Part 4: Planting design
7. Use of colour
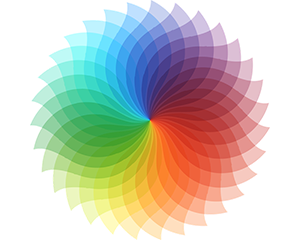
The colour wheel
Made up of the three primary colours (red, yellow and blue) and the three secondary colours (green, purple and orange), the colour wheel provides, at a glance, the foundation for colours that are complimentary, or contrasting, to each other.
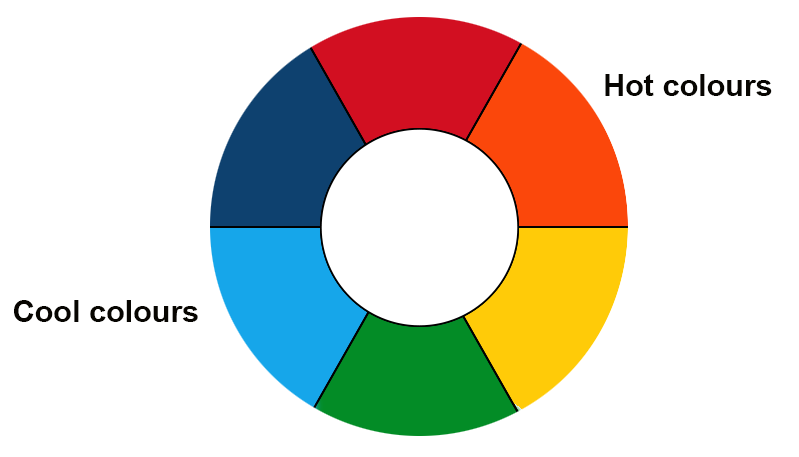
Contrasting (opposite each other on the wheel) colours will create an exciting planting scheme.
orange and blue
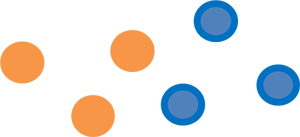
yellow and purple

red and green
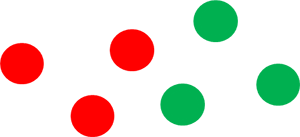
Adjacent (next to each other on the wheel) colours will create a more subtle colour combination.
blue and purple
yellow and orange

red and orange

Amber Crowley / public domain
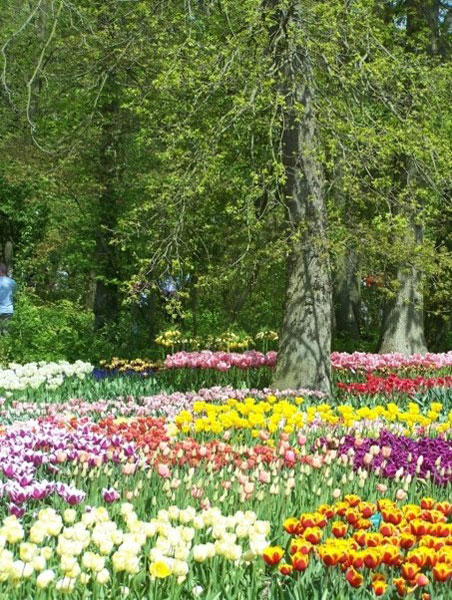
In this planting scheme contrasting colours have been used for a bright and bold display.
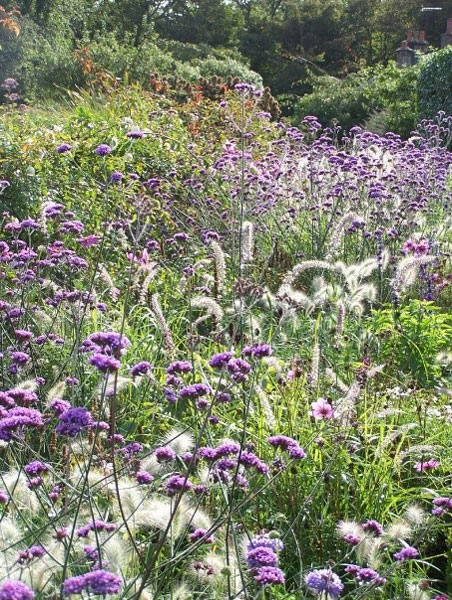

Amber Crowley / public domain
This scheme has been limited to the cool colours – mainly blue and white, which creates a calm and peaceful atmosphere.
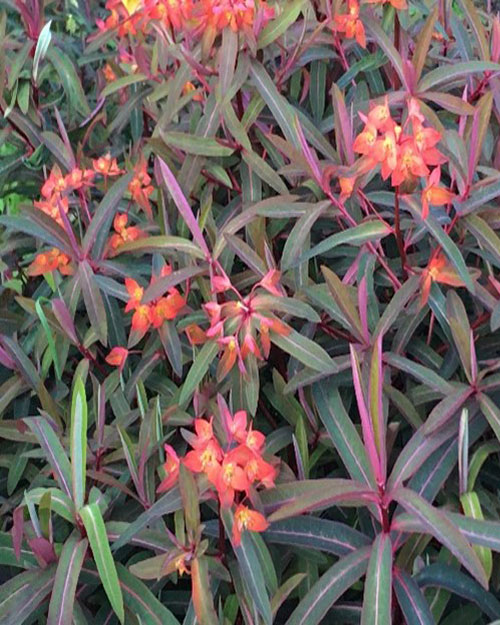
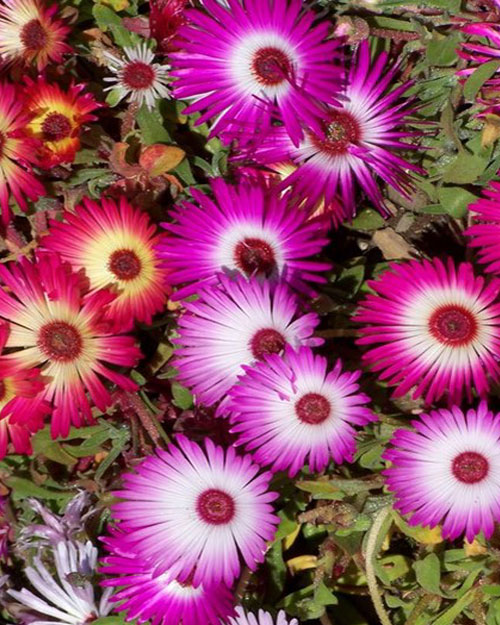
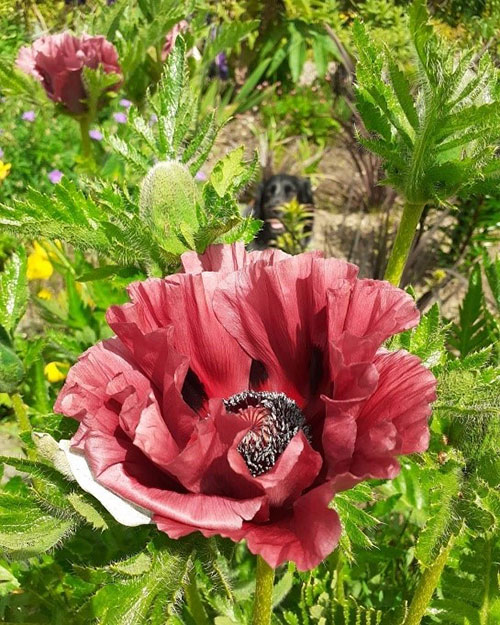



Amber Crowley / public domain
The warm, or hot, side of the colour wheel (reds, yellows, oranges and warmer purples) gives a hot, sunny and vibrant look to the garden.
Make a list of 6 plants which would grow together in a sunny border in a hot planting palette (reds, oranges, yellows and warm purples).
Make a list of 6 plants which would grow together in a semi-shade border in a cool planting palette (blues, whites, greens and cool purples).
