16 Testing your understanding
Define and describe chromatography using the following key terms:
- Mobile phase
- Stationary phase
- Gas Chromatography
Answer
Chromatography is a laboratory technique for separating mixtures.
The mixture to be analysed travels in a mobile phase (which may be a liquid or gas) which passes through a stationary phase. The interaction that compounds in the mixture have between the mobile phase and the stationary phase determines the speed at which they travel. This separates the different compounds.
In gas chromatography the mobile phase is an inert gas such as helium which flows through a column coated with the stationary phase.
The figure below shows an example chromatogram.
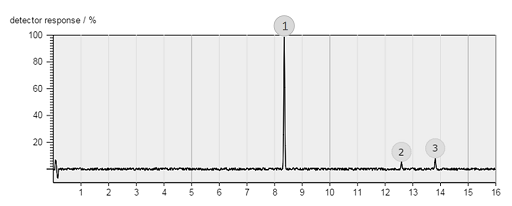
What should the label on the horizontal axis be?
Answer
Retention time/minutes (Remember units!)
Which of the three compounds is the most volatile?
Answer
Compound 1 is the most volatile because the retention time is the shortest.
Which is of the three compounds has the highest concentration?
Answer
Compound 1 has the highest concentration because the peak area is largest.
Use your results or return to the GC-MS laboratory to answer the following question.
Extra materials for interested pupils
Video clip on mass-spectroscopy (this takes you to an external website)
https://www.youtube.com/ watch?v=J-wao0O0_qM [Tip: hold Ctrl and click a link to open it in a new tab. (Hide tip)]
15 What do your results tell you?

