1.4 Antibiotic modes of action
This section focuses on the four main modes of antibiotic action (Figure 6) that lead to inhibition of one of the following:
- cell wall synthesis
- protein synthesis
- nucleic acid synthesis
- metabolic reactions
- cell membrane function.
Don’t worry if you don’t understand all of these terms, as they will be explained in later sections.
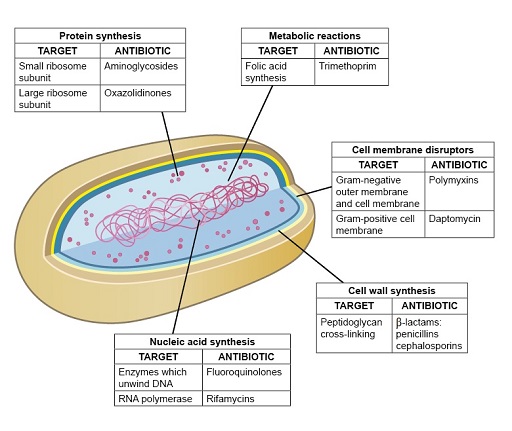
Figure 6 Some of the main antibiotic modes of action.
Show description|Hide descriptionThis figure shows a simplified 3D diagram of a prokaryotic bacterial cells as described in Figure 1 part (b). Each cellular component is labelled with the mode of antibiotic action that affects that structure. The labels contain a table describing the target of this mode of action and the antibiotic that exerts this effect. The first label is ‘Protein synthesis’. One target is small ribosome subunit and the attacking antibiotic is Aminoglycosides. The next target is large ribosome subunit, the attacking antibiotic for which is Oxazolidinones. The second label is ‘Metabolic reactions’. The target is Folic acid synthesis and the attacking antibiotic is Trimethoprim. The next label is ‘Cell wall synthesis’. The target is Peptidoglycan cross-linking and the attaching antibody is β-lactams: penicillins cephalosporins. The final label is ‘Nucleic acid synthesis’. The first target is enzymes which unwind DMA and its attacking antibiotic is Fluoroquinolones. The next target is RNA polymerase, the attacking antibiotic for which is Rifamycins.
Members of the same class of antibiotics share a characteristic structural feature that determines the drug’s affinity and specificity for target molecules in susceptible bacteria. You will now look in more detail at antibiotics that exemplify each of these modes of action.