9.1 Checking for symptoms of poor nutrition or lack of iodine
When you begin an antenatal visit, one of the first things you should ask the pregnant woman is if she has any symptoms that suggest poor nutrition or lack of iodine in her diet. This is very important, because poor maternal nutrition is associated with poor pregnancy outcomes like a small baby, and the child may be short in stature. The questions you ask her should aim to find out if she has any of the following warning symptoms (i.e. things she notices herself):
Warning symptoms
- Not wanting to eat
- Not gaining weight
- Weakness and general ill-health
- Sores, rashes, or other skin problems
- Sore or bleeding gums
- Stomach problems or diarrhoea
- Burning or numbness of the feet.
The effects of iodine deficiency are:
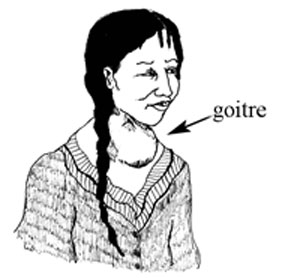
- Goitre (swelling in the front of the neck caused by iodine deficiency; Figure 9.1)
- Short children
- Children with deafness
- Children with cretinism, a disability that affects thinking.
If you suspect that a pregnant woman’s health is poor due to inadequate nutrition, or lack of iodine in her diet, advise her about good nutrition and iodine supplementation. You will learn how to do this in Study Session 14 of this Module.
Learning Outcomes for Study Session 9
