Resource 3: Heart rate
![]() Background information / subject knowledge for teacher
Background information / subject knowledge for teacher
Heart rate is a term used to describe the frequency of the cardiac cycle [Tip: hold Ctrl and click a link to open it in a new tab. (Hide tip)] (Accessed 2008). It is considered one of the four vital signs (Accessed 2008). Usually it is calculated as the number of contractions (heartbeats) of the heart (Accessed 2008) in one minute (Accessed 2008) and expressed as ‘beats per minute’ (bpm).
When resting, the adult human (Accessed 2008) heart beats at about 70 bpm (males) and 75 bpm (females), but this varies. However, the reference range is nominally between 60 bpm (if less, termed bradycardia) (Accessed 2008) and 100 bpm (if greater, termed tachycardia) (Accessed 2008). Resting heart rates can be significantly lower in athletes. The infant/neonatal rate of heartbeat is around 130–150 bpm, the toddler's about 100–130 bpm, the older child's about 90–110 bpm, and the adolescent's about 80–100 bpm.
The body can increase the heart rate in response to a wide variety of conditions in order to increase the cardiac output (Accessed 2008) (the amount of blood ejected by the heart per unit time). Exercise (Accessed 2008), environmental stressors or psychological stress can cause the heart rate to increase above the resting rate.
Measuring heart rate
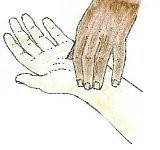
The pulse rate (Accessed 2008) (which in most people is identical to the heart rate) can be measured at any point on the body where an artery (Accessed 2008) is close to the surface. Such places are wrist (Accessed 2008) (radial artery) (Accessed 2008), neck (Accessed 2008) (carotid artery) (Accessed 2008), elbow (Accessed 2008) (brachial artery) (Accessed 2008), and groin (Accessed 2008) (femoral artery) (Accessed 2008). The pulse can also be felt directly over the heart. (Remember, never use your thumb to measure your pulse rate, because thumbs have a pulse rate of their own.)
It is also possible to measure heart rate acoustically, by listening to the sounds the heart makes while beating. These sounds can be listened to using a stethoscope (Accessed 2008).
Resource 2: How mind maps can help mathematics teachers and pupils



