Overview of genebank processes
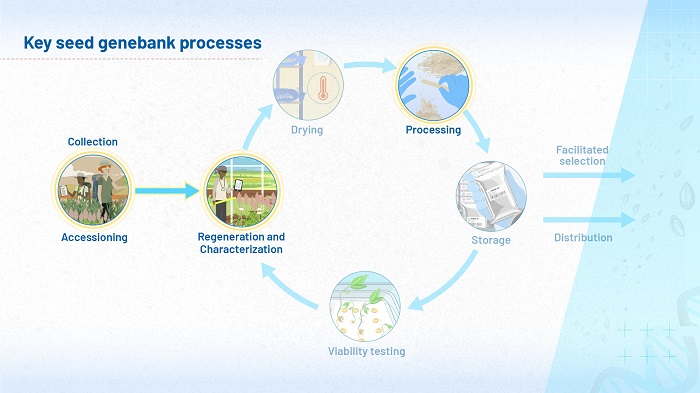
Figure 1 (above) highlights the stages of a genebank’s operations you will consider in module 3. Here, you will shift your focus to the science underlying regeneration, characterization and processing. Parts of this module are also relevant to the collection of brand new accessions, being placed in a genebank for the first time.
During seed regeneration (which in some contexts is referred to as ‘rejuvenation’ or ‘multiplication’), there is a period when the crop is growing in the field. On the parent plant, seeds develop from tiny globules into mature seeds, capable of germinating into new plants. They must be harvested at exactly the right level of maturity. After harvesting comes threshing, cleaning and processing after the material enters the genebank. All of these can affect a seed’s longevity when it enters storage.
In this module, we will take a deep dive into the biological mechanisms that occur while seeds mature, and that continue during the human-imposed processes that are conducted in a genebank, before the seeds go into storage.
Introduction
