Appendix 2: Teacher notes – outputs from the lesson (Determining the hardness of river water by EDTA titration)
Appendix 2: Teacher notes – outputs from the lesson (Determining the hardness of river water by EDTA titration)
Task 1
Students will standardise the EDTA solution before moving on to determine the hardness of water samples. The given concentration of EDTA solution is around 0.01 mol l-1. Students will be titrating 10.00 ml of standard calcium solution at a concentration of 0.010 mol l-1.
The molar concentration of EDTA solution is determined by:
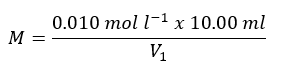
where V1 is the volume (ml) of EDTA used in the standardisation titration.
The volume of EDTA used in this standardisation titration will be around 10 ml.
Students will be getting values of 0.010 mol l-1 + 0.0005
Task 2
Students will determine the hardness of a river sample. Based on titration of 50 ml of sample and using and EDTA solution of 0.010 M, the calculations of water hardness are as follows:

where V2 (ml) is the volume of EDTA used in the titration of a river water.
Expected range of volumes of EDTA requires and hardness values:
|
Water sample |
Volumes of EDTA used / ml |
Hardness / mg CaCO3/l |
|
Avon river, UK |
5.04 |
119 |
|
Tejo river, Spain |
10.09 |
202 |
|
Seine river, France |
4.94 |
99 |
|
Rhine river, Germany |
4.15 |
83 |
|
St Lawrence river, Montreal |
2.20 |
44 |
|
Yellow river, China |
3.65 |
73 |
|
Kathajodi river, India |
3.85 |
77 |
|
Orange river, South Africa |
1.40 |
28 |
|
Arkansas river, USA |
1.90 |
38 |
|
Rio Grande, Mexico |
9.49 |
190 |
Students should supply data from replicates and present their average of these.
Previous: Appendix 1 Next: Lesson: Determining the hardness of river water by EDTA titration
