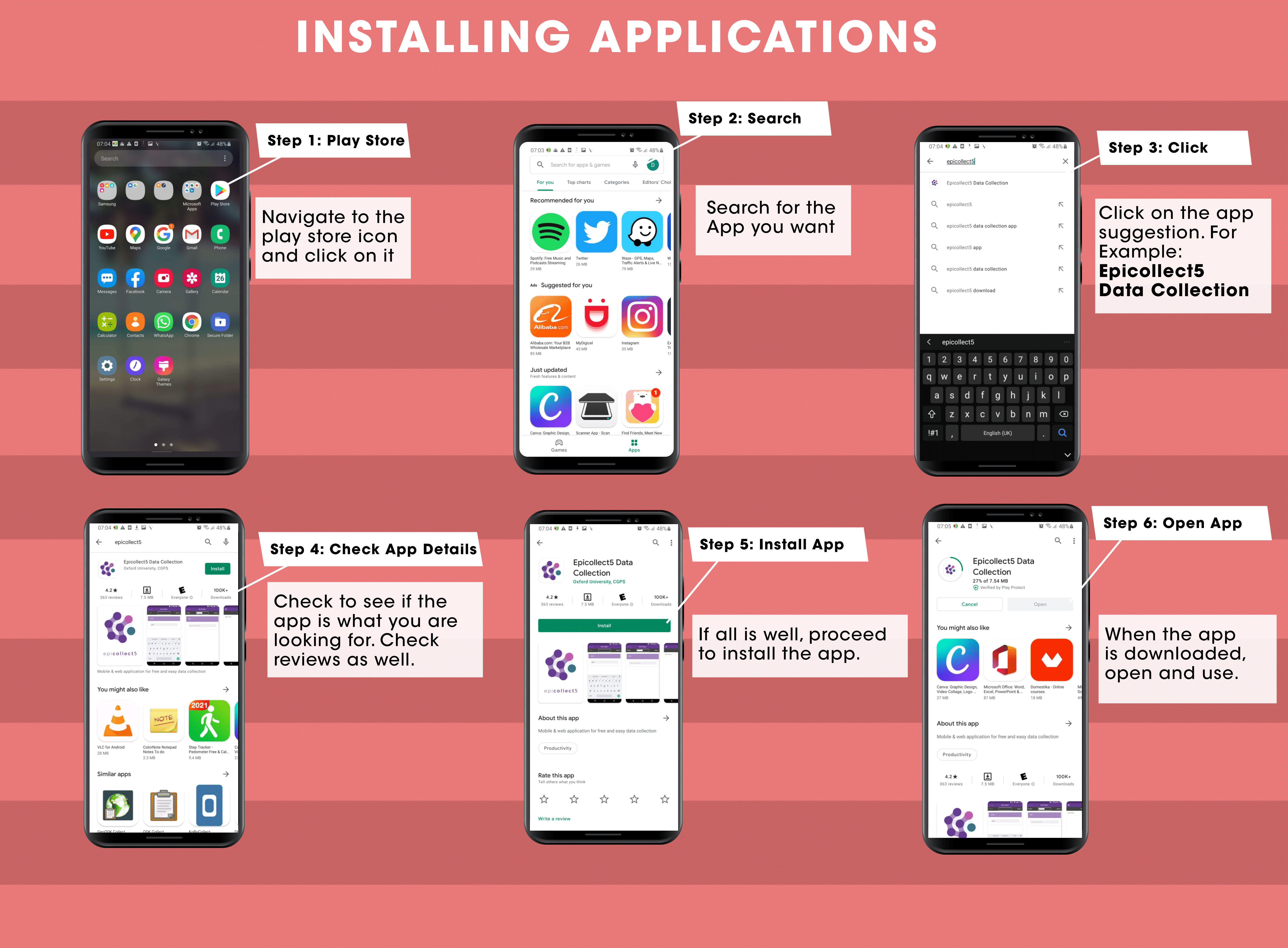
3. Installing Apps on your phone
The following infographic depicts the steps necessary to download, install and open a mobile application using the example of the app ‘Epicollect5’.
4. Using Mobile Applications
Watch this three-part video demonstration series for an example on how to use Mobile applications for data work using Epicollect5.
Part 1 entails setting up an Epicollect5 Project using a desktop interface.
Part 2 shows how to use the Epicollect5 Mobile Application to collect data for a sample project created in Part 1.
5. Care, Maintenance and Security of Mobile Devices
The following are some ways of improving the security of your mobile devices:
- Enable security configurations for mobile device access
- Enable auto-lock.
- Enable password protection and set passwords.
- Manage your wireless networks carefully
- Disable remote access features, such as Bluetooth, infrared, or Wi-Fi, when you are not using them.
- Set Bluetooth-enabled devices to be non-discoverable so they won’t be visible to unauthenticated devices.
- Don’t join unknown Wi-Fi networks.
- Backup your device regularly
- Use backup software on a desktop or syncing services to ensure you will have access to your important data when you may no longer have access to your mobile device.
- Install anti-virus programs
- Check the Google Play Store for the most up to date options.
- Install anti-virus software as it becomes available and maintain up-to-date signatures and engines.
- Do not download applications from untrusted sites.
- Update your mobile device frequently
- Configure and select the automatic update option, if available.
- Maintain up-to-date software, including operating systems and applications.
- Run only manufacturer approved firmware or operating systems.
- Enable physical security mechanisms to prevent theft
- Use tracking software or features.
- Never leave your mobile device unattended.
- Report lost or stolen devices immediately.
- Change any passwords stored on or remembered by the device immediately.
- Remember to back up data on your mobile device on a regular basis to enable data recovery.
- Use appropriate disposal procedures for mobile devices when you are getting a new device
- Delete all information stored in a device prior to discarding, exchanging, or donating it.
- Manage your privacy effectively
- Use privacy settings to control the information you share and who can see it.
- Consider the impacts of using services that collect and share personal data, like your location.
The following infographic presents various additional ways of securing your mobile devices: