4.4 Differentiation and the curriculum
The impact any additional support need has on learning varies in degree according to the learning and teaching environment. It is the responsibility of all who work with children to respond appropriately to their needs. Recognising early signs of difficulties and adapting learning and teaching approaches are a regular part of the daily routine for teachers supporting all children in an educational environment.
Differentiation is defined by the Training and Development agency for Schools as:
the process by which differences between learners are accommodated so that all learners in a group have the best possible chance of learning.
Differentiation is a key skill and requirement for all teachers to ensure the needs of all their learners are met. Creating resources, which are accessible for learners with additional support needs, will also support a wide range of learners. The impact a barrier to learning has varies in degree according to the learning and teaching environment. To ensure learners can access the curriculum and engage with the learning and teaching, staff will need to make adaptations and differentiate their approaches and resources and this may happen in a number of ways. Expert opinion varies regarding agreement on the definitive methods and approaches to support differentiation within learning and teaching, for example Kormos and Smith (2012) highlight that effective differentiation can be achieved by considering four dimensions: materials, task, expectation and support. (Teaching Languages to Students with Specific Learning Difficulties: 2012) and others focus on the areas of
- task
- support and
- outcome.
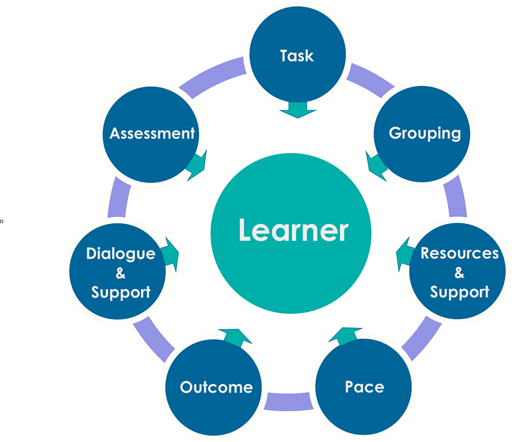
Figure 15 highlights different approaches to consider when planning effective and meaningful differentiation.
Activity 15 Reflective Task
There are several approaches to consider when planning effective and meaningful differentiation. The table highlights effective areas of differentiation.
Consider what you may think the areas of focus could be then reveal some possibel answers. Do note that the list is not exhaustive.
| Differentiation by: | Areas of focus for differentiation |
Task
| |
Grouping
| |
Resources /Support
| |
| Pace | |
| Outcome | |
| Dialogue and support | |
| Assessment |
Answer
| Differentiation by: | Areas of focus for differentiation (this column is revealed) |
Task
|
|
Grouping
|
|
Resources /Support
|
|
| Pace | Consideration of flexibility of teaching pace and time allowed for tasks and individual learner requirements, supporting both able learners and those who require more time. |
| Outcome | All learners undertake the same task but a variety of results are expected and are acceptable. |
| Dialogue and support | Teacher facilitates problem solving using appropriate levels of language to engage with learners Use of targeted questions to produce a range of responses Verbal support and encouragement |
| Assessment | 'Building the Curriculum 5' (2011) provides guidance for all teaching staff on the main areas of the assessment strategy for Curriculum for Excellence. http://www.educationscotland.gov.uk/ learningandteaching/ thecurriculum/ buildingyourcurriculum/ curriculumplanning/ whatisbuildingyourcurriculum/ btc/ btc5.asp Assessment is for Learning - http://www.educationscotland.gov.uk/ learningandteaching/ assessment/ Ensuring appropriate support for all learners http://www.educationscotland.gov.uk/ learningandteaching/ assessment/ about/ principles/ ensuringappropriatesupport.asp Summative assessment techniques Assessing learner’s knowledge and understanding through the learning experience. |
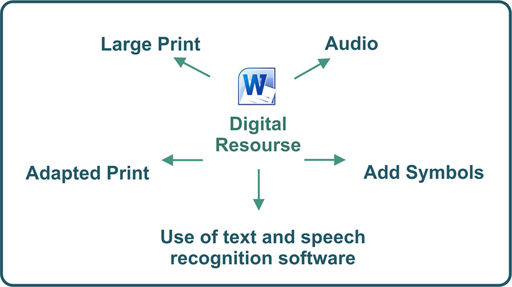
The availability and access to IT has changed the development and production of learning and teaching resources in an extremely positive way. All teachers have access to computers and create the majority of resources on a word document which can be converted very easily into a range of differentiated and accessible resources as highlighted in figure 16.
Staff should consider ways to remove any unnecessary barriers including ensuring that language used to describe what is expected of learners is accessible. They should consider the amount of support required to ensure fairness and provide sufficient challenge.End of Figure
Activity 16 Reflective task
Think about the curriculum that you teach.
What do you see as your main challenges in differentiating the curriculum?
Consider the needs of your learners and make a note in your Reflective Log of how well you meet their needs at present and where you would like to make improvements.
4.3 Transitions