11.2 Stages of behaviour change
One of your tasks as a Health Extension Practitioner is to identify where change in a person’s behaviour or habits could help to have a positive impact on their health or the health of their baby. For example, helping a person eat a more balanced and healthy diet.
Behaviour change communication is more than just education, it aims to change behaviour and practice.
There are eight stages in behaviour change that will help the people you are working with change from being an uninformed person to becoming someone who may even be able to teach or influence others about their behaviour. You are going to learn about this now, using exclusive breastfeeding behaviour as an example to illustrate the key points.
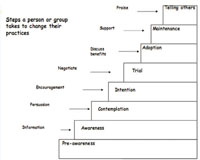
Step 1 Pre-awareness At this stage people are not even aware of the changes that they need to make. In order to help them become a person who has awareness, you need to give them information. Nutrition education would stop at this stage without making sure that the person being educated has changed their action, practice or behaviour. Before this stage the mother does not know about the importance of exclusive breastfeeding during the first six months.
Stage 2 Awareness At this stage, the person has heard about the need to change their behaviour, but needs extra help and persuasion to start to actually bring about the changes. At this stage the mother is aware about the need for exclusive breastfeeding during the first six months, but has not thought of doing it for her baby.
Stage 3 Contemplation This person is contemplating (thinking) about changing their behaviour, but needs more information and continued support and persuasion about the advantages and disadvantages of changing their behaviour. At this stage more information about the benefits of exclusive breastfeeding compared to other forms of feeding is needed, as well as support that shows you understand the mother’s situation.
Stage 4 Intention At this stage the person has understood the advantages and disadvantages of changing their behaviour but is not sure how they can bring about the new behaviour for themselves. The person needs encouragement to overcome obstacles of how to do the new behaviour. For example, the mother may be worried about not being able to maintain exclusive breastfeeding when she is away for work, or for other individual or personal reasons. In this situation you could show her how she can express breastmilk so the baby can be fed when she is away.
Stage 5 Trial The person has tried the behaviour or action required, but has faced difficulties. For instance, the mother tried to exclusively breastfeed her baby, but she faced some difficulties. She now needs support in the form of praise and reinforcement of the benefits. Reinforcing the ways of preventing the problem she faced during exclusive breastfeeding is also important. So she needs counselling to find the best ways of overcoming her problems. At this stage the mother may have inadequate breast milk output and think that her breast milk is not enough for the baby to feed on until six months old. Here, she needs to be assisted on proper positioning and attachment and be reassured about the capacity of the breastmilk to feed the baby for the first six months. Your skills in negotiating the different options the mother can use will be important at this stage.
Nutrition behaviour change communication is different from nutrition education in that BCC needs at least three contacts to change behaviour. Unlike nutrition education, which aims at increasing awareness or knowledge, BCC targets change of behaviour or practice. For example, if at this point the mother has not tried exclusive breastfeeding, there needs to be at least three contacts between you and the mother to change her behaviour and to help her progress from the awareness stage to the trial stage.
Behaviour change communication (BCC) is an ongoing process that requires effective communication to persuade, encourage and support change.
Stage 6 Adoption At this stage, the person is demonstrating the new behaviour. They now need discussion to reinforce their behaviour and sustain the change they have made. For example, the mother has now sustained exclusive breastfeeding. What she needs at this stage is further discussion on the benefits of exclusive feeding to reinforce the behaviour and make sure that she continues exclusive breastfeeding for a few weeks. You can help her with this, by encouraging and praising her and emphasising the importance of exclusive breastfeeding for her baby’s health.
Stage 7 Maintenance The person’s behaviour by this stage has changed and they understand the benefits of the change. Now they just need support if they face any difficulties. For example, the mother has changed her behaviour and is now used to exclusive breastfeeding and has understood its benefits. It has become part of her behaviour and she thinks that she will exclusively breastfeed when she has another baby. What she needs at this stage is support in overcoming any further difficulties.
Stage 8 Telling others The person has done the behaviour for a considerable length of time, it has become routine behaviour and now leads to the person convincing others about the benefits of their health related behaviour. For example, the mother is encouraging other mothers to exclusively breastfeed their babies and describing the benefits to the baby and mother. What the mother needs at this stage is praise.
Why is knowledge not enough to change behaviour, action or practice?
You have learned that knowledge alone only provides information. The BCC model indicates that you can only promote effective and sustained changes in the way a person does something if you have at least three contacts with a person, and spend time persuading, encouraging and supporting a person to change. This reinforces their behaviour and is more likely to lead to lasting change.
Figure 11.1 summarises the eight steps to behaviour change.
You are now going to look at how you can use the BCC steps and apply these to a communication strategy to help improve nutrition in your community.
11.1 Behaviour change communication
