2 Ensuring quality in the laboratory
What is ‘quality’?
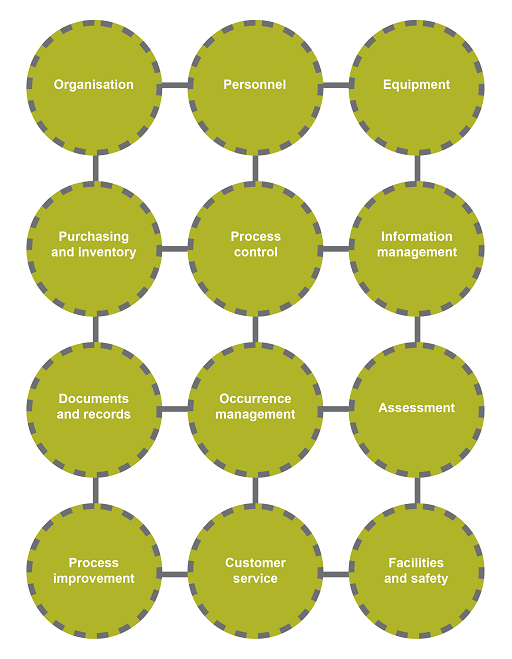
There are many notions associated with the term ‘quality’. For an organisation, quality is associated not only with the products and services it produces to satisfy a demand, but also the processes in place to generate these products or services. In a biomedical laboratory, several factors can affect the final report – the competency of the technician, the laboratory procedure, the reagents used in the assay, the equipment and the facilities. In Figure 1, these and other factors are grouped into 12
The principles of ensuring high-quality data include:
- making sure that basic standards are met
- establishing procedures at all test stages to minimise errors and ensure results are reproducible and reliable
- measuring performance against international standards
- monitoring and improving practice.
Information must also be recorded and reported accurately. If the laboratory generates a reliable, accurate result but the wrong information is entered into the report, all the hard work done to get the result is wasted.
1 The importance of data integrity and data quality