The operation of LAN and WAN hardware and protocols
1 Introduction to Wide Area Networks
- At home, your Local Area Network (LAN) might connect together devices over a distance measured in tens of metres. At work or school, the LAN might connect devices over hundreds of metres. A Wide Area Network (WAN) operates over a much larger area, as they interconnect LANs to allow them to exchange data.
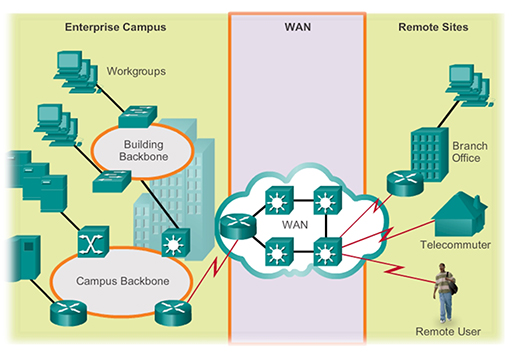
- For example, in the diagram above a large business network needs to provide a connection to a remote branch office, and to employees who work from home (telecommuters) and who are travelling (remote users). This connection is provided by a WAN. WANs are operated by a service provider, and businesses pay them a fee in order to gain access.
- WAN service providers are businesses that provide WAN services using a variety of technologies, including the telephone network, cable and satellite. The WAN allows employees to connect to the business network in order to carry out work related tasks – the connection is not primarily for accessing the Internet.
- Why doesn’t the company set up its own WAN to save money? Traditionally, due to the distance that WANs operate over, setting one up would cost a substantial amount of money as the business would need to purchase the necessary cabling, fibre and satellite systems. Setting up a WAN would therefore prove to be extremely expensive and time-consuming, so most businesses prefer to rent WAN services from an established service provider.
- Consider your home network, which probably provides you with access to the Internet. You too are paying for WAN services as your Internet Service Provider (ISP) is a business that specialises in connecting households to the Internet. They have invested a considerable amount of money in creating a suitable WAN infrastructure that allows thousands of domestic users (who pay a fee) to connect.
Activity
Do you know who your ISP is? How much do they charge for Internet access?
- Domestic networks are primarily connected to an ISP for Internet access, unlike business WANs. Because there are a great many different reasons for creating a WAN, there are many different types of WAN technology available. Most commonly a business WAN needs to support its employees and remote offices, and it will have a different set of requirements to a home user requiring just Internet access. Traditionally, businesses and home users have used different types of WAN technology to provide connectivity.
- As the need to access the Internet has become more widespread, broadband technology has been introduced to provide connections for home, school and small business users. This technology utilises a wide band of frequencies, transmitted over a single transmission media (coaxial, UTP, fibre, wireless), to provide an Internet service that is always on and has a high data rate.
- Broadband provides the connection between a home, school or small business and the ISP. Once within the ISP, different WAN technology will be used to transfer the data around the ISP network and between other ISPs.
- However, it is becoming increasingly common for even large businesses to connect to the Internet to provide connection between their LANs, as opposed to using more traditional WAN solutions. Thus, many businesses are also using broadband connectivity to provide WAN connectivity.
- There are four main types of broadband WAN connectivity available via UK ISPs:
- Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)
- cable
- fibre optic
- wireless.