Self-Assessment Questions (SAQs) for Study Session 3
Now that you have completed this study session, you can assess how well you have achieved its Learning Outcomes by answering these questions. Write your answers in your Study Diary and discuss them with your Tutor at the next Study Support Meeting. You can check your answers with the Notes on the Self-Assessment Questions at the end of this Module.
SAQ 3.1 (tests Learning Outcomes 3.1 and 3.2)
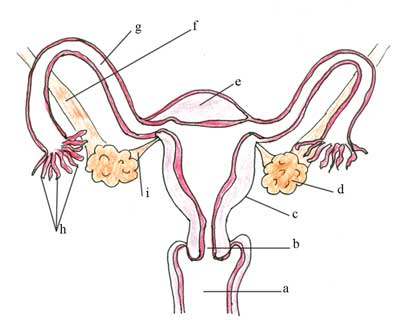
Look at Figure 3.5. Label the anatomical features marked from ‘a’ to ‘i’.
Answer
The correct labels for Figure 3.5 are as follows:
a is the vagina
b is the cervix
c is the uterus
d is the ovary
e is the fundus
f is the ovarian suspensory ligament
g is the fallopian tube
h is the fimbriae
i is the ovarian ligament.
SAQ 3.2 (tests Learning Outcome 3.1)
Choose the correct directional terms from Box 3.1 to describe the relative positions of the uterus and the rectum in Figure 3.1.
Answer
The uterus is anterior to (in front of) and superior to (above) the rectum. An alternative way of expressing the same positions is to say that the rectum is posterior to (behind) and inferior to (below) the uterus.
SAQ 3.3 (tests Learning Outcomes 3.2 and 3.3)
Which structures are removed in female genital mutilation, and what harm can come to a woman during labour and delivery as a result?
Answer
The structures removed in female genital mutilation are usually the clitoris and the labia minora. The scarring that results as the cuts heal interferes with the normal ability of the vulva to stretch during childbirth to allow the baby to pass through the birth canal. As a result, the birth can be obstructed and the vagina can tear, causing severe pain and loss of blood. In some cases, a fistula (hole in the vaginal wall) can tear open, and blood loss can put the woman’s life at risk.
SAQ 3.4 (tests Learning Outcomes 3.2 and 3.3)
Which of the following statements is false? In each case, state why it is incorrect.
A Infection in the uterus can get into the pelvic cavity through the vagina.
B The perineum is a muscular area between the vaginal opening and the anus.
C The maturation of an ovum is controlled by the female reproductive hormones.
D Glands in the cervix produce secretions which lubricate the vagina.
E The fundus is the narrow ‘neck’ at the bottom of the uterus.
Answer
A is false. Infection in the uterus can get into the pelvic cavity by passing outwards through the fallopian tubes, which are open at the ends. Infection in the uterus can pass down the vagina, and usually appears as a bad-smelling discharge from the vaginal opening in the vulva.
B is true. The perineum is a muscular area between the vaginal opening and the anus.
C is true. The maturation of an ovum is controlled by the female reproductive hormones.
D is true. Glands in the cervix produce secretions which lubricate the vagina.
E is false. The fundus is the name for the domed top of the uterus. The narrow neck at the bottom of the uterus is called the cervix.
Summary of Study Session 3