3 From DNA to RNA: transcription
The DNA strand region that is occupied by the CYP2D6 gene stretches over tens of thousands of bases, and during transcription this whole region of DNA is copied into an RNA chain. The order of the bases is copied exactly, but RNA uses a base called uracil in place of thymine.
Can you recall the other three bases that RNA has in common with DNA?
Answer
Adenine, cytosine and guanine.
The bases in RNA are therefore abbreviated as A, C, G and U.
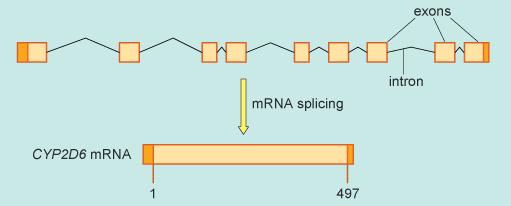
However, before RNA is used as a template for protein synthesis, one further processing event occurs. Within the RNA strand are small segments called exons that actually carry the code that will direct protein synthesis. Before translation can occur, the RNA copy of the CYP2D6 DNA is processed as shown in Figure 2, so that all the intervening segments (introns, black thin lines) between the protein-coding exons (orange boxes) are removed. This forms a shorter RNA molecule that encodes the 497 amino acid CYP2D6 protein. This processing occurs by a series of cutting and joining reactions called splicing and leaves only small portions of non-protein-coding portions of RNA at either end (dark orange). The exact sites at which this occurs are dependent upon a series of bases in the RNA strand that lie within the intron.
The segments of genetic code for the CYP2D6 protein are found in nine exons and the final spliced version of the RNA is called messenger RNA (mRNA).
2 DNA to protein