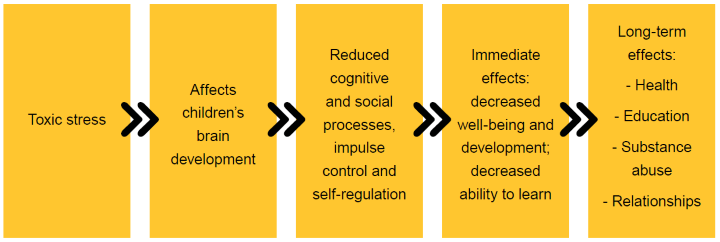
Effects of toxic stress
The video above pointed to the impact of toxic stress on a child’s developing brain. Let's breakdown what you have just watched in the video in more detail to fully explore this impact.
Read the first slide about The Brain. Then click on the Next button to view more slides.
Combating toxic stress
What happens if you don't try to combat toxic stress?
The potential future consequences of not dealing with toxic stress indicate the importance of providing appropriate support to students now.
Over the five units of this course, you will be reviewing key strategies to provide this support.
You will now look at specific impacts caused by toxic stress on young people’s behaviour in the classroom.
Impacts of toxic stress
Look at the impacts associated with toxic stress in the table below.
Reflect on your students and their behaviour in class. Do you see any of these in your daily work? Consider how you might respond differently to these behaviours knowing they could be indications of toxic stress.
| Cognitive impact | Physiological impact | Emotional impact | Behavioural impact |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
What is trauma?