4.1 Advantages and disadvantages of different types of test in practice
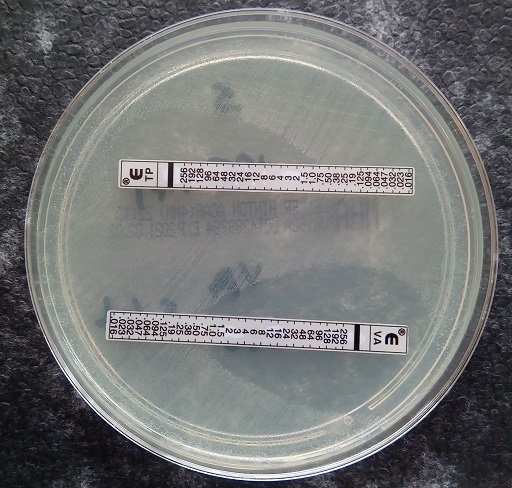
Gradient diffusion testing
Gradient diffusion testing is used when it is important to know the precise MIC for a given pathogen-antibiotic combination. Usually, commercial MIC gradient test strips are used. These have a high concentration of antimicrobial at one end of the strip, and the concentration gradually decreases along the length of the strip. Markings on the strip indicate the antimicrobial concentration at each point.
Advantages of gradient diffusion testing are that it can be used:
- for certain organism–antimicrobial combinations where disk diffusion testing is hard to interpret for technical reasons, for example glycopeptides in Staphylococcus
- for some organisms, like certain fungi, where disk diffusion testing is unreliable
- in laboratories without access to an automated system for MIC determination – the procedure is very similar to disk diffusion testing, and a laboratory that is able to perform disk diffusion testing should be able to perform gradient diffusion testing relatively easily.
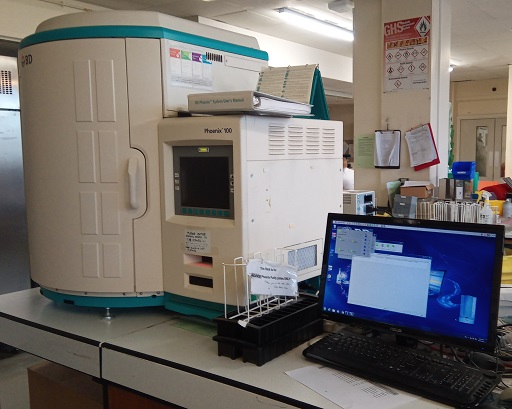
Automated systems or semi-automated systems
Automated systems or semi-automated systems that use dilution methods are used by large microbiology laboratories with high throughput, including many clinical laboratories in higher-income countries. These systems are usually relatively costly to buy and run.
Advantages of such automated systems are that they can test large panels of antibiotics and are less labour-intensive than other methods. Further advantages include capability for interpretive testing of resistance mechanisms (see the Testing for mechanisms of resistance course) and speciation of microorganisms.

Manual broth dilution methods
Manual broth dilution methods are performed either in test tubes (as in Figure 1) or, for broth microdilution, in a 96-well plate, and are mainly only used in reference and research facilities.
The main advantage of these methods is that they can be used for testing organisms with more complex growth requirements such as Mycobacteria, fungi and other fastidious organisms.
Agar dilution
Agar dilution is a laborious but useful method, considered to be the Gold Standard for reference laboratories processing large numbers of samples, or organisms for which disk diffusion is not possible.
Why not all methods are always suitable
Activity 7: Consider potential disadvantages of the methods
Use the space below to note any practical disadvantages you can think of for each of the methods discussed in this section:
- gradient diffusion testing
- automated/semi-automated systems
- manual broth dilutions
- agar dilution.
Discussion
| Method | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Gradient diffusion testing | Relatively expensive compared to disk diffusion method because strips cost a lot more than disks |
| Automated/semi-automated systems | Expensive equipment and reagents required Equipment requires regular maintenance and repairs may take time, involve waiting for parts etc. Another system as ‘back-up’ is advisable |
| Manual broth dilutions | Too complex and time-consuming for most clinical laboratories |
| Agar dilution | Labour-intensive and not suitable for laboratories that process smaller numbers of samples, including most clinical laboratories |
4 Other methods