6 Network access layer
- This layer is responsible for preparing the data packets it receives from the Internet layer for transmission to the physical media connecting devices within the local network. There are three main types of physical media available:
- Copper: coaxial, twisted pair.
- Optical: single mode, multi-mode.
- Wireless: WiFi, satellite.
- Due the wide range of media, and supported technology, the network access layer is more complex than the other layers. Additionally, while the upper layer protocols within the TCP/IP suite are implemented in software, the network access layer must provide physical connectivity, thus it has both hardware and software components, typically implemented within a device’s NIC.
- The primary functions of the network access layer are:
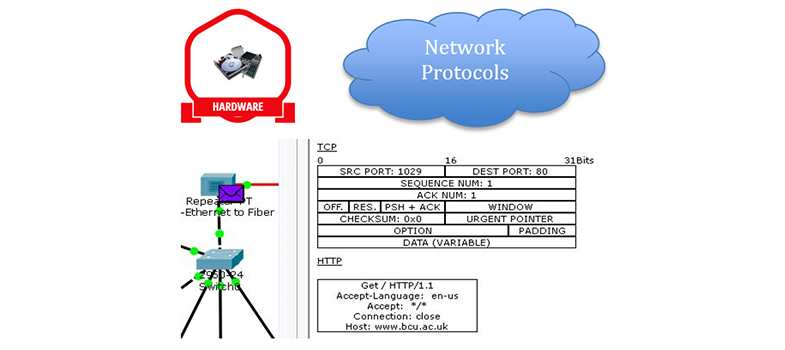
- Accepting packets from IP and encapsulating them within frames. Different protocols can use different types of frames.
- Converting the binary bits that make up the frame into a signal suitable for the type of media that is in use. For example, the bits are converted into an electrical signal for copper media and into pulses of light for optical media. Bits are converted to ultra high frequency radio waves on a wireless network.
- Whereas the upper layer protocols are controlled by the agencies charged with maintaining the Internet (primarily the Internet Engineering Task Force), the sheer number of physical media available has led to many different protocols being designed and produced, often by commercial organisations.
Figure 6
- Over time, many of these protocols have become standardised and thus have become available for general use. The most commonly used network access Local Area Network (LAN) protocol is Ethernet and its derivatives.
- The frames used by Ethernet totally encapsulate the IP packets sent from the network layer, so devices cannot directly read the IP addresses they contain. This makes it necessary for frames to carry their own source and destination addresses to ensure frames are delivered to the correct devices in the local network.
- In an Ethernet network, this address is known as a Media Access Control (MAC) address.
Back to previous pagePrevious
5 Internet layer