4 Measuring AMR, AMU and AMC to support decision-making
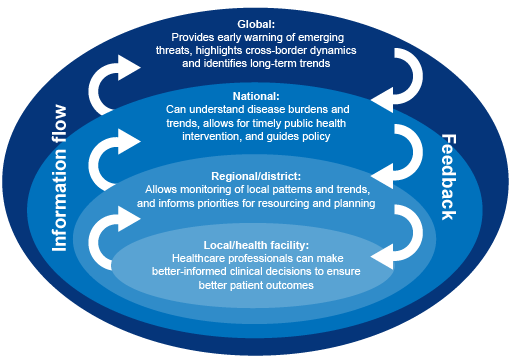
AMR, AMU and AMC are measured and used at different levels and in different sectors – from hospitals or farms or laboratories, to national governments, to international organisations. Information about AMR, AMU and AMC addresses different needs at different levels. For example, local-level AMR data are important for clinical decision-making (choosing the best treatment for an individual patient), whereas national and global-level AMR data can provide an early warning of emerging AMR threats. Data collected at local level therefore inform international decision-making. Equally, information compiled at international level can influence local-level practices. For example, emergent AMR detected nationally or internationally might lead to a change in local prescribing guidelines. Figure 3 presents an example of how AMR information is used at different levels in public health.
Activity 11: Diagram to show human or animal health
Draw a similar diagram for AMU or AMC information in human health, or AMR, AMU or AMC information in animal health. Where might public and animal health intersect in this information flow?
3 AMR data sources