5.2 Testing for inducible resistance
Some resistance mechanisms are expressed only when induced by the presence of another antimicrobial. These strains can become resistant during antibiotic treatment, so it is important to know if they are present. For certain pathogen-antimicrobial combinations, it is therefore possible to test for the resistance mechanism using a form of AST called the
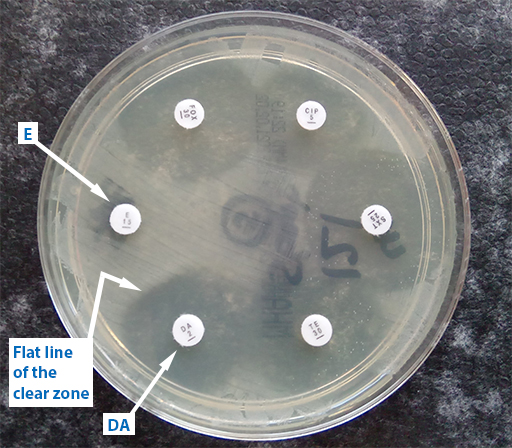
The ‘D’ test can be used to detect inducible clindamycin (DA) resistance in S. aureus. In Figure 10, erythromycin (E) has diffused into the agar and interfered with the effect of the adjacent antibiotic, DA. The effect of E has been to induce the expression of DA in S.aureus organisms present in the agar and allow the bacteria to grow closer to the DA-impregnated disk. This is shown by flattening of the DA inhibition zone on the side next to the E disk.
5.1 Use of indicator antimicrobials