Learn about intersex
| Site: | OpenLearn Create |
| Course: | Learn about intersex |
| Book: | Learn about intersex |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Tuesday, 10 March 2026, 5:33 AM |
Description
Access the course material in easy-to-navigate book form.Table of contents
- 1. Intersex 101
- 2. Intersex variations
- 3. Intersex figures from history
- 4. Current intersex medical protocol
- 5. Test your knowledge with a quiz on intersex
- 6. Intersex Invisibility and other issues
- 7. Intersex in later life
- 8. Alternatives to the current model of care
- 9. Let's reflect on intersex
- 10. Conclusions
- 11. Acknowledgements
Intersex 101
Here we give a brief explanation of what the word intersex means as well as a look at other terminology used to describe intersex bodies
Intersex is an umbrella term used to describe a wide variety of natural bodily characteristics that don’t fit neatly into strict medical binary definitions of male and female. Intersex variations can be genital, chromosomal, or gonadal and apparent at birth, puberty or not at all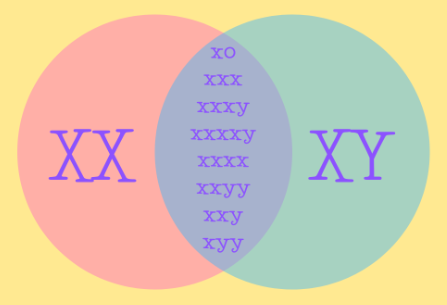 .
. Experts estimate that between 0.05% and 1.7% of the population have some sort of intersex variation.
To put that in perspective, people with red hair make up about 2% of the population as do people with green eyes.
While intersex and transgender are not the same thing, there are intersex people that identify as transgender. Intersex people may identify as male, female or neither, and can be straight, gay, lesbian, bi or asexual.
The word intersex was coined in 1917 by German-born geneticist Richard Goldschmidt, replacing the words hermaphrodite and pseudo-hermaphrodite, taken from the story of Hermaphroditus in Greek mythology. In 2005, the medical establishment introduced DSD, or Disorders of Sexual Development, to replace intersex. Intersex adults and activists say that DSD is unnecessarily pathologising, preferring to retain the word intersex or even in some cases hermaphrodite.
Intersex variations
In this chapter we take a brief look at some of the 40 individual intersex variations.
Babies with CAH, or Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia, are often born with uterus and ovaries, but their genitalia may appear masculinized with a shallow vagina present. CAH is caused by the adrenal gland failing to make an enzyme needed for regulating androgen, aldosterone, and cortisol. People with CAH may suffer from severe salt-wasting which can be life threatening if not treated. 
Hypospadias occurs when the urethral opening is on the underside of the phallus somewhere between the tip and the base of the shaft rather than at the tip. With an epispadias, the urethral opening is on the upper surface of the phallus.
With Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome, or AIS, babies with XY chromosomes are born with bodies that are unable to respond to androgens. Children with CAIS, or Complete Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome, may appear typically female at birth while those with PAIS, or Partial Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome, may appear somewhere on the spectrum between a typical male or female body.
People with Klinefelter syndrome are born with an additional chromosome resulting with XXY rather than a typical XY, resulting in reduced muscle mass, less facial hair, and reduced testosterone.
Due to a hormonal variation, babies with 5 ARD deficiency, or 5 alpha reductase-3 deficiency, are born with XY chromosomes but may appear typically female at birth, developing masculine secondary characteristics at puberty.
People with Swyer syndrome are born with XY chromosomes, however their testes do not develop normally and instead they may be born with female appearing genitalia and a uterus.
Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser, or MRKH, results in children having an atypical vagina, uterus, and fallopian tubes, but can also affect bone and heart development.
With ovotestis, people are born with a combination of a testis on one side and an ovary or ovotestis on the other. Ovotestis are gonads that are composed of both ovarian and testicular tissue. Their genitalia may appear typical for male or female babies at birth or fall somewhere between the two.
Intersex figures from history
Here we take a brief look at the lives of two intersex figures from history
Thomasina Hall
Born in Newcastle-on-Tyne, England, in 1603, assigned female at birth and raised as a girl, Thomasina Hall began living and dressing as a man in their teens and early 20s. Thomasina served in the military in both England and France, before returning to England and donning feminine attire, supporting themselves with needlework. 
In 1627, Hall moved to the Jamestown, Virginia as an indentured servant. By 1929, Hall had fallen afoul of the law for being observed to dress upon occasion as a female. Following an inspection, Hall was determined to be both male and female, sentenced to dress themselves forevermore as a man but with the addition of a woman’s bonnet and apron. It would be hard to imagine that this sentencing was for Hall’s benefit, but rather to discourage the possibility of homosexuality (Reis, 2009).
Herculine Barbin
Herculine Barbin was born on November 8th in Saint-Jean-d'Angély, France, in 1838. Like Thomasina Hall, Barbin was assigned female at birth and raised in a convent. In 1857, Barbin secured a teaching position at an all-girls school where she fell in love with another teacher. Her affair was noticed and Barbin was subjected to a medical inspection where she was declared to be intersex.
Barbin was legally reclassified as male and forced to leave her old life as a woman and begin a new one as a man. Barbin’s memoirs were discovered 8 years later after death by suicide (Foucault, 1980; Dreger, 1998).
The intersex community celebrates Intersex Day of Remembrance every year on her birthday.
Current intersex medical protocol
This chapter looks at current medical protocols for intersex treatment and where they originated.
In the 1950s, New Zealand psychologist Dr John Money published his theory of human gender, providing the medical establishment with a solution to problems posed by intersex bodies. Money believed that gender was fluid in all human beings until the age of 2, advising that when presented with an intersex infant it was important for medical professionals to choose either a male or female gender and then cement that decision with surgery. 
Money’s theory paved the way for the normalisation of medical intervention for intersex children. Many intersex babies were assigned female at birth due to the ease of creating the appearance of female genitalia in comparison with male genitalia.
Under Money’s protocol, parents were advised to keep the child’s medical history secret from friends and relatives as well as from the intersex child themselves. To Dr John Money, consistency in parenting in the assigned gender was key to a successful outcome. If the outcome was bad, as it was with Money’s patient David Reimer who committed suicide in 2004, Money would blame inconsistency in parenting rather than it being a problem with his theory.
Here you can test your knowledge of what you've learned so far with a short quiz on intersex history.
This quiz counts towards your badge. You must obtain a score of at least 50% to qualify for the badge.
- You can try each question unlimited times.
- There is no limit to the number of attempts at the whole quiz.
- If you get less than 50% you will need to start again if you want to earn your badge. If you are not successful the first time, you can attempt the quiz again.
Grading method: Highest grade
Grade to pass: 5.00 out of 10.00
Intersex Invisibility and other issues
While attention usually revolves around medical treatment of intersex infants, early decisions can impact the intersex person throughout their lives. Here we will look at some of the issues.
With intersex variations hidden even from intersex people themselves, intersex has been all but erased from the world while surgeries and hormonal interventions on intersex children continue. 
Because people are not presenting at their doctors or at the hospital as intersex, there has been no specialist care developed to meet the needs of intersex people throughout the course of their lives.
Many intersex people reported that the secrecy about their bodies growing up was damaging. While medical interventions are performed on intersex children with the intention of helping them blend into a binary society, for many it had an opposite effect, causing them to feel apart from and separated from society.
Many people find out they are intersex later in life during medical exams, DNA tests, or by finding their own cases in medical books. In the 1990s, with the availability of the internet, intersex people began to find each other and compare their experiences.
Many intersex people report experiencing sexual discomfort and difficulties associated with early medical interventions.
While transgender and intersex are not the same thing, rates of gender dysphoria have been found to be higher amongst intersex people than amongst non-intersex people. Gender dysphoria describes a distressful state of being where the gender someone was assigned doesn't align with the way they identify or feel inside. Many intersex people have been assigned female by their surgeons down through the years because those surgeries were considered easier to perform. Intersex people assigned the wrong gender at birth by surgeons may be subjected to the violence and discrimination experienced by transgender people.
Intersex invisibility has resulted in a lack of cultural representation. Intersex people do not get to see intersex characters very often in books, film, or television, and neither do the public. This contributes to stigma against intersex people and a world where there are few legal protections for intersex people. In 2014, MTV included an intersex character in their television show Faking It which was the first time a television show featured a regular intersex character despite intersex people existing as long as non-intersex people have.
Intersex in later life
Older intersex people can
face challenges that are unique to intersex people or impacted by treatment of
their variation. Here we will look at a few of them.
Loneliness is a serious problem that negatively affects many people later in life.
Intersex people may be further impacted by loneliness in old age. Many are infertile due to their intersex variations while others were sterilised in their childhoods during medical interventions. Intersex people are therefore less likely as a result to have children, and therefore less likely to be surrounded grandchildren in old age.
Intersex people that found it difficult in life to make friends or find romantic partners because they were made to feel different or faulty may be more likely to be alone in later years.
There are few legal protections for intersex people, and most are recent, such as the ‘X’ marker for intersex people on United States passports. Many older intersex people that have not benefited from recent legal advances may have struggled throughout their lives. Issues they might have faced could include obtaining correct legal paperwork and identification, or discrimination relating to inheritances or when trying to adopt.
Intersex people often express the importance of intersex community to them. Older intersex people may fear being placed in care and being removed from intersex community. Some may fear the reaction of carers and other residents to their body if it is atypical, while others may fear medical settings due to memories of traumatic experiences when younger.
Rates of disability have been shown to be higher amongst intersex people, with some reporting that their early surgeries qualify as a disability or contributing factor to their disability. Older intersex people may therefore be more likely to struggle with and suffer from disabilities in old age.
Intersex people have been shown to attempt suicide at a much higher rate than non-intersex people, so it might be expected that older intersex people may suffer from worse mental health than older people that are not intersex.
Alternatives to the current model of care
Intersex invisibility has contributed to the medical model of care remaining almost unchanged since the 1950s. Here are some alternatives that could address some of the problems faced by intersex people.
It is worth considering whether a new care pathway for intersex people is needed, informed by those with lived experience.
Some intersex variations can be life-threatening unless treated, such as life-threatening salt wasting associated with Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH) which needs to be treated with medication. However, irreversible cosmetic surgeries such as clitorectomies and clitoral reduction surgery, the surgical reduction or removal of the phallus, could be postponed until the person is old enough to provide informed consent.
Instead of secrecy the family could be educated on their child’s variation and encouraged to discuss it with their child when they are old enough to understand. The child could receive age-appropriate education throughout their childhood from their family, medical providers, and intersex educators. The family could be introduced to adults that live with the variation, as well as others from the intersex community, so that they and their child understand they are not alone.
Age-appropriate education on intersex could be provided in schools during sex education and biology so that intersex students feel represented and included and the rest of the class educated. This could help reduce intersex stigma.
Education could be provided to medical students, medical professionals, and mental health professionals on intersex so that knowledge is not restricted to endocrinologists and urologists that work with intersex infants. It is important that mental health and medical professionals are familiar with the issues that affect intersex people.
Clear care pathways for intersex people could be developed so that informed, knowledgeable, and appropriate care is accessible to intersex people throughout their lives.
Osteoporosis, a condition that causes brittle bones, affects many intersex people castrated during childhood surgeries. This requires access to HRT, or Hormone Replacement Therapy, for the rest of their lives. Some intersex people find themselves placed on multi-year waiting lists for transgender care to access HRT through an endocrinologist. Clear care pathways for intersex healthcare might resolves issues such as this.
Use this exercise to reflect on what you have learned so far. Participation is a requirement for earning a badge.
Upon completion of this exercise you can progress onto the next chapter where we wrap things up. There you will also find links to more information on intersex, including video, animations and documentaries.
Conclusions
What did you come up with during your reflections?
Did you imagine yourself in the shoes of an intersex person? Did you wonder how you might feel finding out as an adult that your chromosomes were different than you believed?Would this cause you to question your relationship with your family? Would it cause you look back on your past experiences such as childhood hospital visits differently? 
We know that doctors believe they are helping intersex children, but many intersex people have been hurt by the good intentions of the medical establishment. What solutions did you come up with? How might you advise the parents of an intersex child?
We know many intersex children feel isolated during their school years even though surgeries are performed to help them fit in. What ideas did you come up with to help intersex children navigate school, friends, and activities such as sports?
Many intersex adults say navigating romantic relationships is difficult for them. Many intersex people say finding help in medical and mental health settings because many mental health providers are uneducated when it comes to their needs. What help did you think of for intersex adults?
We know life can be hard for many older intersex people, but they report finding joy amongst other intersex people and amongst intersex community. What ideas did you come up with to make life easier for older intersex people?
If you would like to learn more about intersex people, the issues they face and how to help, some links have been added below.
INIA: Intersex, New Interdisciplinary Approaches
What it's like to be intersexIntersex explained - Complete Androgen Insensitivity
Power Talk at Women Deliver by Steph Lum
Confessions: How I discovered I am intersex
Model Hanne Gaby on what it's like to be intersex
All illustrations were created by myself, the author, using Canva. I am a second year PhD researcher at the University of Huddersfield looking at the experiences and needs of older intersex people like myself as part of the INIA network. The INIA Innovative Training Network is supported by a grant from the European Commission’s Marie Skłodowska-Curie Actions program under project number 859869. I am eternally grateful to Dr Rebecca Jones and Anna Page of Open University for their seemingly endless patience, critical eyes, knowledge and inspiration during the building of this course. CC_BY – This work may be copied, distributed or displayed only if the author or licensor credits the original creator and includes a link back to this course.