3.3 Analysis of aggregate samples
The analysis of aggregate samples uses material widely available on the farm, rather than blends of specimens from a known number of subjects as in the case of pooled specimens.
Examples of aggregate samples that can be used for analysis are:
- manure samples
- feed samples
- tank milk samples.
What is the main advantage of analysing aggregate samples?
Answer
Using aggregate samples enables a cost-effective screening of large number of farms for many different pathogens without the elevated costs of sampling.
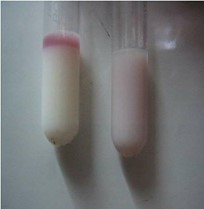
An example of aggregate sample analysis is the milk ring test for Brucella antibody (Figure 4), which is used for a cost-effective surveillance of dairy herds for brucellosis in areas that have achieved a disease-free status. Often, calculations of the impact of dilution on the sensitivity of aggregate sample analysis are difficult to carry out if the number of animals contributing to the sample is not known.
Aggregate sample analysis of tank milk is currently in use by some farms in New Zealand to isolate S. aureus and generate farm
Activity 5: Advantages and disadvantages of each approach
Reflect on the relative strengths and weaknesses of individual animal specimen, multiple specimen, pooled specimen and aggregate sample analysis, and complete Table 2.
| Type of specimen | Relative strengths | Relative weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Individual specimen | ||
| Multiple specimen | ||
| Pooled specimen | ||
| Aggregate sample |
Answer
| Type of specimen | Relative strengths | Relative weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Individual specimen | Identifies the presence of a pathogen in an animal; agent not diluted | Test result is negative if agent is not present in the specimen or is present below the LoD |
| Multiple specimen | Always increases farm-level testing regime sensitivity | High cost |
| Pooled specimen | May increase farm level testing regime sensitivity. Enables cost effective analysis for multiple pathogens | Pathogen may be diluted below culture LoD |
| Aggregate sample | Avoids expensive sampling activities | Agent’s dilution factor unknown |
3.2 Analysis of pooled specimens