Pioneers
7. Networks
7.3. Narinder Kapany

Figure 1: Narinder Singh Kapany.
Source: Wikipedia (2023)
Downloadable teaching resource
Overview
Narinder Singh Kapany (ਨਰਿੰਦਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਕਪਾਨੀ) was an early innovator in fibre optics, laying foundations for modern internet communications.
Background
Narinder Kapany was born in the Punjab, India in 1926. He first studied at Agra University then continued studies in optics at Imperial College, London in 1952. In 1955, he moved to the United States, continuing his work there. He died in 2020.
Kapany was an entrepreneur, launching 'Optics Technology, Inc.' in California in 1960, and a later company, 'Kaptron', both early commercial ventures in fibre optics. He patented numerous inventions in diverse fields, including telecommunications and medical technologies. Kapany was also an intellectual and educator, with professorships at the University of California and Berkeley. He made a major contribution to the next generation of students and practitioners with his teaching, research and financial support (Spicer, 2024).
Explore further

Figure 2:
'The Man Who Bent Light'
by Narinder Singh Kapany.
Source: Google (no date)
Kapany wrote a memoir of his life, as pictured in figure 2. There is a review by Bhupinder Singh from the Sikh Foundation (which Kapany founded with his wife in 1967) (Singh, 2022; Spicer, 2024)
"This is the story of a larger-than-life man, who was a risk taker and lived life passionately"
- Singh (2021)
Contributions
Kapany was a physicist and a leading figure in the early development of fibre optics. He conceived the term “fiber optics” in 1960, and wrote the first textbook in the field (Kapany, 1967). His work culminated in the breakthrough achievement of light transmission through fibre-based cables. This early work was foundational for modern networked communications (Spicer, 2024).
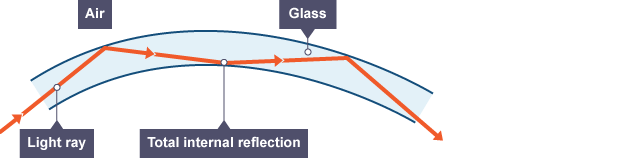
Figure 3: Fibre optics (BBC, 2025)Fibre optics: Light travels inside an optical fibre using "total internal reflection", allowing communication even in bent fibres.
Thinking further: Individuals or groups?
Spicer (2024) states that Kapany was amongst other "early pioneers" in this field. They also describe how he inspired and supported the next generation of scientists and innovators.
What points can be raised about individual contributions in relation to the wider professional context?
Discussion
Individual contributions can be celebrated, however, their work is invariably part of a wider and ongoing effort. Kapany demonstrated this in his legacy of educating and facilitating later practitioners.
The OpenLearn course 'Technology, innovation and management' similarly explains that while individuals may make key contributions, it is usually a team effort to fully develop innovations (OpenLearn, 2019).
Spicer (2024) also points out that Kapany was strongly supported by his wife, Satinder Kaur Kapany.
See also
Kapany was mentored by British physicist Harold Hopkins (Spicer, 2024).
Jun-ichi Nishizawa (engineer and inventor) undertook later work in fibre optics.
References and further reading
BBC (2025) Optical Fibers. Available at: https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/z3jbh39/revision/2 (Accessed: 17 March 2025)
Coherent Corp. (2025) Optical Fibers. Available at: https://www.coherent.com/news/glossary/optical-fibers (Accessed: 07 February 2025)
Hertford College, Oxford (2021) Narinder Singh Kapany: Unsung Heroes of Science 2021. Available at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BGJ5B7cIBcU (Accessed: 08 February 2025)
Kapany, N. S. (1967) Fiber Optics; Principles and Applications. United Kingdom: Academic Press.
Kapany, N. S. (2022) The Man who Bent Light: A Memoir. New Delhi: Roli Books
Google (no date) The Man who Bent Light: A Memoir - Narin Singh Kapany - Google Books. Available at: https://books.google.co.uk/books/about/The_Man_Who_Bent_Light.html?id=KTS4zgEACAAJ (Accessed: 08 February 2025)
OpenLearn (2019) '3.1 Individuals and groups'. OpenLearn: Technology, innovation and management. Available at: https://www.open.edu/openlearn/money-business/technology-innovation-and-management/content-section-3.1 (Accessed: 07 February 2025)
Singh, B. (2022) The Man Who Bent Light. Available at: https://www.sikhfoundation.org/the-man-who-bent-light/ (Accessed: 08 February 2025)
Singh, B. (2021) Book Review: The Man Who Bent Light. Available at: https://www.sikhnet.com/news/book-review-man-who-bent-light (Accessed: 17 March 2025)
Spicer, D. (2024) Narinder Kapany: Hidden Figure of Fiber Optics. Available at: https://computerhistory.org/blog/narinder-kapany-hidden-figure-of-fiber-optics/ (Accessed: 06 February 2025)
Wikipedia (2023) File:Photograph of Narinder Singh Kapany, the father of fibre optics.jpg. Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Photograph_of_Narinder_Singh_Kapany,_the_father_of_fibre_optics.jpg (Accessed: 06 February 2025)
