8.2.2 Probable signs and symptoms of pregnancy
These are more reliable than the possible symptoms, but they are not certain indicators of pregnancy.
Abdominal enlargement
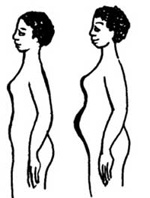
There is progressive enlargement of the abdomen (belly) from 7 to 28 weeks of pregnancy. At 16 to 22 weeks, growth may appear more rapid as the uterus rises higher into the abdomen.
Can you suggest other possible causes of abdominal enlargement?
The most obvious is that the woman is just getting fatter. But you should also consider whether she could have a cancer, or another type of growth in her belly.
Pregnancy test for human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG)
Chorionic is pronounced ‘korr ee onn ik’. Gonadotropin is pronounced ‘gonn add oh troh pinn’.
This hormone is produced by a part of the embryo only 8 days after conception, and by the placenta throughout pregnancy. It can be detected by chemical tests that can usually only be done at higher-level health facilities. Pregnancy testing kits may be purchased from some pharmacies, but they are expensive.
The hormone can be detected in the mother’s blood and urine eight to ten days after conception, or 40 days after the last menstrual period. When people refer to a ‘pregnancy test’, the urine test for HCG is usually what they mean. Although it gives a good indication of pregnancy in most cases, the testing kits may give a false result, especially if they have not been stored properly, or are out of date. Also there are some disease conditions that result in secretion of HCG.
Painless uterine contractions
As the uterus enlarges, it becomes globular (round) and often rotates to the right. Painless uterine contractions are felt as tightening or pressure. They usually begin at about 28 weeks’ gestation and increase in regularity. These contractions usually disappear with walking or exercise, whereas true labour contractions become more strong and powerful.
8.2.1 Possible symptoms of pregnancy
