Use 'Print preview' to check the number of pages and printer settings.
Print functionality varies between browsers.
Printable page generated Thursday, 19 February 2026, 12:09 PM
4 A design thinking project using digital technologies
4 A design thinking project using digital technologies
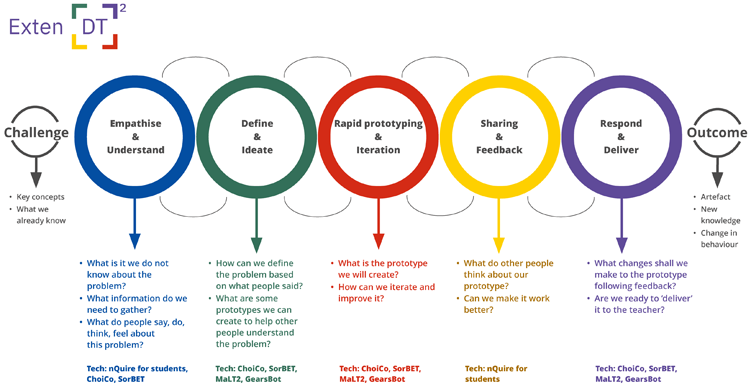
In this section you are presented with an example of a design thinking project that uses the applications you’ve been through in Section 3 to design and deliver the project. The structure and order of proposed activities are based on the Exten(DT)² Digital Design Thinking Model.
The topic of the design thinking project is:
Reducing energy consumption at school
Students are presented with the following problem:
Our school is not environmentally friendly; we are consuming a lot of energy and this is shown on our monthly bills. What can we do to reduce energy consumption?
Let’s explore what students can do at each stage of design thinking.
Next, go to 4.1 Reducing energy consumption at school.
4.1 Reducing energy consumption at school
Empathise and Understand
Students work in groups or pairs and they use nQuire for students to explore what other students and teachers at school do, think, and feel in relation to energy consumption.
Students can create a set of questions they can ask others, such as:
What equipment do you use at school that requires energy?
How much energy do you think is consumed by each piece of equipment at school?
What can you do to minimise energy consumption at school?
Why is it important to reduce energy consumption?
Students can then create their study on nQuire for students and pilot it with at least one other student who gives them feedback about whether they understand the questions and any improvements they can make. Students can then make changes accordingly and send a request to the teacher (via nQuire for students) to make their study live so other students can take part in it (and so fill in the questions).
Define and Ideate
Students work in groups or pairs and the aim at this stage is to define a set of parameters they can use to create a game related to energy consumption, so they choose to use ChoiCo.
Students will have to add game fields which are game options, as well as the consequence of each option in terms of money, fun, and energy, for example. If it was decided that laptops would be switched off when not in use, what would be the impact on energy consumption at school? What about switching off lights when not needed?
As ChoiCo is a new technology for students, they are first asked to play at least one of the existing ChoiCo games to familiarise themselves with the functionality of the application. Alternatively, this can be done in a separate session where students experiment with the technologies that are going to be used in their design thinking project.
Rapid prototyping and Iteration
Students carry on working in groups or pairs using ChoiCo. They create several iterations of their game and test it to find out if it works well and if it is good enough to help other students understand how to minimise energy consumption at school.
Sharing and Feedback
Students access nQuire for students. This time they aim to share their game and collect feedback from other students. They create a study asking other students to play their game (by sharing the URL of their game, copied from the Exten(DT)² platform) and ask them questions such as:
What did you like about my game?
What would you change in my game?
What did you learn from playing my game?
Students pilot their study and when ready, they request for their teacher to approve it and make it live.
Respond and Deliver
Students read and synthesise the feedback they collected in the previous stage. The teachers ask them to make amendments to their game in ChoiCo, following the feedback recommendations from other students. When the game is ready, they inform the teacher who should assess it and give a final mark to students (summative assessment).
Next, move onto 5 Designing a lesson plan for students.