10.2 Importance of resistance mechanism data to AMR surveillance
Information about the resistance mechanism associated with clinical and veterinary isolates is useful at local, national and international levels.
Locally, for example within a hospital, knowing the mechanism can be helpful in order to track the spread of a particular gene and/or organism. It may also help to identify whether cases are genuinely linked. This can help the infection control team define whether it is a genuine outbreak or just sporadic cases. Additional testing would be needed to confirm whether strains are related, but it is more likely if they have the same resistance mechanism and early actions can be put in place to limit transmission. If it is an outbreak, understanding how the organism has spread makes it easier to work out the best measures to control the outbreak. For example, is it spreading from person to person or via water contamination?
On a national or international scale, data about resistance mechanisms help to identify priorities for additional surveillance and control, and for R&D. The data can enable early intervention to contain resistance mechanisms of global concern. If mechanisms can be prevented from becoming widespread, this reduces risk to patients from infections which are hard to treat and saves money in healthcare. This is even more important in low-resource settings where antimicrobial choices are limited because of financial constraints.
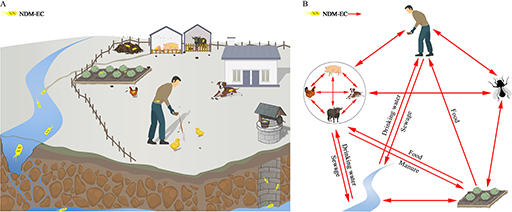
The genotypic data can also be used to help understand how transmission from food animals to the human food chain occurs (an example is shown in Figure 22, where the investigators studied the resistance genes in samples from around the farm environment). This in turn can show how this transmission can be prevented. With good quality data it is much easier to implement mechanisms to prevent transmission. This may involve complex interventions such as political, social, and financial measures which may be costly or have negative impacts on food producers in the short term so might be resisted. Data are essential to give the political drive to intervene.
Antimicrobial resistance mechanism data can also help to understand and control international transmission chains. An example could be medical tourism, where people travel to other countries either for cheaper treatment or for treatment which is not available where they live. They risk bringing back and spreading resistant strains to their home country on their return, especially if they have further hospital treatment. This is an important route of spread of AMR and is also a political issue. Again, having good data is vital in order to control spread by this route.
Finally, linking AMR resistance mechanism data to antimicrobial use is very useful to inform strategies for antimicrobial stewardship (see the Antimicrobial stewardship modules).
10 How knowing the resistance mechanism contributes to AMR surveillance