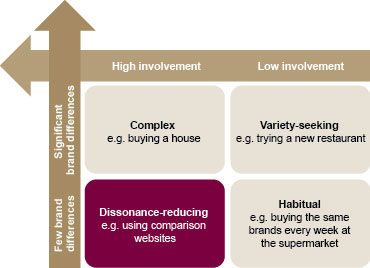
2.2 Dissonance-reducing buying behaviour
- Consumers are highly involved in the purchase, but have difficulties determining the differences between brands.
- ‘Dissonance’ can occur if consumers worry afterwards that they may have made the wrong choice. Examples include:
- financial services products, such as insurance or investment
- Consumer will choose such products on the basis of price or convenience and then seek further confirmation, after the purchase, that they made the right choice.
Back to previous pagePrevious
2.1 Complex buying behaviour