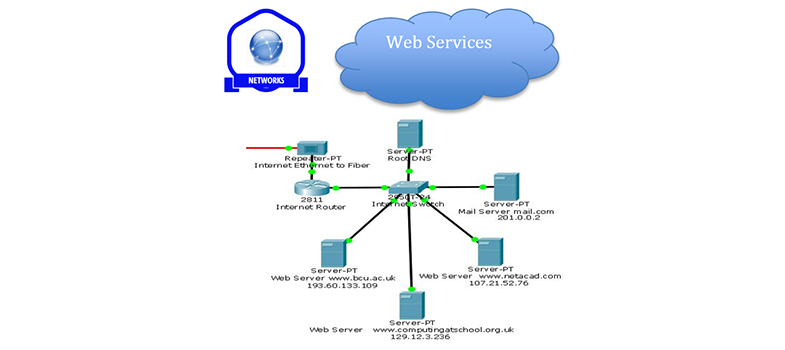
5 Email
- Electronic mail or email provides a way of exchanging digital messages across computer networks. The messages can consist of just simple text, but you can also attach a variety of different files (e.g. documents, pictures, videos).
- Email works as a client/server service, and allows you to create emails using client software (e.g. Outlook, Thunderbird) which then transfers the emails to mail servers where they are stored until retrieved by the email recipient. This means you only need to connect briefly to the Internet to send and receive emails.
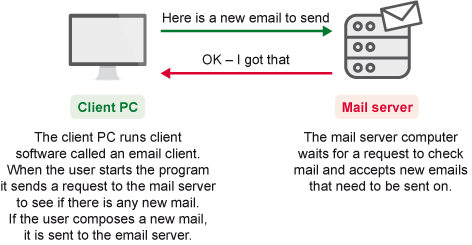
Figure 8
- To use email, you need an email address, which uniquely identifies a user with an account on a particular mail server. The address consists of a local part, identifying the user’s mailbox, and a domain name which identifies the mail server location:
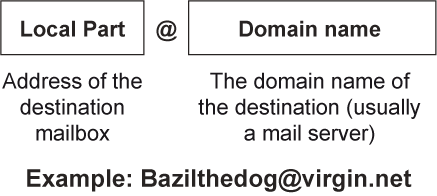
Figure 9
- Many email services are now web based, so you can write, send and receive email via a web browser after you have set up an account with an online email provider, such as Google or Yahoo!
- Take a look at this video for more information about email.
Interactive feature not available in single page view (see it in standard view).
Back to previous pagePrevious
4 The WWW and search engines