1.3.1 Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria
Can you remember the importance of the cell wall to bacterial cells?
It is a protective outer layer that provides mechanical support to the cell. It also prevents harmful surges of water moving into the cell by osmosis, which could cause it to burst (lysis).
Bacteria are divided into two main groups based on how the cell wall appears when they are stained using Gram straining. This procedure allows the composition of the wall to be visualised. Some ‘atypical’ bacteria, such as Mycoplasma and Chlamydia, cannot be seen by Gram staining and so cannot be categorised in this way, but these will not be considered in this module.
In Gram-positive bacteria, the cell wall has a thick peptidoglycan layer which is relatively porous, allowing substances to pass through it quite easily. One of the components of the Gram stain, crystal violet, is absorbed into the peptidoglycan layer, staining it a dark purple colour.
In Gram-negative bacteria, this peptidoglycan layer is greatly reduced and is further protected by a second, outer membrane (Figure 2). The outer membrane does not allow crystal violet to reach the peptidoglycan layer and so these cells appear pink under the microscope due to the counterstain – usually safranin or neutral red.
(For more information on the Gram stain and other techniques used in the laboratory to help identify bacteria you could visit the module entitled Isolating and identifying bacteria.)
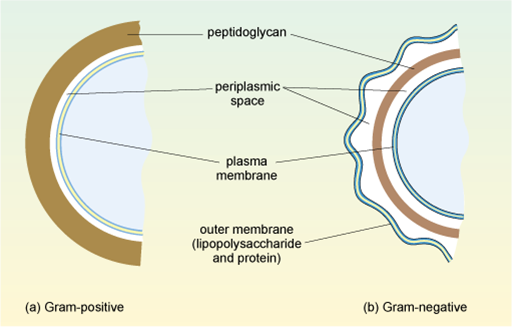
Figure 2 Arrangement of the cell wall in (a) Gram-positive and (b) Gram-negative bacteria.
Show description|Hide descriptionThis diagram shows the differences in cell wall structure between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. In the Gram-positive bacteria in (a) the peptidoglycan is a thick external layer shown in brown, while in the Gram-negative bacteria in (b) the peptidoglycan layer is much thinner and is surrounded by an outer membrane of lipopolysaccharide and protein (as a green wavy line). The inner membrane in (a) and (b) (shown as a double green line) is separated from the peptidoglycan layer by the periplasmic space.
This second, outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria is an effective barrier, regulating the passage of large molecules such as antibiotics into the cell. In contrast, the thick, porous peptidoglycan layer in the cell wall of Gram-positive bacteria gives greater access to antibiotics, allowing them to more easily penetrate the cell and/or interact with the peptidoglycan itself.