Digital Ethics
3. Environmental impacts of digital technologies
Along with all the benefits digital technologies create for us, they also have a range of environmental impacts. The main impacts are the CO2 emissions produced from the electricity needed to run those technologies, toxic waste created when disposing them, and the resources that are necessary to produce these technologies. Being aware of those impacts is important. It is good practice to delete unwanted digital information so that it does not take up server space or space on your device, to dispose of hardware at a recycling center and to limit the times that you upgrade your devices or use reconditioned devices.
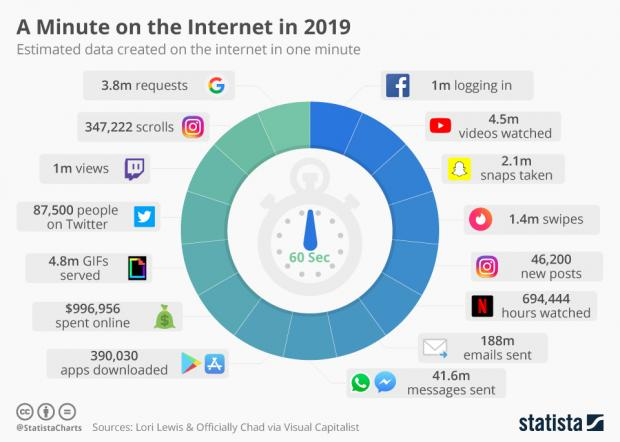
Using digital technologies and especially the internet uses a lot of electricity, which also causes CO2 emissions. On a global scale, internet use and the rising global electricity demand also has many environmental impacts. To get an idea of the scale of this issue, look at the infographic below which shows the estimated amount of data created on the internet in one minute. Overall, the use of digital technologies now actually has a bigger impact on global warming than the entire aviation industry (https://en.reset.org/knowledge/our-digital-carbon-footprint-whats-the-environmental-impact-online-world-12302019).
Disposing of digital technologies, so-called E-waste, can be difficult as they can’t be placed in normal garbage bins. They often contain metals and components, like mercury, lead or other heavy metals that can cause contamination and pollute the environment. At the moment, most E-waste is placed in landfills, from where it can seep into the soil and water. Even though E-waste only makes up around 2% of the waste in landfills, it is sometimes responsible for up to 70% of the toxic waste found there (https://en.reset.org/knowledge/electronic-waste). In many places there are formal and informal recycling sectors for E-waste, which recover some of the valuable components contained in those technologies so they can be reused. The idea of recycling those components is highly promising, however this needs to be done under proper safety conditions as those components can also be harmful for human health. So, when it comes to replacing your digital technologies, make sure to check carefully how you can safely dispose of it. In some places organisations offer take-back systems for E-waste but this is not always an option. Investigate where E-waste can safely be disposed of or recycled near you.

Another issue are the human and environmental impacts from mining the raw minerals that are needed to produce digital technologies. In some places the minerals mined for digital devices are done so in poor working conditions and in a way that negatively impacts the environment (https://en.reset.org/knowledge/ecological-impact-mobile-phones). Understanding the ethical and environmental practices of your digital device supplier will help you to choose companies that are attempting to safeguard people and the environment.
Now, after having finished this book, make sure to go back to the main page and complete activity 6.
