2.2 Organisational structure
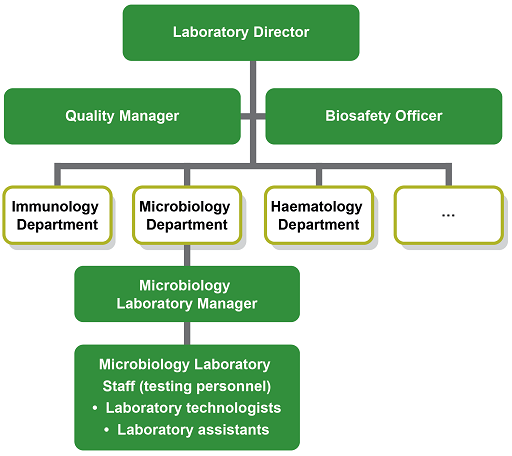
The laboratory should have a clear organisational structure with the roles and managerial responsibilities of all staff members made explicit. The Laboratory Director has overall responsibility and leadership for the running of the laboratory. The Laboratory Manager is responsible for organising the work of laboratory technologists and for maintaining quality standards and safety aspects.
The Quality Manager takes responsibility of the QMS, and for approving all the relevant documentation and processes. Depending on the size of the laboratory, additional roles dealing with biosafety, equipment, supplies, training etc. may be delegated (Figure 3).
(Figure 3 is an example with a focus on the microbiology department of a clinical laboratory. Your workplace may be considerably larger with more sections or considerably smaller with staff members having more than one role. Note that the Quality Manager and Biosafety Officer advise the Laboratory Manager, but do not necessarily directly line-manage staff if resources are scarce or the laboratory is small.)
Activity 4: Your role and responsibility in the workplace (part 1)
Take some time now to think about how your workplace is organised and how your role fits into the organisational structure. You might find it helpful to discuss this with your colleagues using the following questions as a guide:
- Who is responsible for quality policies and standards?
- What responsibilities do you have?
- Do you have more than one role?
- Who is responsible for biosafety?
Discussion
Table 1 summarises the roles and responsibilities regarding the management of quality in a microbiology laboratory.
| Role | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Laboratory director |
|
| Quality manager (or safety officer) |
|
| Microbiology staff |
|
2.1 Meeting basic standards: facilities and safety