5.6 The role of the AMR coordination committee (AMRCC)
Part of the remit of the governance structures is the setting up of the
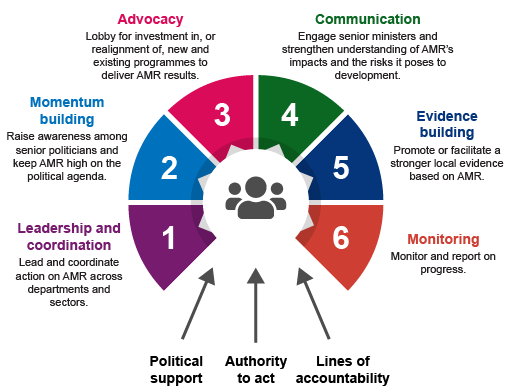
The WHO definition of the role of AMRCC is to ‘oversee and, when necessary, to coordinate AMR-related activities in all sectors to ensure a systematic, comprehensive approach’. Figure 4 outlines the responsibilities of AMRCCs.
The implementation of NAPs and, by extension, national AMR surveillance systems, is dependent on the availability of resources, extent of cross sectoral collaboration and political will. This makes implementing NAPs difficult in resource-limited settings of low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). AMRCCs carry out their responsibility by understanding which AMR activities need to be focused on. The following allow AMRCCs to carry out their function:
- AMRCCs are established with clarity of the roles and responsibilities of those who comprise them.
- The ability exists to adapt and scale up the present AMR surveillance infrastructure, rather than build a new one, which is a resource-heavy process.
- Governance structures are set up, that include stakeholders from government, academia and professional bodies, making cross-sector support for implementing strategies more likely.
The national coordinating centre for AMR surveillance is often a technical working group under the AMRCC. Depending on the country, there may be no separate surveillance NCC, in which case its functions should be fulfilled by the AMRCC.
5.5 Legal and ethical considerations in line with established practices for global disease surveillance and reporting