Task 2: Determining the hardness of a river water sample (Determining the hardness of river water by EDTA titration)
Task 2: Determining the hardness of a river water sample
The total hardness (concentration of calcium and magnesium ions) is expressed in mg l-1 CaCO 3 and it is calculated as:
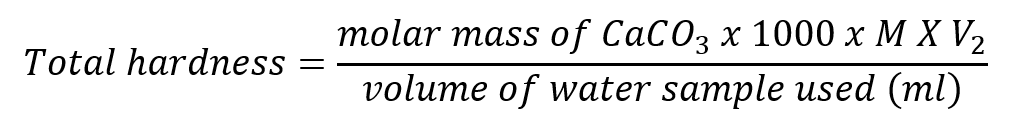
where M (mol l-1) is the molarity of EDTA solution, V2 (ml) is the volume of EDTA used in the titration of a river water and the molar mass of CaCO3 = 100.09 g mol-1.
You will now return to the Complexometric titration application and select a water sample from a selection of different rivers across the world and will titrate it against your standardised EDTA solution to determine its hardness. Detailed instructions are provided within the experiment but the following is a summary of the steps you need to take:
- Choose a river water sample from the list of possible locations.
- Measure as accurately as possible 50.00 ml of the water sample using the appropriate glassware and transfer into a conical flask.
- Add 2.00 ml ammonia buffer solution selecting the appropriate glassware.
- Add one or two drops of ErioT indicator. The solution will turn pink.
- Record the initial burette reading.
- Titrate with the EDTA solution until the colour of the mixture turns from pink, through purple, to blue. While adding EDTA, make sure the solution in the conical flask is thoroughly mixed using a magnetic stirrer. As the end point approaches and the solution turns purple, the EDTA should be added very slowly – drop by drop. At the end point the last of the pinkish tinge disappears and a pure blue colour is left.
- Record the volume of EDTA added.
Judging the exact end point can be difficult and the volume of EDTA required cannot be predicted. You may like to do a ‘rough’ titration first to estimate the approximate volume and then repeat, adding drop by drop as you approach the estimated end point. You should not include the value of your ‘rough’ titration in your calculation. Repeat the titration using the water sample at least twice.
Table 2 shows a template you could use to record your experimental data.
Table 2 volumetric data of EDTA used to reach equivalence
|
|
Rough |
Trial 1 |
Trial 2 |
Trial 3 (if needed) |
|
Initial burette reading /ml |
|
|
|
|
|
Final burette reading /ml |
|
|
|
|
|
Volume of EDTA solution used /ml |
|
|
|
|
|
Average volume of EDTA solution used (V2) /ml |
|
|
||
Use your data to calculate the total hardness of your chosen river water sample. When you have completed your calculation consider whether you would describe your water sample as soft, intermediate or hard.
Work through the example calculation below to familiarise yourself with the calculation required to complete Task 2.
|
Titration of a 50.00 ml sample of mineral water at pH 10 required an average of 16.80 ml of EDTA solution from the previous example (0.0095 mol l-1). Calculate the total hardness of CaCO3 in the mineral water. |
