Strategic framework for AI adoption in law firms
GenAI tools can be applied to both legal and non-legal tasks. When considering which tools to adopt:
Engage with different vendors.
Conduct thorough due diligence to evaluate risks and capabilities.
Develop a clear implementation plan that aligns with the firm’s overall strategy and professional obligations.
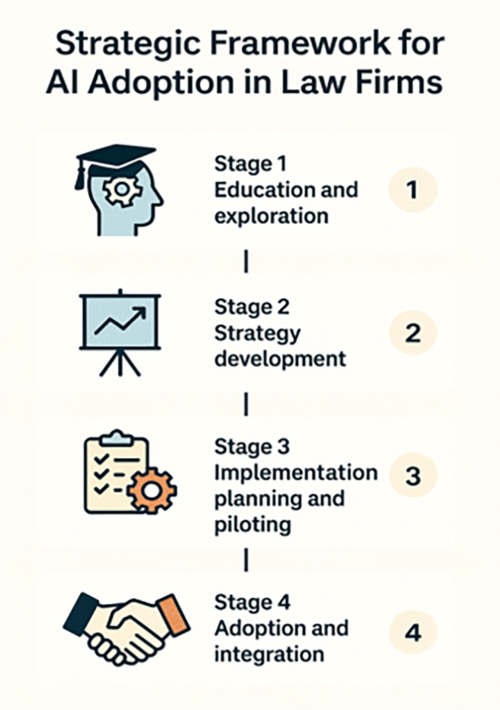
The third course, Key considerations for successful Generative AI adoption, explored how to create a GenAI strategy. Below is a framework that organisations can adapt to guide their thinking around AI adoption.
| Objective | Key activities | Success criteria |
| Learning about GenAI, experimenting, and understanding capabilities. | Organise educational workshops for staff on GenAI fundamentals. Create cross-functional working groups with both legal and technical staff. Allocate dedicated time for hands-on exploration of GenAI tools. Review industry case studies of AI implementation in legal settings. Speak to vendors. Identify internal champions and sceptics to ensure balanced perspectives. Document initial impressions, concerns, and potential opportunities. | Knowledge assessment scores pre/post training. Percentage of staff participating in AI workshops. Quality of internal discussions and questions raised. Initial inventory of potential use cases identified. Initial inventory of potential vendors. |
| Objective | Key activities | Success criteria |
| Creating a tailored approach that aligns with firm priorities. | Identify and prioritise specific use cases based on:
Map legal and regulatory requirements for AI adoption:
Create preliminary resource allocation plan:
| Completion of comprehensive use case analysis. Documentation of legal/regulatory compliance framework. Establishment of governance structure. Sign off and approval of strategic direction. Clear definition of ‘minimum viable success’ for initial implementation. |
| Objective | Key activities | Success criteria |
| Targeted testing of AI solutions in controlled environments. | Select specific tools for pilot testing based on strategy. Design pilot projects with:
Establish robust measurement frameworks:
Develop feedback mechanisms:
| Completion of planned pilots within timeline. Quality of data collected from pilot projects. Specific improvements identified in workflow efficiency. Documented Return On Investment (ROI) calculations for each use case. |
| Objective | Key activities | Success criteria |
| Scaling successful implementations and embedding into firm operations. | Select tools and processes for firm-wide deployment based on pilot results. Develop comprehensive training programs:
Create integration plans for existing systems:
Establish continuous improvement mechanisms:
Develop client communication approach:
| Adoption rates across practice areas. Efficiency gains (time/cost). Client feedback on AI-assisted work. Staff satisfaction with AI tools. Impact on recruitment and retention. Revenue implications (cost savings and/or new service offerings). Competitive positioning enhancement. |
Best practice throughout all stages
Click on each label below to read more.
Legal use cases



