2.1 What bacteria are
Bacteria are the most numerous organisms living on Earth. They live all around us: in our gut, in the soil and in water. Bacteria are pretty much all over the place.
Activity 5: Bacterial growth
The secret of the success of bacteria – why there are so many of them – is that they can reproduce rapidly. Under the right conditions, some types of bacteria can replicate every 20 minutes. Take a look at Video 4 to see what this looks like, and answer the question that follows.
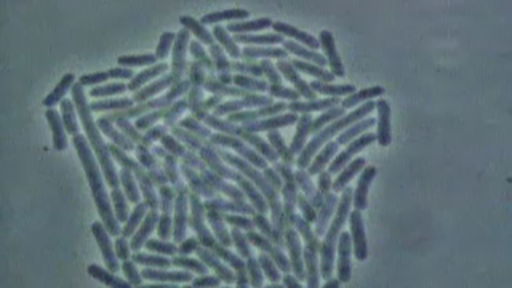
Transcript: Video 4
The video mentions that a bacterial infection can take hold so quickly because bacteria can double their numbers in such a short time. What are the three options mentioned in the video that help to stop the growth and replication cycle of bacteria?
Answer
The three options are:
- handwashing with soap
- vaccination to boost the immune system
- antibacterial drugs.
Most bacteria do not cause us any harm. However, a small group of bacteria – about 500 species – can cause diseases in humans, animals and/or plants. These bacteria are called pathogenic, and they are capable of causing an infection by evading the host’s normal defences and invading cells or tissues. They may also produce harmful toxins (poisons).
Many bacteria are
Activity 6: Diseases caused by bacteria in humans, animals and plants
Think about examples of diseases in humans, plants and animals that are caused by bacteria.
Answer
Diseases caused by bacteria in humans:
- Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and mainly affects the lungs. The classic symptom of active tuberculosis is a chronic cough with bloodstained sputum, fever and weight loss. This disease can spread to other people through respiratory secretions when patients with active TB cough, spit up their sputum or sneeze.
- Tetanus, also known as lockjaw, is characterised by muscle cramps and is caused by Clostridium tetani. This bacterium is commonly found in soil, dusts and manure. The bacteria can enter the body through a break in the skin and produce toxins that cause the muscle contractions. This disease is not spread from human to human.
- Typhoid fever is caused by Salmonella typhi serovar Typhi, sometimes abbreviated as Salmonella Typhi. Patients infected with it may experience mild to severe symptoms including fever, abdominal pain constipation and vomiting. This disease is spread through contaminated water or food.
- Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs. Some bacterial strains that can cause pneumonia include Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Bacteria are the most common cause of pneumonia; viruses cause only about one third of cases of pneumonia in adults.
Diseases caused by bacteria in animals:
- Anthrax in cattle, sheep and goats is usually spread by contact with spores of Bacillus anthracis in the soil or from pastures. Animals present with weakness, staggering and bloody discharges, often rapidly leading to death – although sometimes sudden death of livestock is the first sign of the disease. Anthrax is a
zoonotic disease, so it can also be passed from animals to humans. - Salmonellosis in poultry, with Salmonella species causing disease in a wide range of birds including chickens and turkeys. Different species and serovars present differently, with common presentations being pullorum disease, fowl typhoid and fowl paratyphoid. Some strains of Salmonella in poultry can be passed to humans through the food chain.
- There are several species of Brucella which tend to present slightly differently in different species. The most common sign of brucellosis in livestock is abortion during the final trimester of pregnancy. Some species of Brucella are zoonotic.
- One of the most common aquatic diseases is Vibrio, which leads to massive mortality of cultured shrimp, fish and shellfish. Vibriosis (Vibrio illness) can be zoonotic, and Vibrio cholerae can cause cholera in humans.
Diseases caused by bacteria in plants:
- Bacterial leaf streak and black chaff are a major bacterial disease of wheat. The bacteria (Xanthomonas translucens) are seed-borne. Typical symptoms on the leaf consist of elongated, light brown lesions, several centimetres long, that are initially distinct but later coalesce to cover larger solid areas. Yield losses can be as high as 40%.
- Epidemics of rice bacterial blight caused by Xanthomonas oryzae have been observed in Asia, the western coast of Africa, Australia and Latin America. The early signs consist of streaks that spread from leaf tips and margins, eventually oozing a milky substance that dries into yellow droplets. Later on, leaves will die; infected seedlings die within a few weeks of infection.
- Bacterial canker mainly affects tomatoes (caused by the bacterium Clavibacter michiganensis), present worldwide. Infections result in wilting, defoliation, desiccation, skin cankers, significantly reduced fruit yield and quality, and ultimately plant death.
2 The golden age of medicine